Understanding Aplastic Anemia:
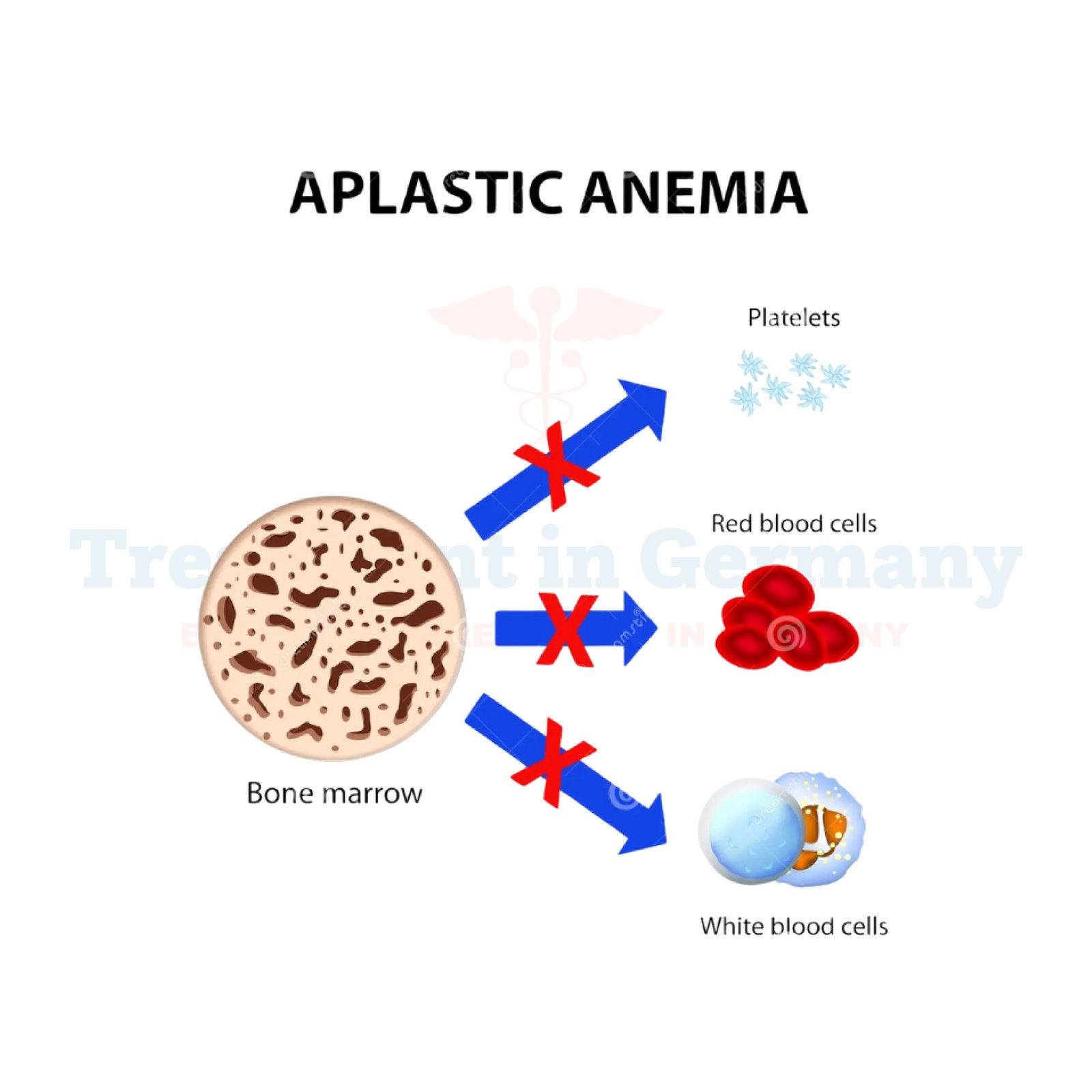
Aplastic Anemia is a rare but serious condition where the body's bone marrow fails to produce enough red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This deficiency in blood cell production can lead to various complications and put the patient at risk of severe infections, bleeding, and fatigue.
Side Effects of Aplastic Anemia:
The symptoms of Aplastic Anemia can vary from person to person but often include fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, dizziness, pale skin, and frequent infections. In severe cases, patients may experience excessive bleeding, bruising, and an increased risk of developing other serious health conditions.
How is Aplastic Anemia Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Aplastic Anemia typically involves a series of tests conducted by healthcare professionals. These may include blood tests to measure the levels of different blood cells, bone marrow biopsy to examine the marrow cells directly, and other diagnostic procedures to rule out other potential causes of the symptoms.
Potential Treatments of Aplastic Anemia:
The treatment approach for Aplastic Anemia depends on various factors, including the severity of the condition and the patient's overall health. Some common treatments may include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
