Aneurysms are a major health concern, mainly resulting from structural deformities of blood vessels caused by weakening of the arterial walls. When left unattended, some aneurysms cause rigorous conditions, including internal bleeding, stroke, and organ dysfunction.
When it comes to aneurysm cases, Germany has committed to treating patients for such conditions and treatment using the latest technologies in medical facilities to support patient care.
An aneurysm is an outward bulge of a blood vessel wall, frequently seen in an artery wall due to the disease of the arterial wall. For instance, blood vessels that supply oxygen throughout parts of the body after it has been pumped by the heart are at risk of being impaired, especially in areas with high pressure.
Cerebrovascular aneurysms are clinically occult, and aneurysmal disease is often identified only when aneurysmal complications arise, most commonly rupture.
Types of Aneurysms
The types of aneurysms are as follows:
Aortic Aneurysms
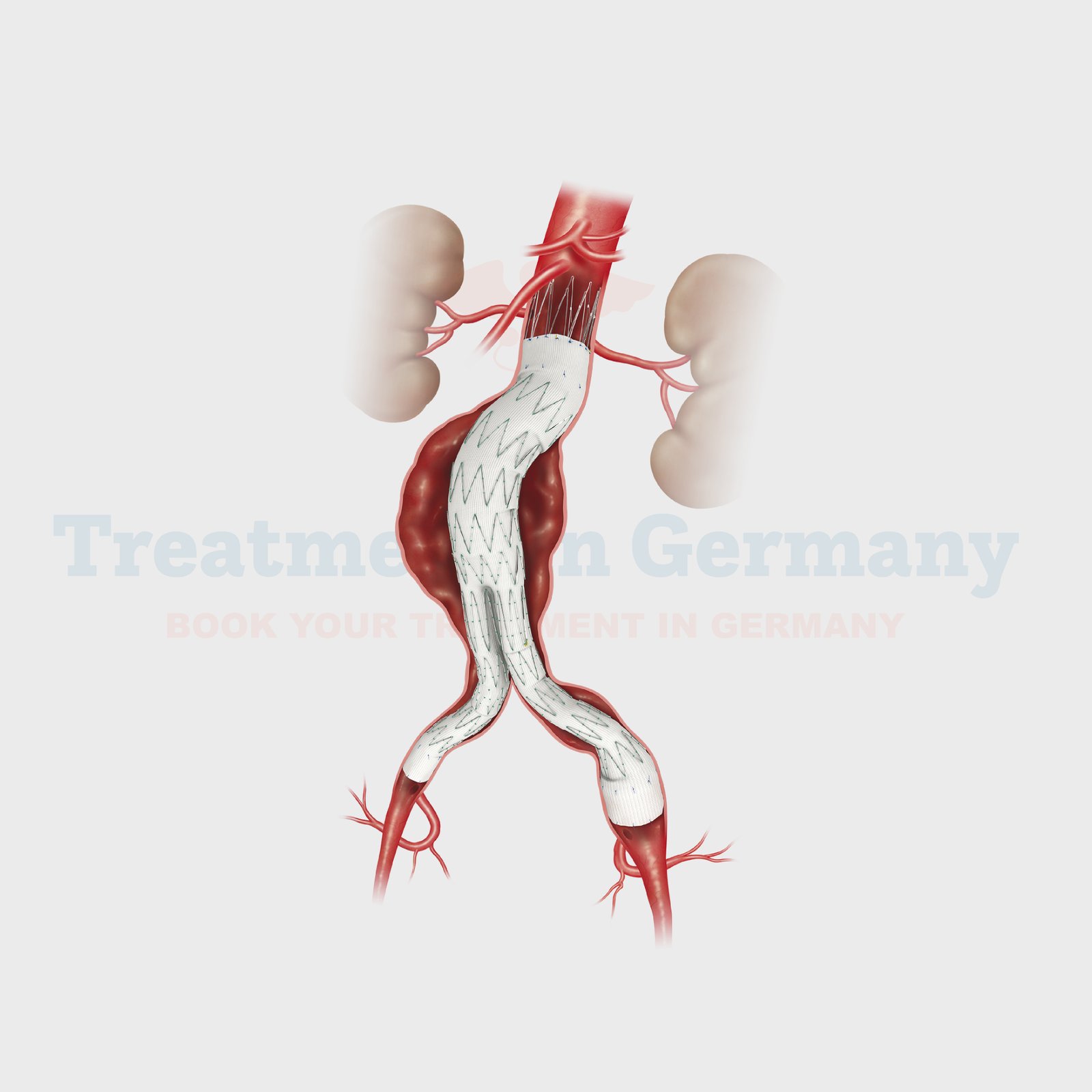
By far the most prevalent are aortic aneurysms. The main artery in your body, the aorta, is where they form. Blood leaves your heart through your aorta. Peripheral aneurysms are aneurysms that form in arteries other than the aorta.
Carotid Artery Aneurysms
Found in the carotid arteries, which serve the brain, neck and face, that is why these aneurysms are rare but life-threatening.
Popliteal Aneurysms
These occur in the artery behind the knee and are the most frequent type of peripheral aneurysm.
Symptoms of Aneurysms
Most aneurysms are asymptomatic and are discovered only after they have ruptured. Instead, the symptoms depend upon the location and size of the cysts. Common signs include:
Nausea or vomiting
This contains abdominal pains, blaming chest pains and backaches.
Pulsating abdominal mass
A ruptured aneurysm can result in catastrophic internal bleeding or a stroke; it is a medical emergency.
Risk Factors for Aneurysms
Aneurysm development is influenced by several factors, including:
Diagnosis of Aneurysms in Germany
Hospitals in Germany have state-of-the-art equipment to diagnose aneurysms to minimize the wrong diagnosis of the situation. Common diagnostic methods include:
They allow diagnosis of diseases with major emphasis on the type of treatment that is required in each case.
Management of Aneurysms in Germany
Germany’s healthcare has modern facilities equipped with the best aneurysm treatment experts in the world. It means that conservative and surgical management plans depend on the patient’s health and the aneurysm’s size and localization.
Supervision and Clinical Supervision
Asymptomatic aneurysm may well not necessarily demand surgical intervention. Instead, doctors in Germany often adopt a conservative approach involving:
Endovascular Surgery
Minimally invasive procedures, such as endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR), are widely used in Germany.
An operation involves passing a catheter into the artery that requires support and then using a graft to wrap the walls of a blood vessel in the body without using large incisions.
Open Surgery
Sometimes, where the aneurysm is large or there is a rupture, it will require an open surgical operation. This is where part of an artery that has been affected is removed and replaced by an artificial one.
Innovative Techniques
Germany is a leader in pioneering techniques for aneurysm treatment such as:
Preventing Aneurysms
While not all aneurysms are preventable, certain measures can significantly reduce the risk:
Why to Choose Germany for Treatment of Aneurysm?
Germany can be regarded as the country of choice for those individuals who need aneurysm treatment of the highest quality. Key advantages include:
Living with Aneurysms
Therefore, for patients who are having an aneurysm, it is very important to do some changes in their lifestyles and to have frequent checkups. Recommendations include:
Frequently asked questions
What makes Germany a popular country for aneurysm surgical procedures?
Modern diagnostic technologies, experienced physicians, as well as progressive treatment methods for aneurysm are available in Germany.
How is the aneurysm detected in a patient in Germany?
Aneurysms are diagnosed through today’s efficient diagnostic methods like CT scans and ultrasounds.
Can all types of aneurysm be operated on?
In this case, not all aneurysms need to be operated on. Small asymptomatic aneurysms can be closely watched and treated by medication or changes in lifestyle.
Which lifestyle modifications are most important for preventing aneurysms?
Eating a low-cholesterol diet, not smoking, and controlling high blood pressure are the measures that can prevent heart disease.
What can I do if I have an aneurysm?
You should go for professional help as early as possible, particularly once you develop severe signs like abdomen or chest pains, dizziness, or you feel a throbbing lump.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
