What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
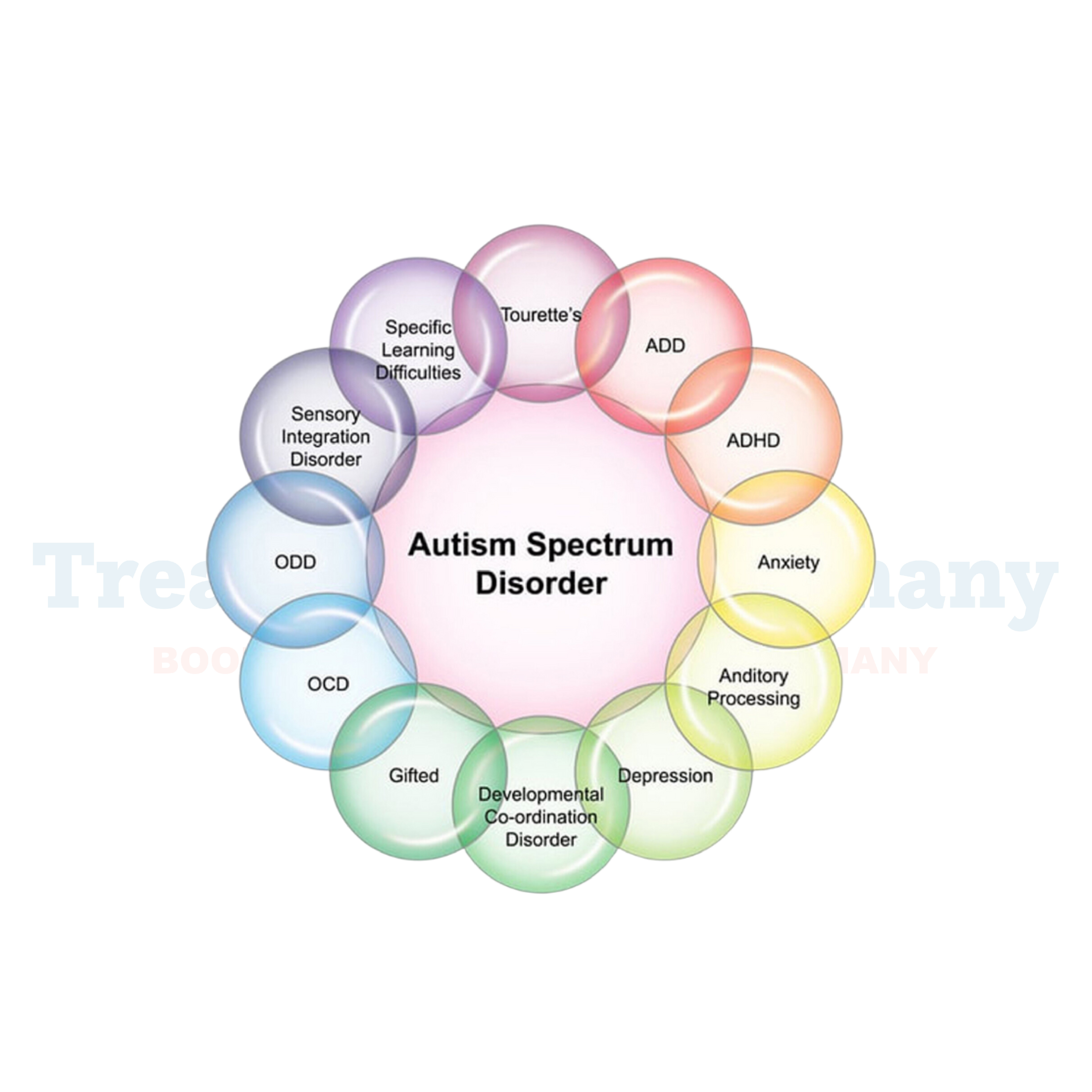
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurological condition that affects an individual's ability to communicate, interact socially, and perceive the world around them.
It is characterized by a wide range of symptoms, behaviors, and levels of impairment, which is why it is referred to as a "spectrum" disorder.
Side Effects of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder may experience a variety of challenges, including:
- Social difficulties: Difficulty understanding social cues, maintaining eye contact, or engaging in typical social interactions.
- Communication challenges: Delayed or impaired speech development, difficulty understanding language nuances, and using language for social purposes.
- Repetitive behaviors: Engaging in repetitive movements (e.g., rocking, hand-flapping) or insisting on routines.
- Sensory sensitivities: Heightened sensitivity or reduced sensitivity to sensory stimuli such as light, sound, touch, or taste.
How is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorder involves a comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals, typically including:
- Developmental history: Gathering information about the individual's early development and behavior.
- Observation: Assessing social interactions, communication skills, and behavior patterns.
- Screening tools: Using standardized tests and questionnaires to evaluate developmental milestones and symptoms associated with ASD.
Potential Treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
While there is no cure for Autism Spectrum Disorder , early intervention and targeted therapies can significantly improve symptoms and quality of life. Treatment options may include:
- Behavioral therapies: Such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), which focuses on improving specific behaviors and teaching new skills.
- Speech-language therapy: To improve communication skills and language development.
- Occupational therapy: Addressing sensory sensitivities and developing daily living skills.
- Medication: Sometimes prescribed to manage associated symptoms such as anxiety, hyperactivity, or aggression.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
