Understanding Bronchitis:
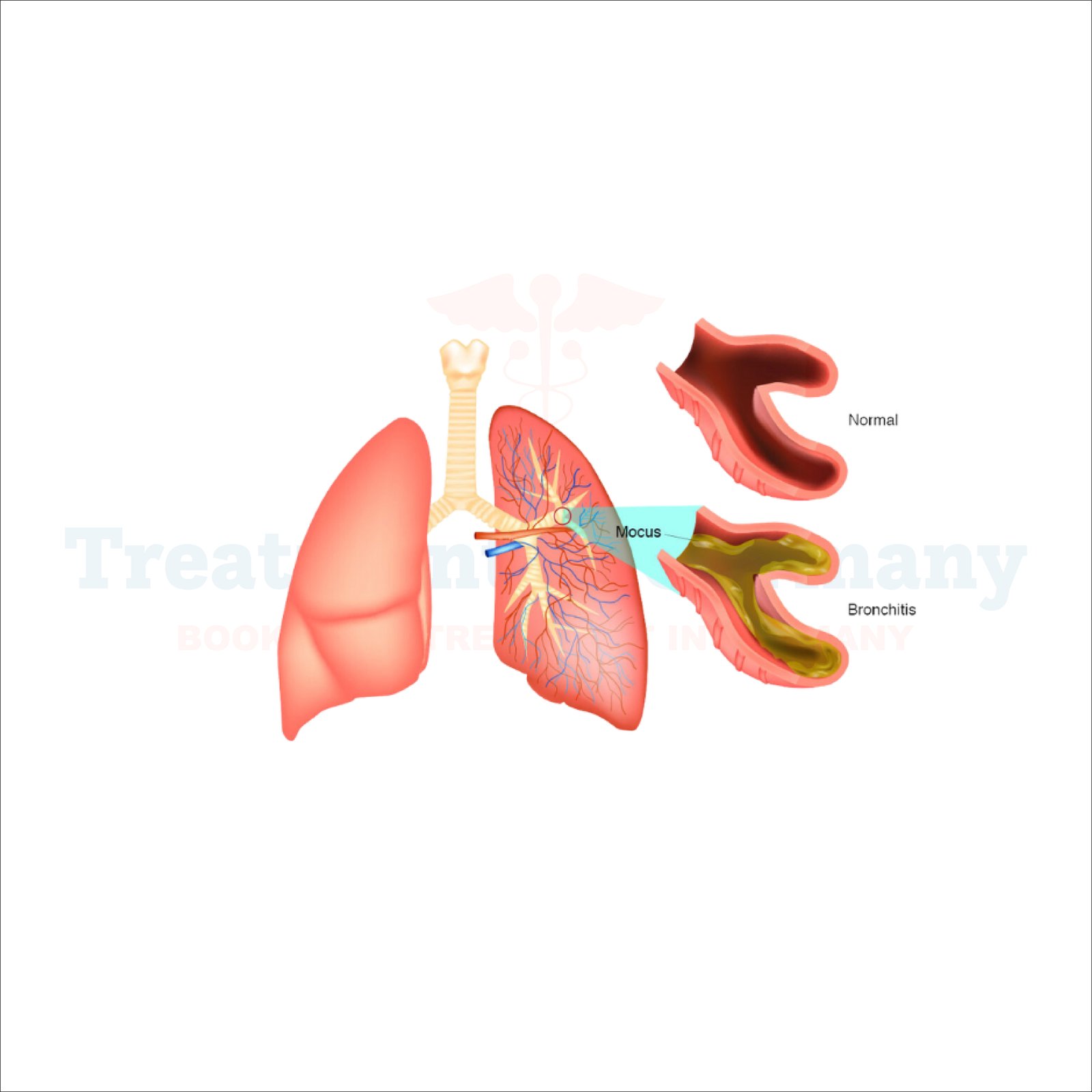
Bronchitis is a respiratory condition characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the air passages in the lungs. It can be acute, lasting for a few weeks, or chronic, lasting for months or recurring frequently over time. Bronchitis is often caused by viruses, particularly those that cause the common cold or flu.
However, bacteria, irritants such as tobacco smoke or air pollution, and underlying health conditions can also contribute to its development.
Side Effects of Bronchitis:
The symptoms of bronchitis can vary in severity and may include:
1. Coughing: Persistent coughing is a hallmark symptom of bronchitis. It may produce mucus, which can be clear, white, yellow, or greenish.
2. Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath, especially during physical activity, is common.
3. Chest Discomfort: Chest tightness or discomfort may occur due to inflammation in the bronchial tubes.
4. Fatigue: Bronchitis can cause fatigue and weakness, impacting daily activities.
5. Sore Throat: Irritation of the throat may lead to a sore or scratchy throat.
6. Fever and Chills: In some cases, bronchitis can be accompanied by fever and chills, especially if it is caused by a bacterial infection.
Diagnosis of Bronchitis:
Diagnosing bronchitis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Your doctor may listen to your lungs with a stethoscope to check for abnormal sounds such as wheezing or crackling. They may also ask about your symptoms and perform other tests, such as:
1. Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray may be ordered to rule out other conditions, such as pneumonia.
2. Pulmonary Function Tests: These tests measure how well your lungs are functioning and can help determine the severity of bronchitis.
3. Sputum Culture: If bacterial infection is suspected, a sample of mucus coughed up from your lungs may be tested to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection.
Potential Treatments of Bronchitis:
Treatment for bronchitis depends on whether it is acute or chronic and its underlying cause. In most cases, acute bronchitis will resolve on its own with rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms such as pain and fever. However, if bacterial infection is present, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
For chronic bronchitis, long-term management may be necessary to control symptoms and prevent complications. This may include:
1. Bronchodilators: These medications help open the airways and make breathing easier.
2. Corticosteroids: Inhaled corticosteroids can reduce inflammation in the airways.
3. Pulmonary Rehabilitation: This program includes exercise training, education, and counseling to improve lung function and overall quality of life.
4. Oxygen Therapy: Supplemental oxygen may be prescribed for severe cases of chronic bronchitis to ensure adequate oxygen levels in the blood.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
