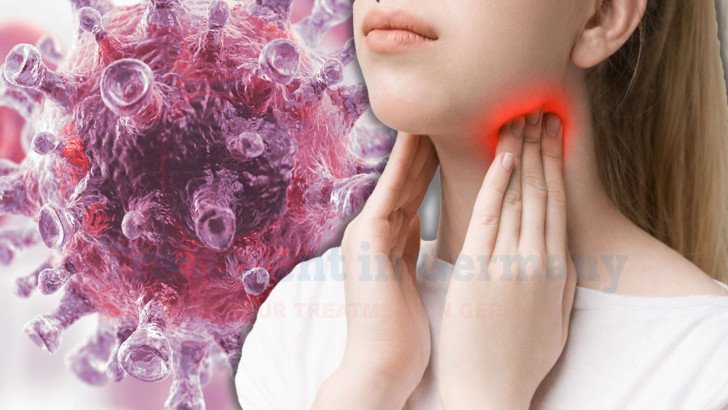
Lymphoma cancer symptoms include swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, fever, night sweats, itching, and weight loss. Learn signs and dendritic cell therapy options in Germany.
Lymphoma is a type of cancer that begins in the lymphatic system, which plays a central role in immune defense. This system includes lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels, the spleen, thymus, and bone marrow. When lymphoma develops, abnormal lymphocytes multiply uncontrollably and interfere with normal immune regulation. Because of this close link to immunity, Lymphoma Cancer symptoms can often resemble common infections or inflammatory conditions, making early recognition challenging.
Many patients who later seek cancer treatment in Germany report that their early symptoms were mild or easily dismissed. Germany is frequently chosen for evaluation because its oncology system emphasizes structured diagnostics, specialist review, and individualized planning using modern cancer treatments in Germany. Medical organizations such as the American Cancer Society also highlight that symptoms alone cannot confirm lymphoma, reinforcing the importance of proper diagnostic pathways.
One reason Lymphoma Cancer symptoms are overlooked is that lymph node swelling and fatigue are common in everyday illnesses. In lymphoma, symptoms may progress slowly or fluctuate, especially in indolent subtypes. Some patients experience symptoms for months before seeking evaluation, assuming stress or infection is responsible.
When patients begin considering treatment in Germany, they often do so after symptoms persist or worsen. German specialists typically assess symptom patterns alongside imaging, blood tests, and biopsy results to avoid misinterpretation and delayed diagnosis.
Painless swelling of lymph nodes is one of the most recognized Lymphoma Cancer symptoms. These swollen nodes are commonly noticed in the neck, armpits, or groin. They may feel firm, rubbery, and persist for weeks or months. Unlike infection-related swelling, lymphoma nodes often do not shrink with time or antibiotics.
In cancer treatment in Germany, persistent lymph node swelling is usually evaluated using ultrasound or CT imaging, followed by biopsy when clinically indicated. Early evaluation helps clarify whether swelling is reactive or cancer-related.
Persistent fatigue and weakness in Lymphoma Cancer
Fatigue associated with lymphoma is different from ordinary tiredness. Patients often describe overwhelming exhaustion that interferes with daily activities, work, and concentration. Rest may provide little relief. This fatigue can be related to inflammation, anemia, disrupted sleep, or ongoing immune activation.
German oncology teams typically evaluate fatigue in context, considering other Lymphoma Cancer symptoms and laboratory findings before attributing it to lymphoma or another cause.
Fever and night sweats in Lymphoma Cancer symptoms
Unexplained fever is a common systemic symptom of lymphoma. These fevers may occur intermittently and are not always linked to infection. Night sweats are another key symptom and may be severe enough to soak bedding or clothing.
Although fever and sweating can occur for many reasons, their recurrence alongside lymph node swelling or weight loss often prompts further evaluation within modern cancer treatments in Germany.
Unintentional weight loss and appetite changes
Unplanned weight loss is another recognized Lymphoma Cancer symptom. Patients may notice reduced appetite, early fullness, or nausea. Weight loss reflects changes in metabolism and inflammatory signaling and is more concerning when it occurs with fatigue or fever.
During treatment in Germany, nutritional assessment is often part of the initial evaluation, as maintaining strength supports better tolerance of therapy.
Itching and skin discomfort as Lymphoma Cancer symptoms
Persistent itching without a visible rash can occur in lymphoma. It may affect large areas of the body and worsen at night. This symptom is believed to be linked to immune signaling rather than skin disease itself. While itching is common in benign conditions, unexplained itching combined with other Lymphoma Cancer symptoms should be medically assessed.
Chest symptoms and breathing changes
When lymphoma involves lymph nodes in the chest, patients may experience cough, chest pressure, or shortness of breath. These symptoms occur when enlarged nodes press on airways or blood vessels. Some patients notice breathing difficulty during normal activity. Chest-related symptoms are evaluated carefully in cancer treatment in Germany, often using imaging to determine the cause and extent of involvement.
Infection patterns and immune system changes
Because lymphoma affects immune regulation, patients may experience frequent infections or slow recovery. This may appear as repeated respiratory infections or prolonged illness. Immune dysfunction is an important clue when seen with other Lymphoma Cancer symptoms.
Immunotherapy Dendritic Cell Therapy for Lymphoma in Germany
Immunotherapy Dendritic Cell Therapy in Germany is a personalized approach designed to support immune recognition of cancer cells. Dendritic cells play a key role in immune communication by presenting abnormal markers to other immune cells. This therapy focuses on enhancing that process rather than directly destroying cancer cells.
Patients seeking innovative treatment options in Germany often explore dendritic cell therapy because it reflects individualized planning and regulated laboratory preparation.
Step-by-step process of dendritic cell therapy in Germany
The process begins with a comprehensive medical review including imaging, pathology, blood tests, and symptom assessment. Once suitability is confirmed, immune cells (Monocytes) are collected from the patient’s blood under clinical supervision.
These immune cells are processed in an EU GMP certified laboratory, where they are developed into dendritic cells. The dendritic cells are then trained using tumor-related markers associated with the patient’s lymphoma. After preparation, the dendritic cell vaccine is administered back to the patient according to a planned schedule. Follow-up monitoring is part of the treatment pathway to assess tolerance and immune-related changes. This structured process reflects standards followed in cancer treatment in Germany.
Leading specialist for dendritic cell therapy in Germany
For patients exploring Immunotherapy Dendritic Cell Therapy in Germany, Prof. Gansauge in Berg, Germany is a recognized specialist in cellular immunotherapy. The cost of Immunotherapy Dendritic Cell Therapy in Germany is €24,000, typically covering immune cell collection, laboratory processing, vaccine preparation, and administration. Any additional diagnostics are discussed transparently.
Prof. Gansauge has authored over a hundred scientific publications in renowned medical and research journals.
Radiation therapy for lymphoma in Germany
Radiation therapy for lymphoma in Germany is commonly used in lymphoma when disease is localized or when specific lymph nodes cause discomfort or pressure. Treatment planning uses imaging to focus radiation precisely on affected areas. Sessions are delivered over a defined schedule, depending on clinical goals. Radiation may also be used to reduce symptoms from bulky nodes. Decisions about radiation are individualized and based on lymphoma subtype, location, and patient condition.
New clinical trials for lymphoma in Germany
Germany supports ongoing oncology research, including new clinical trials for lymphoma in Germany related to lymphoma and immune-based therapies. Patients interested in innovative treatment options in Germany often seek centers that provide eligibility screening and ethical trial participation. Trial availability depends on subtype and clinical criteria and is discussed during specialist consultation.
International patient support with TIG, Treatment in Germany
International patients often need assistance beyond medical care. TIG, Treatment in Germany, at www.treatmentingermany.de, manages international patients with complete logistical support including a medical visa support if required. This coordinated approach allows patients to focus on treatment in Germany without logistical stress.
🌍Why Patients Worldwide Prefer Our Medical Services in Germany – Key Benefits Explained:
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common Lymphoma Cancer symptoms?
Persistent swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, fever, night sweats, itching, and unexplained weight loss are common signs.
Are lymphoma lymph nodes always painful?
No, lymphoma-related nodes are often painless and firm.
Can fatigue be an early lymphoma symptom?
Yes, ongoing fatigue that does not improve with rest can occur early.
Do night sweats always indicate lymphoma?
Not always, but recurring drenching night sweats should be evaluated.
Can lymphoma cause itching without a rash?
Yes, itching can occur due to immune signaling changes.
Can lymphoma affect breathing?
Chest lymph node involvement may cause cough or shortness of breath.
Is weight loss common in lymphoma?
Unintentional weight loss can occur, especially with other systemic symptoms.
How is lymphoma diagnosed in cancer treatment in Germany?
Diagnosis usually involves imaging and biopsy, not symptoms alone.
What is Immunotherapy Dendritic Cell Therapy in Germany?
It is a personalized therapy using immune cells (Monocytes) to support immune recognition.
Is dendritic cell therapy approved by FDA in Germany?
No, dendritic cell immunotherapy in Germany is not FDA-approved in the USA but adheres to strict EU-GMP standards, ensuring safety and quality for international patients.
Who provides dendritic cell therapy in Germany?
Prof. Gansauge in Berg, Germany specializes in this therapy.
Are new clinical trials for lymphoma cancer available in Germany?
Some centers offer new clinical trials depending on eligibility.
How can international patients arrange lymphoma cancer treatment in Germany?
International patients can access lymphoma cancer treatment in Germany, with full logistical coordination provided by TIG (Treatment in Germany) at www.treatmentingermany.de covering appointments, travel, medical visa assistance (if needed), and follow-up care.
Kindly complete the form below, and our dedicated team will reach out to you promptly. We look forward to connecting with you soon!
Trierer Straße, 56072 Koblenz, Germany

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
