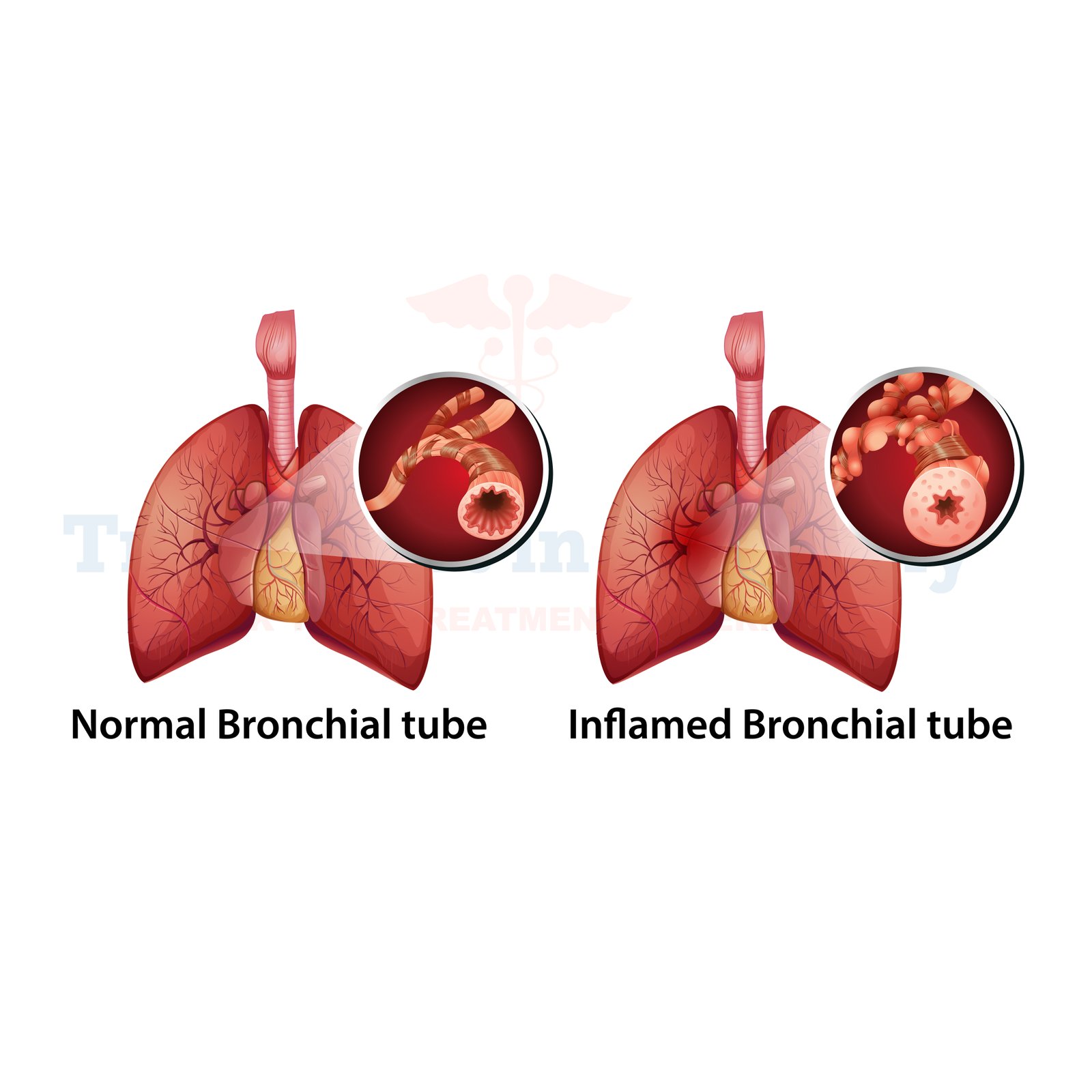
What is Bronchiectasis?
Bronchiectasis is a chronic lung condition characterized by the widening and damage of the airways in the lungs. This damage inhibits the normal clearance of mucus, leading to its accumulation in the affected airways. Over time, this buildup can result in recurrent lung infections and inflammation, further worsening the condition.
Side Effects of Bronchiectasis
The symptoms of bronchiectasis can vary from person to person but often include:
If left untreated, bronchiectasis can lead to complications such as respiratory failure or heart problems.
How is Bronchiectasis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Bronchiectasis typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, including:
1. Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs can reveal abnormalities in the lungs, such as widened airways or areas of inflammation.
2. Pulmonary Function Tests: These tests assess lung function, including how well you can inhale and exhale air.
3. Sputum Culture: Analyzing a sample of mucus from the lungs can help identify the presence of bacteria or other pathogens.
4. Bronchoscopy: A procedure in which a thin, flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the airways to visualize the lungs and collect tissue samples if needed.
Potential Treatments of Bronchiectasis
While bronchiectasis is a chronic condition with no cure, treatment aims to manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life. Treatment options may include:
1. Airway Clearance Techniques: Techniques such as chest physiotherapy or using devices like a flutter valve or oscillatory positive expiratory pressure (OPEP) device can help clear mucus from the airways.
2. Medications: Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat infections, while bronchodilators or inhaled corticosteroids can help improve airflow and reduce inflammation.
3. Vaccinations: Annual flu vaccines and pneumococcal vaccines are recommended to prevent respiratory infections.
4. Lifestyle Modifications: Quitting smoking, staying hydrated, and maintaining a healthy weight can help manage symptoms and reduce exacerbations.
5. Surgery: In severe cases, surgery to remove damaged portions of the lung or to repair bronchial abnormalities may be considered.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
