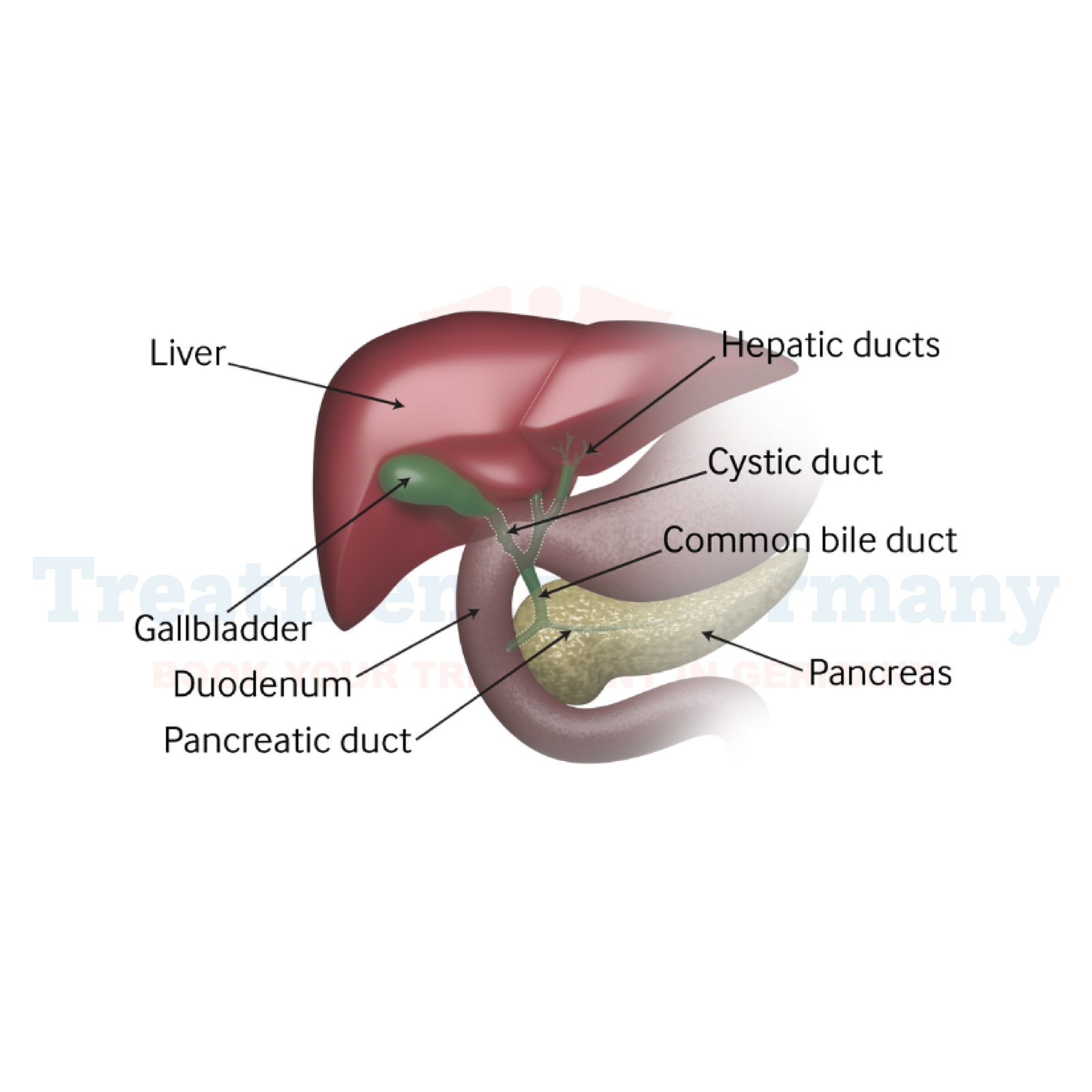
Acute cholecystitis is a severe condition that is occasioned by inflammation of the gall bladder, in most instances due to gallstones blocking the biliary. The gallbladder is a small pear-shaped organ positioned below the liver and plays the role in storing and secreting digestive bile.
This implies that, when bile flow is prevented, then inflammation, infection, and possible complications may occur. Chapter five of this work centers on acute cholecystitis and it is divided into sub- topics such as symptomatology of acute cholecystitis, causes of acute cholecystitis available advanced treatment in Germany.
Acute cholecystitis is a sudden onset inflammation of the gallbladder wall, usually due to the impact of a gallstone on the cystic duct. This blockage provokes the accumulation of bile, leading to swelling and infection and therefore causing pain in the gallbladder.
If not administered in good time, it can progress to serious life- threatening conditions.
Types of Acute Cholecystitis
The types of acute cholecystitis are as follows:
Signs and Symptoms of Acute Cholecystitis
This is especially important if the problem is to be tackled at an early stage as indicated by the symptoms.
Common Symptoms
Causes of acute Cholecystitis
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing cholecystitis:
Pending disease of either chronic liver disease or diabetes.
Acute cholecystitis diagnosis
The appropriate diagnosis of such disorders is crucial to management to facilitate appropriate treatment.
Blood Tests:
Imaging Techniques:
Treatment Options of Acute cholecystitis in Germany
When it comes to gallbladder diseases, Germany is renowned for its modern facilities and modern approaches to getting rid of the problem.
Initial Management
Stabilizing the patient with supporting measures is the first step in treatment such as:
Surgical Interventions
A surgical procedure in which excess gallbladder is surgically removed through small cuts that are made on the body.
Favoured as it is less likely to be complicated and takes longer time to heal as compared to the open procedure.
Open Surgery:
When gangrene or acute inflammation is extreme, this medicine is utilized.
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP):
Complements endoscopic visualization along with radiographic techniques to eradicate the gallstones in the bile ducts non-operatively.
Drainage Procedures:
Percutaneous therapy involves emptying the gallbladder to release pressure in a particular circumstance, specifically in susceptible patient candidates for surgery.
Innovative Treatment Options in Germany
Germany's healthcare system offers cutting-edge solutions:
In the case of gallbladder removal, the liver still secretes bile, and this is transported to the small intestine. This adaptation might produce acute manifestations such as impaired lipid absorption.
Why Choose Germany for the Treatment of Acute Cholecystitis?
The treatment of acute cholecystitis is well comprehensively in Germany and well backed by modern healthcare facilities.
Advantages of Treatment in Germany
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes acute cholecystitis?
Acalculic cholecystitis causes include stones impacted in the neck of the gallbladder or difficult-to-visualize stones not seen on imaging studies.
How is it diagnosed?
Diagnosis of the condition involves carrying out physical blood as well as ultrasounds or CT scans.
What types of treatment can be gotten in Germany?
Services that Germany affords their patients include IV therapy, antibiotics, minimally invasive laparoscopic surgical operations, and, In addition, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) techniques.
Is getting back to normal possible after the removal of the gallbladder?
Yes, at least ninety percent of the population employs a normal living standard and moderate alteration in diets once they undergo surgery.
What happens if acute cholecystitis is left unchecked?
The untreated conditions can result in gangrene, peritonitis, septicemia, or even life-threatening complications.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
