Arteriovenous malformations are complex of arteries and veins that form anomalous circuitry that does not participate in the exchange between arterial and venous blood. This can cause several problems, including tissue death, bleeding, or even such serious conditions as a stroke or aneurysm.
AVMs can occur in any part of the body, but they often localize to the brain, brain stem, and spinal cord. Germany has become a center for AVM treatment and has access to new developments in approaches and modern equipment.
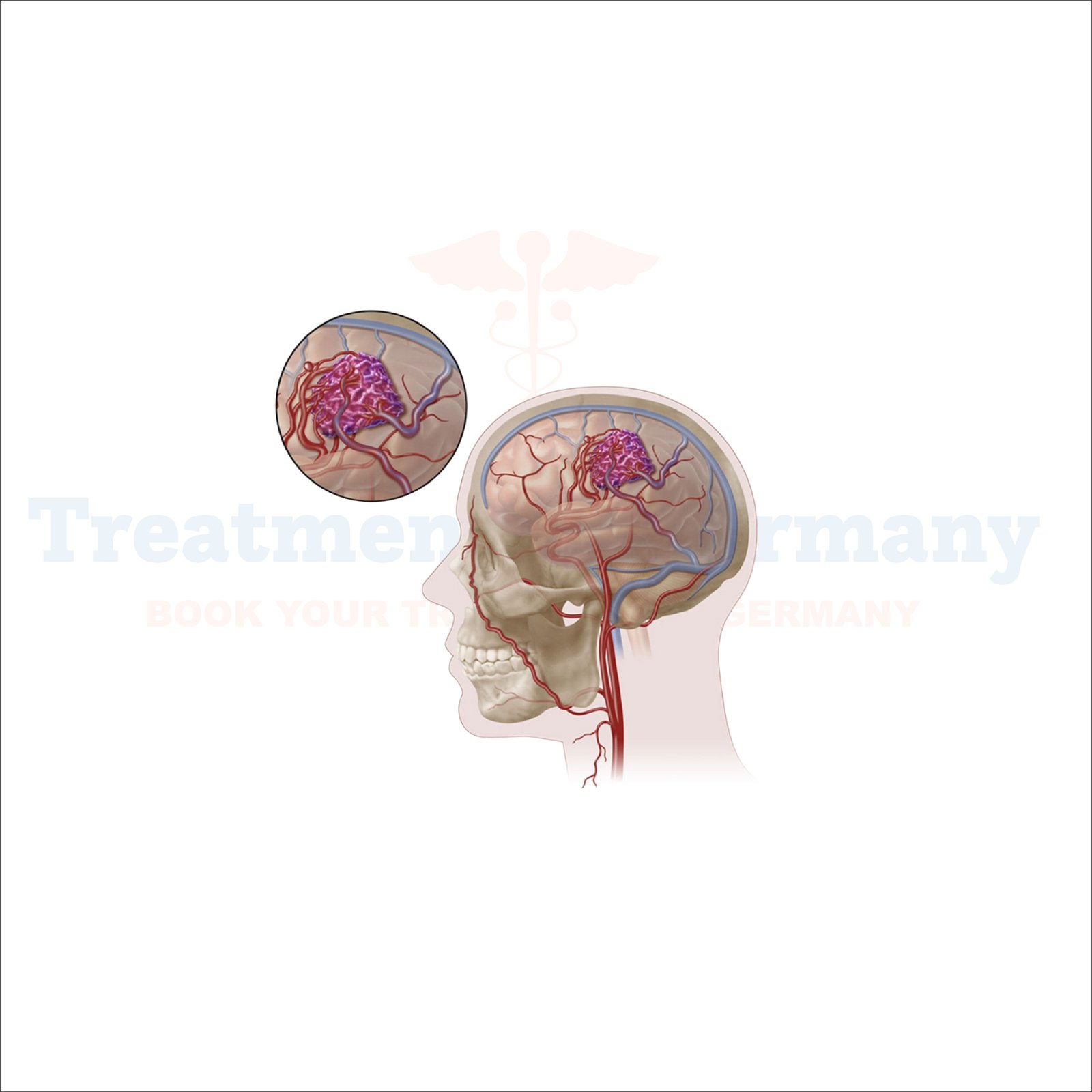
An AVM is an abnormal group of blood vessels that have arteries anastomosing with veins without the intervening network of capillaries. This lack of capillaries means that arteries directly discharge high-pressure blood into venues, which are not built to withstand such pressure.
This may therefore lead to some kind of damage to vessels, tissue injury, or inadequate oxygen reaching the affected area.
Types of AVMs
The types of arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are as follows:
Common Symptoms of AVMs
Most AVMs do not produce symptoms, but when symptoms are present, they depend on the size of the AV malformation and its location. Symptoms include:
Risks and Complications
AVMs pose significant health risks, such as:
What Causes AVMs?
It has also remained unclear what causes the formation of AVMs. It is thought that they develop before birth and are therefore generally considered congenital structures. Occasionally, AVMs are hereditary.
Diagnostic Techniques
Germany employs state of the art diagnostic methods to identify AVMs:
Therapies in Germany for AVMs
Germany has presented one of the most developed and sophisticated healthcare systems, which provides complete and individualized treatment. Management strategies applied depend on the extension of the AVM, its localization, and the patient's general state.
Medication
Surgical and Non-Surgical Operations
Open Surgery:
Surgery applied in the treatment of AVM entails complete resection of the lesion. Surgeons ligature neighboring arteries and veins to stop bleeding, and they then remove the AVM. This procedure affords a complete elimination of the AVM’s pathologic
Embolization:
Broader categories of endovascular treatment involve a less intrusive approach where glue-like substances or coils are inserted via a catheter to address blood flow to the AVM. The most common use of embolization is in cases as a preliminary procedure ahead of surgery or as an option in patients for whom open surgery is contraindicated.
Gamma Knife Radiosurgery:
A modern procedure that entails focusing radiation beams directly on the AVM in a successful attempt to reduce its size. Nonetheless, the effects may take several months to years to manifest themselves.
Innovations in AVM Treatment
Germany has only embraced the most sophisticated equipment, such as Gamma Knife® and some of the latest techniques in embolization; hence, more efficient result-oriented procedures are conducted.
Regular Monitoring
After the treatment, an MRI or CTA is taken from the site of the AVM to assess for possible recurrence or complications.
Prevention and Awareness
AVMs are congenital disorders and cannot be prevented. However, if diagnosed at an early stage, there are plenty of ways to minimize risks associated with lethal consequences, including strokes, the formation of aneurysms, or even brain-destructive conditions. Any patient with complaints like recurrent headaches, seizures or neurological deficits should be reported to a health facility.
Frequently asked questions
How are AVMs found in people who don't exhibit any symptoms?
Most patients with AVMs present without any symptoms, and the diagnosis is made when the AVM is noticed on imaging of the head for other disorders, for example, headaches or injuries.
What is embolization, and how do these approaches help treat AVMs?
Embolization entails placing substances into an AVM to limit blood flow and reduce surgery difficulty in case of rupture.
Can AVMs reappear following therapy?
It can reoccur sometimes if the AVM was not excised fully from the body in the first place. Interested persons are supposed to be followed up.
Are AVMs a constant threat to life?
Life-threatening AVMs are not all of them. It is only upon autopsy or imaging studies for other illnesses that many are found to be asymptomatic.
Why is Germany chosen for the treatment of AVM?
Everything in Germany regarding AVM is highly developed, from diagnostics to treatments with the help of innovative surgical methods and a high level of healthcare.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
