Ataxia is a neurological condition characterized by a lack of muscle coordination, which can affect movement, speech, eye control, and other bodily functions. It is often a symptom of underlying conditions rather than a disease itself. Ataxia can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, symptoms can be managed effectively.
Germany is at the forefront of providing innovative and comprehensive treatment for Ataxia, combining advanced diagnostic tools like MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and CT (Computed Tomography) scans with multidisciplinary care from world-class specialists. Patients from all over the world seek treatment in Germany for the exceptional care and cutting-edge therapies offered.
The term “ataxia” means “without order” in Greek, signifying the loss of control over body movements. Ataxia occurs due to damage to the cerebellum (the brain region responsible for balance and coordination) or its connections with other parts of the nervous system. It is a progressive condition that may result from genetic factors, injuries, or other health issues.
Ataxia is categorized based on its cause and progression. The three main types are:
Cerebellar Ataxia
Results from damage to the cerebellum.
Symptoms include difficulty walking, tremors, and slurred speech.
Sensory Ataxia
Occurs due to issues in the sensory nerves that transmit information to the brain.
Symptoms include difficulty with balance, especially in the dark, and numbness in the limbs.
Vestibular Ataxia
Caused by problems in the inner ear or vestibular system.
Symptoms include vertigo, dizziness, and loss of balance.
Risk Factors for Ataxia
Certain factors may increase the risk of developing Ataxia, including:
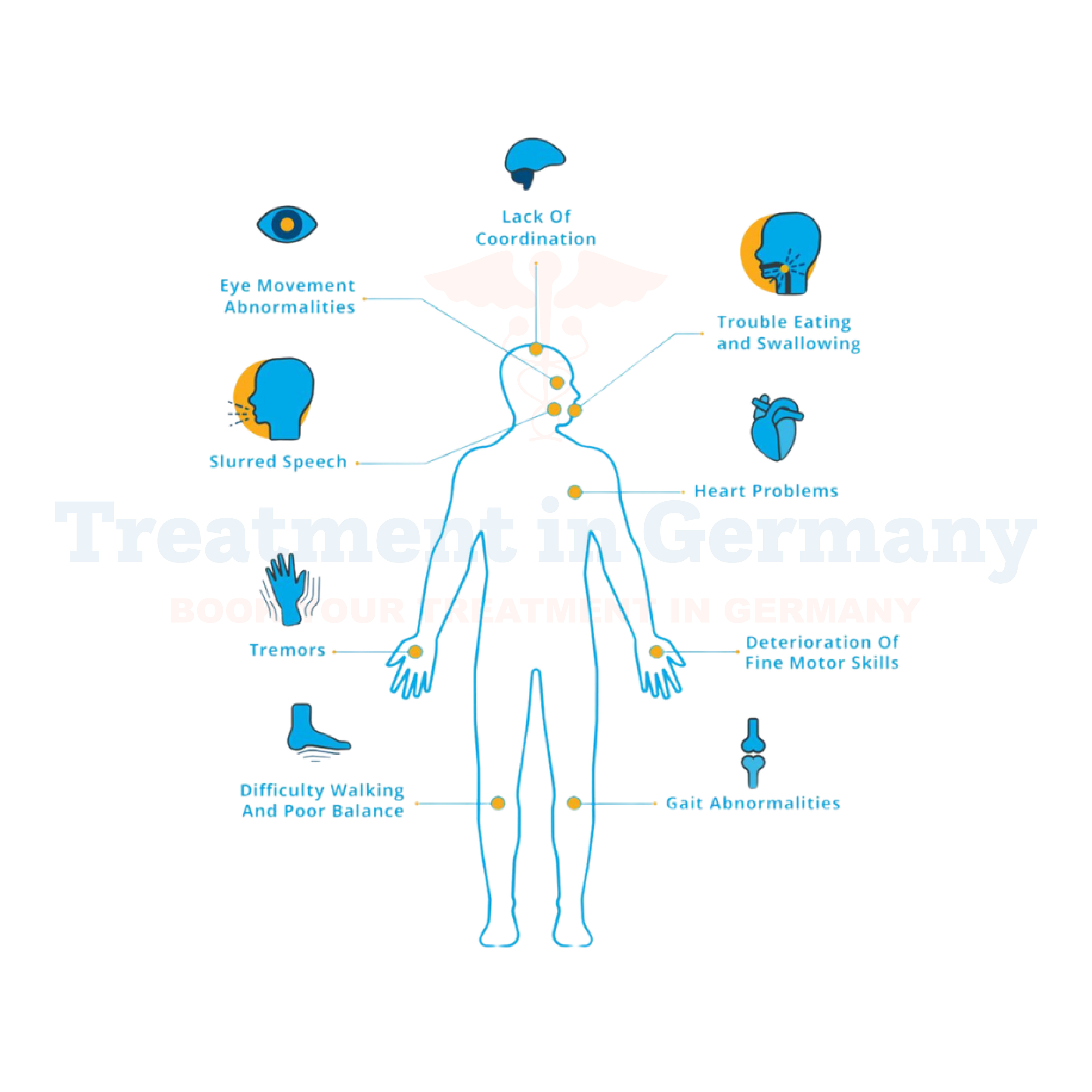
Symptoms of Ataxia
The symptoms of Ataxia can vary depending on its type and severity but may include:
Diagnosis and Diagnostic Tools for Ataxia
Diagnosing Ataxia requires a thorough assessment by a neurologist and the use of advanced diagnostic tools. In Germany, state-of-the-art hospitals and specialists ensure precise and early diagnosis.
Diagnostic Steps:
Physical and Neurological Examination:
Tests to assess balance, coordination, and muscle strength.
Reflex testing and evaluation of sensory functions.
Imaging Tests:
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed images of the brain and spinal cord to identify abnormalities in the cerebellum.
CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: Useful for detecting brain injuries or tumors.
Blood Tests:
Used to rule out infections, vitamin deficiencies, autoimmune conditions, or other metabolic disorders.
Genetic Testing:
Identifies hereditary forms of Ataxia like Friedreich’s Ataxia or Spinocerebellar Ataxia.
Electromyography (EMG):
Evaluates the health of muscles and the nerve cells controlling them.
Treatment for Ataxia in Germany
Germany is recognized as a global leader in providing innovative treatments for Ataxia, thanks to its cutting-edge technologies, highly skilled specialists, and multidisciplinary care approach.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Physical Therapy:
Enhances muscle strength, balance, and coordination.
Specialized exercises tailored to individual needs.
Occupational Therapy:
Helps patients regain independence in daily activities, such as eating or dressing.
Speech Therapy:
Improves communication and swallowing difficulties.
Medications:
Muscle relaxants, pain relievers, and anti-spastic drugs may be prescribed.
Medications to treat underlying conditions like diabetes or autoimmune diseases.
Advanced Therapies in Germany
Stem Cell Therapy:
A promising treatment under research, aimed at regenerating damaged nerve cells.
Dendritic Cell Therapy:
Explores ways to strengthen the immune system to reduce nerve damage in autoimmune-related Ataxia.
Complementary Therapies:
Hydrotherapy, music therapy, and yoga to promote overall physical and emotional well-being.
Surgical Treatments
In cases where Ataxia is caused by treatable structural issues like tumors or hydrocephalus, surgery may be necessary. German hospitals employ minimally invasive techniques to ensure faster recovery and better outcomes.
Why Choose Treatment in Germany?
Germany has earned its reputation as a hub for innovative medical treatments, attracting patients from around the globe. Here’s why:
Solutions and Management for Ataxia
While there is no definitive cure for most types of Ataxia, effective management can improve quality of life:
Conclusion
Ataxia is a challenging neurological condition, but with the right care and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Germany’s innovative treatments, advanced diagnostic tools, and highly skilled specialists make it a global leader in Ataxia management. By choosing treatment in Germany, patients can access personalized care designed to address their unique needs, offering hope for improved outcomes and quality of life.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
