What is Burns?
Burns are injuries to the skin and sometimes deeper tissues caused by heat, electricity, chemicals, or radiation.
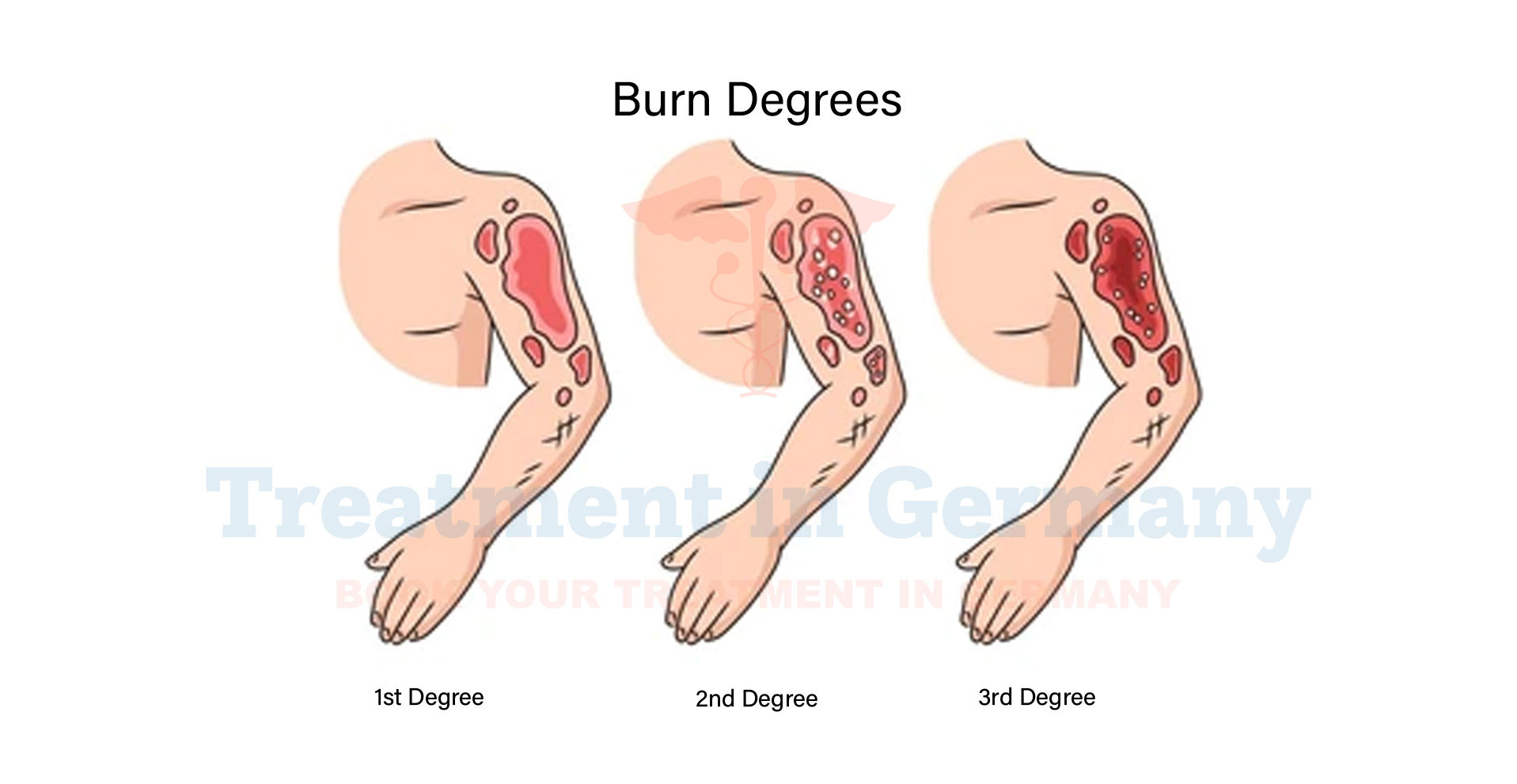
They can vary in severity from mild to life-threatening and are categorized into first-degree, second-degree, and third-degree burns based on their depth and extent.
Side Effects of Burns
The side effects of burns can range from mild discomfort to severe complications, depending on the extent and depth of the injury. Common side effects include:
- Pain and discomfort: Burns can be very painful, especially when nerve endings are affected.
- Swelling and redness: The injured skin often becomes swollen and may appear red or discolored.
- Blisters: Second-degree burns can cause fluid-filled blisters to form on the skin.
- Scarring: Severe burns can lead to permanent scarring and loss of function in affected areas.
- Infection: Burned skin is more susceptible to infection, which can delay healing and worsen outcomes.
- Fluid loss and electrolyte imbalance: Extensive burns can lead to fluid loss and imbalance of electrolytes in the body, requiring careful management.
How is Burns Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of burns typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional. They assess the extent and depth of the burn and classify it accordingly.
In some cases, additional tests such as imaging studies or blood tests may be required to evaluate the severity of the injury and assess for associated complications like inhalation injury or systemic effects.
Potential Treatment of Burns
Treatment of burns aims to relieve pain, prevent infection, and promote healing. Depending on the severity of the burn, treatment options may include:
- First Aid: Immediate first aid involves cooling the burn with cool (not cold) water, covering it with a sterile dressing, and seeking medical attention promptly.
- Medications: Pain relievers and antibiotics may be prescribed to manage pain and prevent infection.
- Wound Care: Proper wound care is crucial, which may include cleaning the burn, applying topical medications or dressings, and monitoring for signs of infection.
- Fluid Replacement: For severe burns, intravenous fluids may be necessary to prevent dehydration and maintain electrolyte balance.
- Surgical Interventions: In cases of deep or extensive burns, surgical procedures such as skin grafting may be performed to promote healing and minimize scarring.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
