What is Angelman Syndrome?
Angelman Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that primarily affects the nervous system, causing developmental delays, intellectual disability, and specific physical characteristics.
Individuals with Angelman Syndrome often exhibit a happy demeanor, frequent smiling, and have a distinctive gait characterized by jerky movements.
Side Effects of Angelman Syndrome
The syndrome manifests with several key symptoms:
- Developmental Delays: Delayed milestones such as sitting, crawling, and walking.
- Intellectual Disability: Individuals typically have severe to profound intellectual disability.
- Speech Impairments: Minimal or no verbal communication abilities.
- Seizures: Epilepsy is common among those with Angelman Syndrome, typically starting between the ages of 2 and 3.
- Behavioral Characteristics: Hyperactivity, short attention span, and fascination with water are common.
How is Angelman Syndrome Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Angelman Syndrome involves:
- Clinical Assessment: Recognizing characteristic behaviors and physical features.
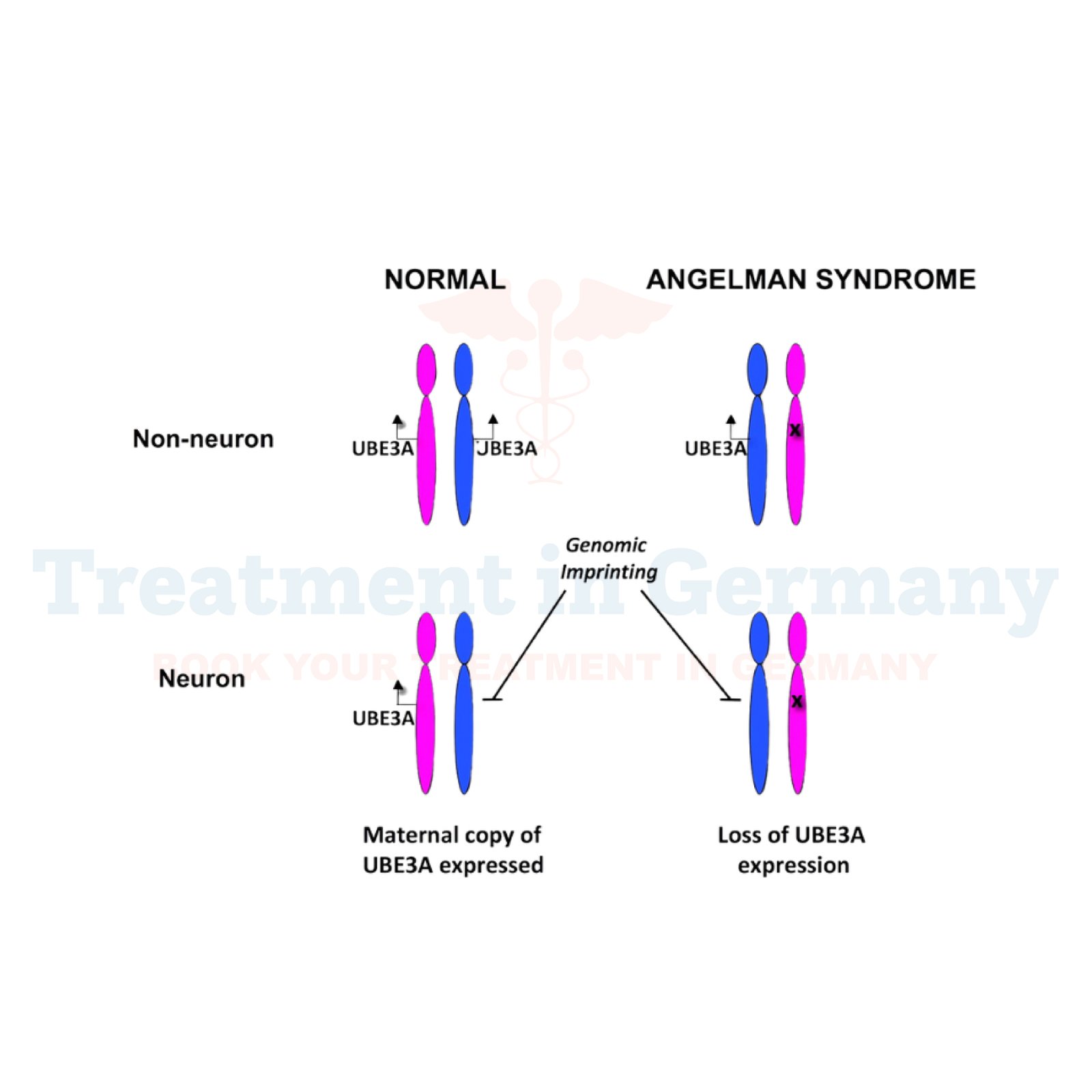
- Genetic Testing: Identifying abnormalities on chromosome 15, such as a deletion or mutation in the UBE3A gene.
- Molecular Testing: Methylation testing to confirm a diagnosis when genetic testing is inconclusive.
Potential Treatments for Angelman Syndrome
Currently, there is no cure for Angelman Syndrome, but treatments aim to manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Medications: Antiepileptic drugs to manage seizures, and medications to address sleep disorders and behavioral issues.
- Therapies: Early intervention programs including physical therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy to improve motor skills, communication abilities, and independence.
- Behavioral Interventions: Strategies to manage hyperactivity and improve attention span.
- Research and Clinical Trials: Investigating potential treatments targeting the genetic cause of Angelman Syndrome, such as gene therapies and UBE3A reactivation strategies.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
