Understanding Aortic Stenosis (AS)
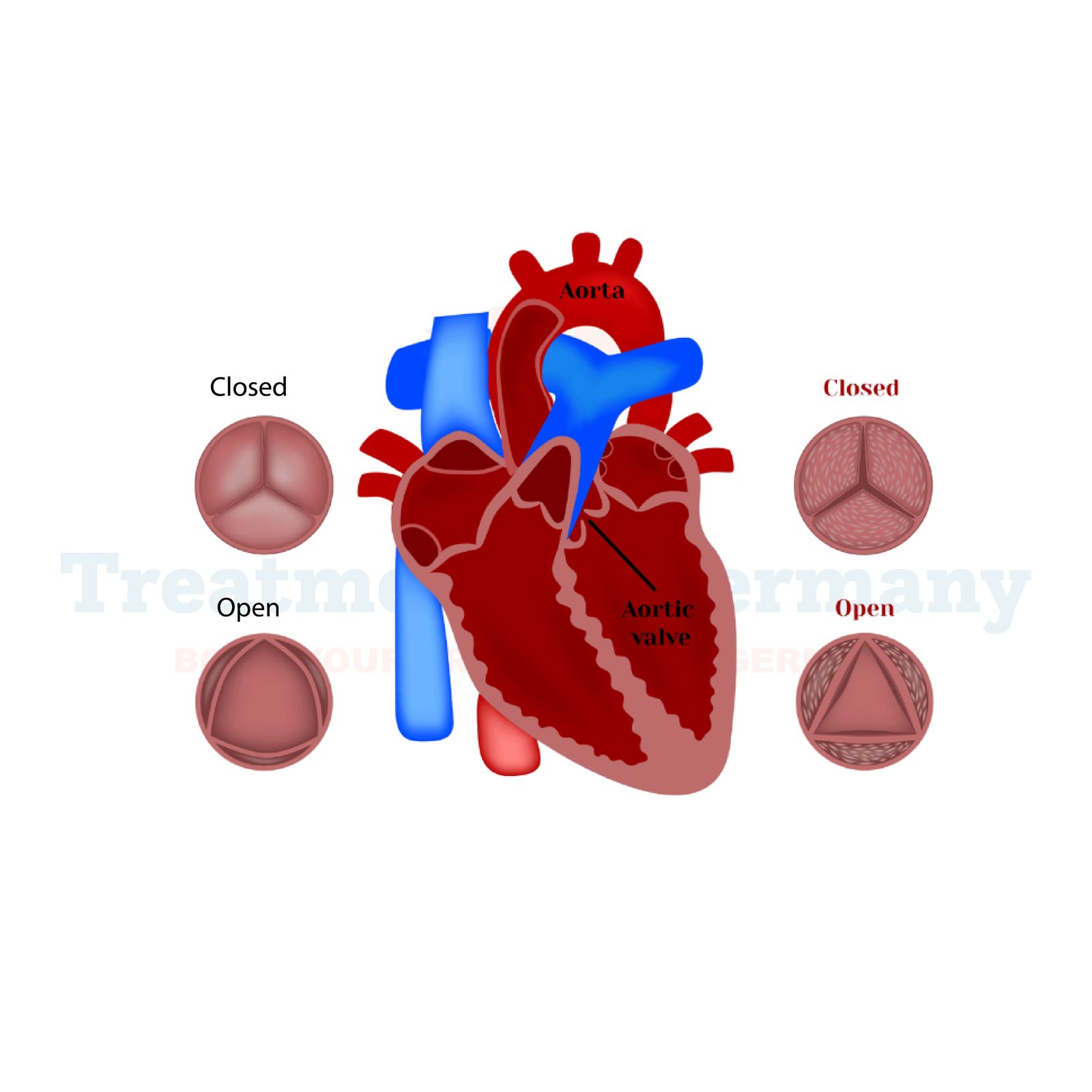
Aortic Stenosis (AS) is a heart condition that involves the narrowing of the aortic valve opening, which restricts the blood flow from the heart to the rest of the body.
This narrowing is typically caused by the thickening or stiffening of the valve leaflets, reducing the valve's ability to open fully. As a result, the heart must work harder to pump blood through the narrowed valve, leading to potential complications if left untreated.
Side Effects of Aortic Stenosis (AS)
The symptoms of Aortic Stenosis can vary from mild to severe and may include:
- Chest pain (angina): Due to reduced blood flow to the coronary arteries.
- Shortness of breath: Especially during exertion or when lying flat (orthopnea).
- Fatigue: Resulting from the heart having to work harder to pump blood.
- Heart palpitations: Sensations of rapid, fluttering, or pounding heartbeats.
- Fainting episodes: Particularly during physical activity or exertion.
If left untreated, severe Aortic Stenosis can lead to heart failure, arrhythmias, and even sudden cardiac death in some cases.
How is Aortic Stenosis (AS) Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Aortic Stenosis typically involves several tests and examinations, including:
- Physical examination: Listening to the heart with a stethoscope to detect a heart murmur.
- Echocardiogram (Echo): An ultrasound of the heart that provides detailed images of the heart valves and blood flow through them.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Measures the electrical activity of the heart to detect any abnormalities.
- Cardiac catheterization: Invasive procedure to directly measure pressures within the heart and the extent of valve narrowing.
Potential Treatment of Aortic Stenosis (AS)
The treatment options for Aortic Stenosis depend on the severity of the condition and the patient's overall health. Common treatments include:
- Medications: Although medications cannot reverse the narrowing of the valve, they may help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
- Aortic valve replacement: This is the most effective treatment for severe Aortic Stenosis. It can be done through open-heart surgery or minimally invasive transcatheter procedures, where a new valve is inserted to replace the diseased valve.
- Balloon valvuloplasty: A less common procedure where a balloon is inflated inside the narrowed valve to widen it.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
