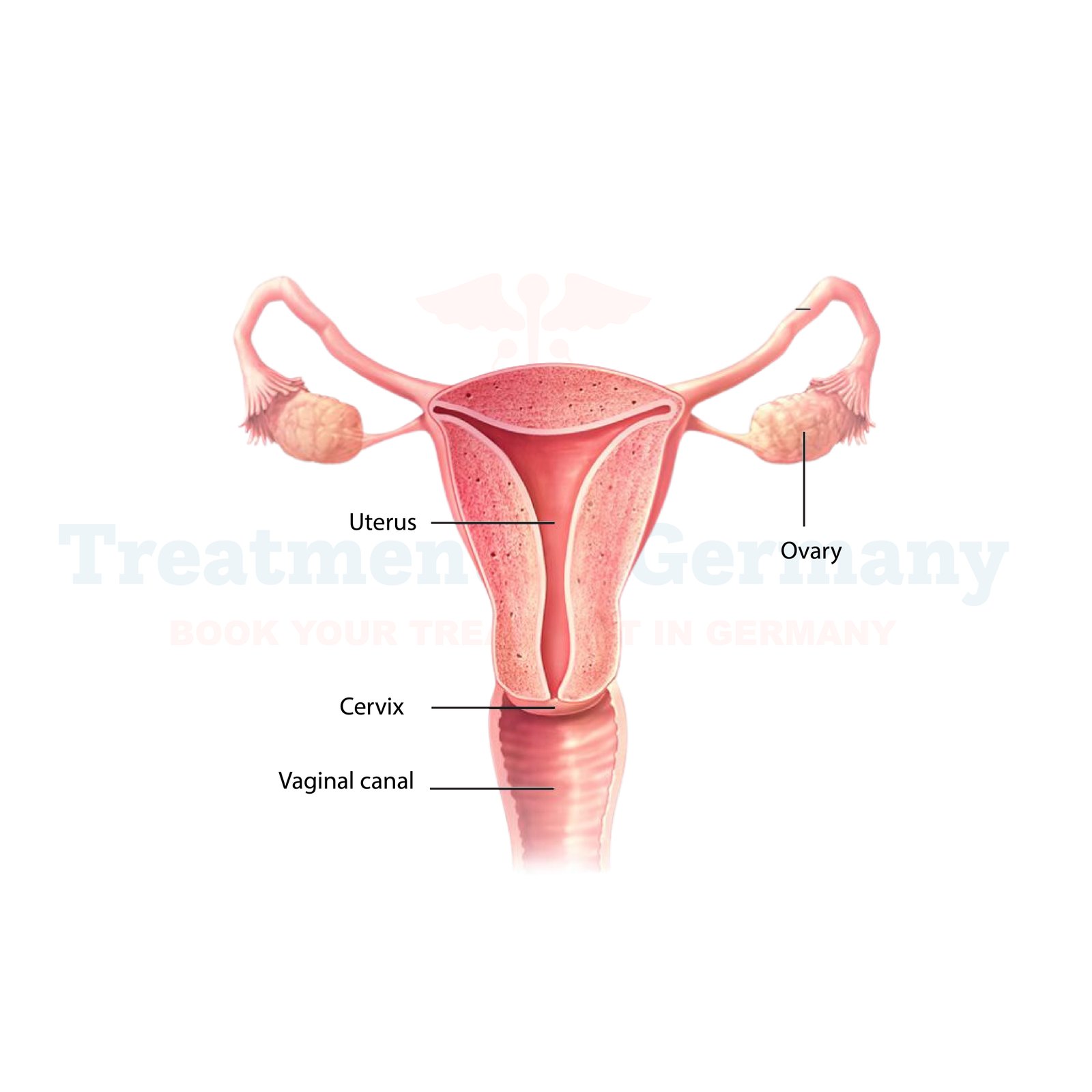
What is Amenorrhea?
Amenorrhea is a condition characterized by the absence of menstruation in women of reproductive age. It can be classified into two main types: primary amenorrhea, where menstruation has not started by the age of 16, and secondary amenorrhea, where menstruation stops for at least three consecutive menstrual cycles after previously having a regular menstrual cycle.
Side effects of Amenorrhea:
Amenorrhea can have various physical and emotional side effects. These may include:
How is Amenorrhea diagnosed?
Diagnosing Amenorrhea involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider. This typically includes:
Potential treatments of Amenorrhea:
Treatment for amenorrhea depends on the underlying cause and may include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
