What is Adrenoleukodystrophy?
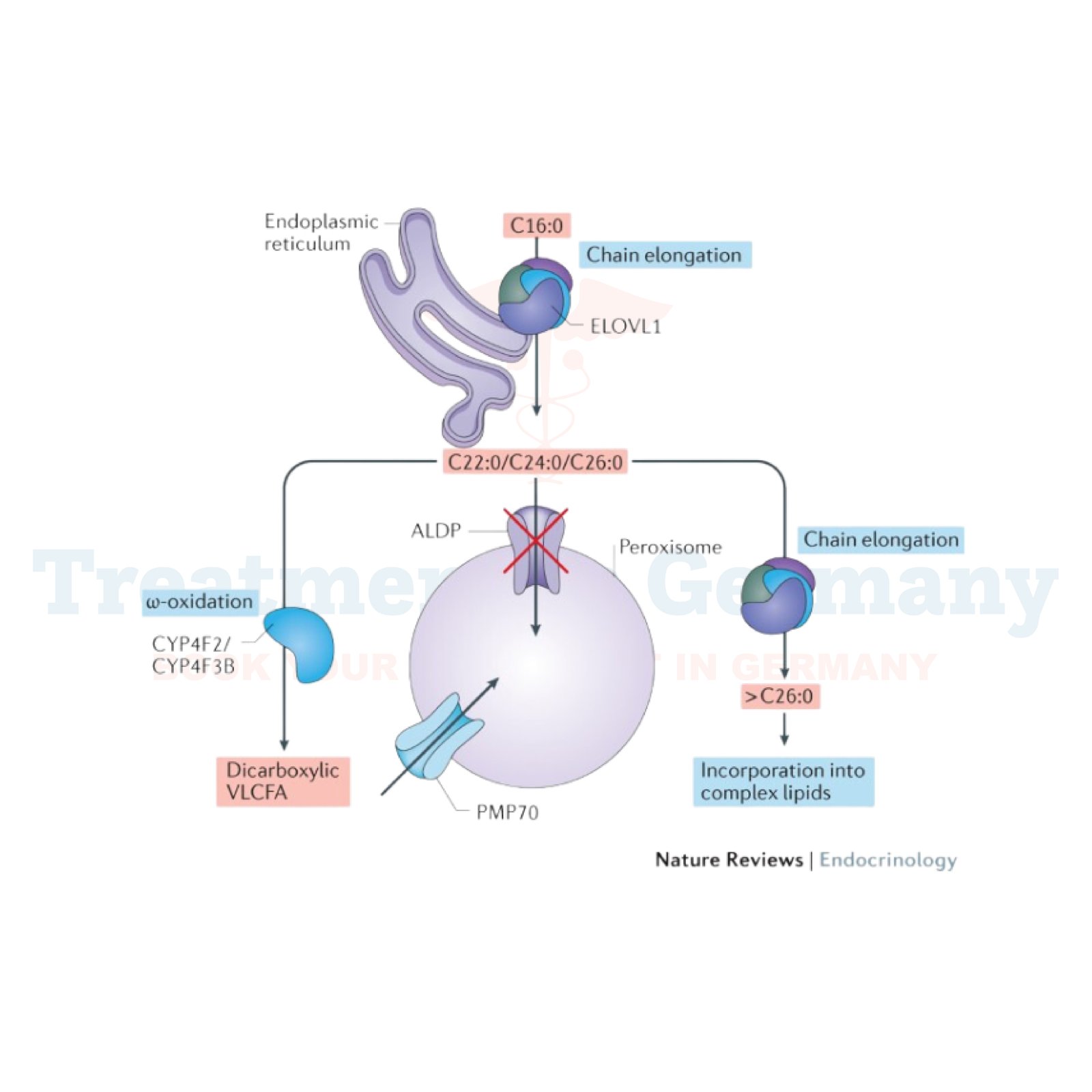
Adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the nervous system and the adrenal glands. It is characterized by the buildup of very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) in the body, which can cause damage to the myelin sheath that insulates nerve cells in the brain.
Side Effects of Adrenoleukodystrophy
The symptoms and side effects of Adrenoleukodystrophy vary depending on the type and progression of the disease. In its most severe form, cerebral ALD (cALD), symptoms typically appear in childhood and can include:
In milder forms of Adrenoleukodystrophy , symptoms may appear later in life and primarily affect the adrenal glands, causing adrenal insufficiency.
How is Adrenoleukodystrophy Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Adrenoleukodystrophy often involves a combination of clinical evaluation, genetic testing, and biochemical testing to measure levels of VLCFAs in blood samples. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain can also show characteristic changes in the white matter, which helps in confirming the diagnosis.
Potential Treatment of Adrenoleukodystrophy
Currently, there is no cure for Adrenoleukodystrophy , but treatment aims to manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. In Germany, treatment options may include:

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
