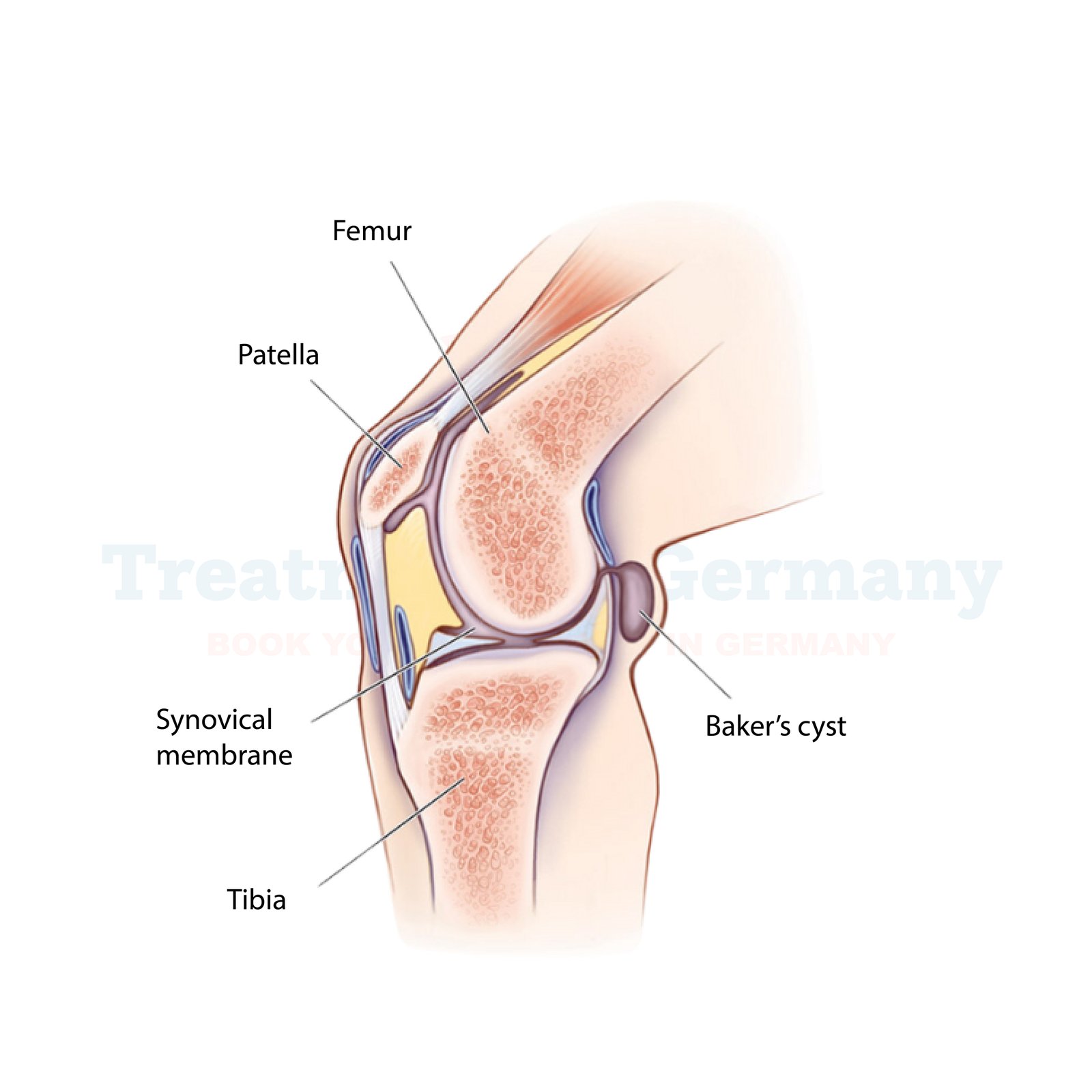
A Baker’s cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst, is a fluid-filled swelling that develops at the back of the knee. It is usually caused by underlying joint conditions such as arthritis or meniscal tears, leading to excess synovial fluid accumulation. While a Baker’s cyst is not always painful, it can cause discomfort, stiffness, and restricted movement, affecting daily activities. Germany is renowned for its advanced medical treatments and cutting-edge technologies for joint-related conditions, making it an excellent choice for Baker’s cyst diagnosis and treatment.
A Baker’s cyst develops when excessive fluid accumulates in the knee joint, typically due to:
Osteoarthritis & Rheumatoid Arthritis: Chronic joint inflammation leads to fluid buildup.
Meniscus Tears: Damage to the knee cartilage triggers excess fluid production.
Gout & Other Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like lupus contribute to joint inflammation.
Knee Injuries: Past trauma or repetitive knee strain increases the risk.
Obesity & High BMI: Excess weight puts added stress on the knee joint.
Risk Factors for Baker’s Cyst
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing a Baker’s cyst:
Age: Common in middle-aged and older adults.
Pre-existing Joint Diseases: Arthritis and cartilage injuries increase risk.
Diabetes & High Cholesterol (Hyperlipidemia): These conditions contribute to joint degeneration.
Autoimmune Disorders: Lupus and rheumatoid arthritis cause joint inflammation.
Excessive Knee Use: Repetitive bending or high-impact activities stress the knee joint.
Symptoms of Baker’s Cyst
Swelling at the back of the knee
Stiffness and limited knee mobility
Pain that worsens with activity
Feeling of tightness or pressure behind the knee
Fluid leakage, causing bruising or swelling in the lower leg
In severe cases, the cyst can rupture, leading to sharp pain and swelling in the calf
Diagnosis & Diagnostic Tools
Germany’s top hospitals use state-of-the-art technology to diagnose Baker’s cyst accurately:
X-rays: Identify arthritis or bone abnormalities causing the cyst.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides a detailed view of soft tissues, detecting meniscus tears or joint inflammation.
CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: Offers cross-sectional images to assess the cyst and surrounding structures.
Ultrasound: Helps visualize the cyst, its size, and whether it’s fluid-filled or solid.
Blood Tests: Rule out underlying conditions like infections or autoimmune diseases.
Joint Fluid Analysis: Detects infections or inflammatory markers in synovial fluid.
Baker’s Cyst Treatment in Germany
Germany is at the forefront of treating Baker’s cyst, offering conservative therapies, minimally invasive procedures, and advanced regenerative treatments.
Conservative Treatments
Pain Relievers (NSAIDs): Ibuprofen and naproxen help reduce pain and swelling.
Corticosteroid Injections: Reduce inflammation and relieve discomfort.
Aspiration (Fluid Drainage): Removes excess fluid from the cyst to reduce swelling.
Physical Therapy: Strengthening exercises improve knee stability and reduce fluid buildup.
Compression Therapy: Knee braces or compression sleeves minimize swelling.
Activity Modification: Avoiding excessive knee strain helps prevent cyst enlargement.
Surgical Treatments
Arthroscopic Surgery: A minimally invasive procedure to remove the cyst and repair underlying joint damage.
Open Surgery: Reserved for large or persistent cysts that do not respond to other treatments.
Joint Debridement: Removes inflamed tissue to prevent cyst recurrence.
Meniscus Repair: If a meniscus tear is the underlying cause, surgeons repair or remove the damaged cartilage.
Joint Replacement Surgery: For severe arthritis-related cysts, knee replacement may be necessary.
Innovative Therapies in Germany
Germany excels in pioneering treatments for Baker’s cyst and joint regeneration:
Stem Cell Therapy: Uses a patient’s own stem cells to regenerate damaged cartilage and reduce inflammation.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Injects concentrated platelets to promote tissue healing and reduce cyst formation.
Dendritic Cell Therapy: Boosts the immune system’s ability to reduce chronic joint inflammation.
Shockwave Therapy: Uses sound waves to break down scar tissue and improve fluid drainage.
Laser Therapy: Reduces inflammation and speeds up recovery.
TACE (Transarterial Chemoembolization): A targeted approach to reduce inflammation in complex joint conditions.
Why Choose Germany for Baker’s Cyst Treatment?
Germany offers unparalleled advantages for patients seeking Baker’s cyst treatment:
World-Class Hospitals: Equipped with the latest medical technology.
Highly Skilled Specialists: Experienced orthopedic surgeons and rheumatologists.
Innovative Treatment Options: Access to regenerative medicine and minimally invasive techniques.
Efficient Healthcare System: Short waiting times and comprehensive patient care.
Personalized Rehabilitation Programs: Tailored physical therapy and recovery plans.
Medical Tourism Services: International patient assistance, including translation and accommodation support.
Solutions & Prevention of Baker’s Cyst
Preventive Measures
Maintain a Healthy BMI: Reducing weight decreases knee joint stress.
Regular Exercise: Low-impact activities like swimming and cycling strengthen the knee.
Proper Warm-up & Stretching: Prevents knee injuries that could lead to cyst formation.
Joint Protection Strategies: Using knee braces during high-impact activities
Managing Underlying Conditions: Controlling arthritis, diabetes, and cholesterol levels to prevent inflammation.
Nutritional Support: A diet rich in omega-3s, calcium, and vitamin D supports joint health.
Regular Medical Checkups: Early detection and treatment of joint conditions can prevent cyst formation.
Complementary Therapies
Acupuncture & Massage Therapy: Helps reduce pain and improve circulation.
Hydrotherapy: Water-based exercises for joint mobility and reduced impact on knees.
Mind-Body Techniques: Stress management strategies like meditation for chronic pain relief.
Herbal Medicine: Some natural remedies are being explored in Germany for their potential in joint health.
Conclusion
Baker’s cyst can cause significant discomfort and mobility issues, but Germany’s advanced medical treatments provide effective solutions. From conservative management to cutting-edge therapies like stem cell treatment and PRP therapy, Germany offers world-class healthcare tailored to each patient’s needs. Choosing Germany for treatment ensures access to top specialists, modern diagnostic tools, and innovative solutions for long-term joint health. With the right medical intervention, lifestyle changes, and preventive measures, individuals can effectively manage Baker’s cyst and maintain an active, pain-free life.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
