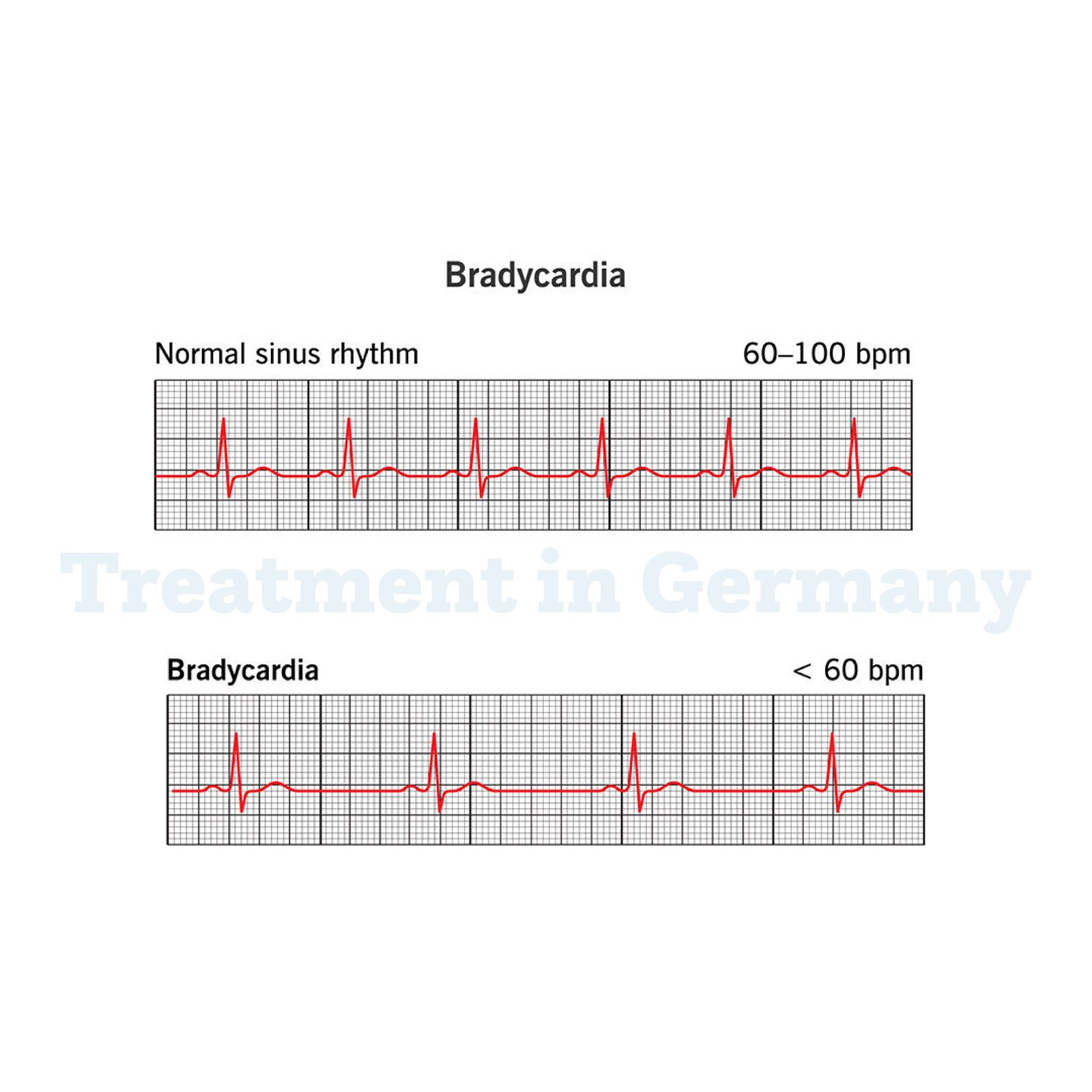
Understanding Bradycardia
Bradycardia is a condition characterized by an unusually slow heart rate, typically fewer than 60 beats per minute in adults. This can result in insufficient blood flow to the body, affecting overall health and wellbeing.
Side Effects of Bradycardia
Bradycardia can lead to various symptoms and complications, including:
Diagnosis of Bradycardia
Diagnosing Bradycardia involves several diagnostic tests and evaluations:
Potential Treatments for Bradycardia
The treatment of Bradycardia depends on its underlying cause, severity, and symptoms:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
