What is Calcinosis?
Calcinosis is a medical condition characterized by the abnormal accumulation of calcium salts in soft tissues of the body.
These deposits can occur in various parts of the body such as the skin, muscles, tendons, and other tissues.
Calcinosis can present itself in different forms, including dystrophic calcinosis where deposits occur in damaged or inflamed tissue, and metastatic calcinosis where deposits happen due to underlying metabolic disorders like hypercalcemia.
Side Effects of Calcinosis
The presence of calcium deposits in soft tissues can lead to several complications for patients. Common side effects include pain, swelling, stiffness, and restricted movement in affected areas.
In severe cases, calcinosis can cause skin ulcerations, infections, and damage to underlying tissues and organs.
How is Calcinosis Diagnosed?
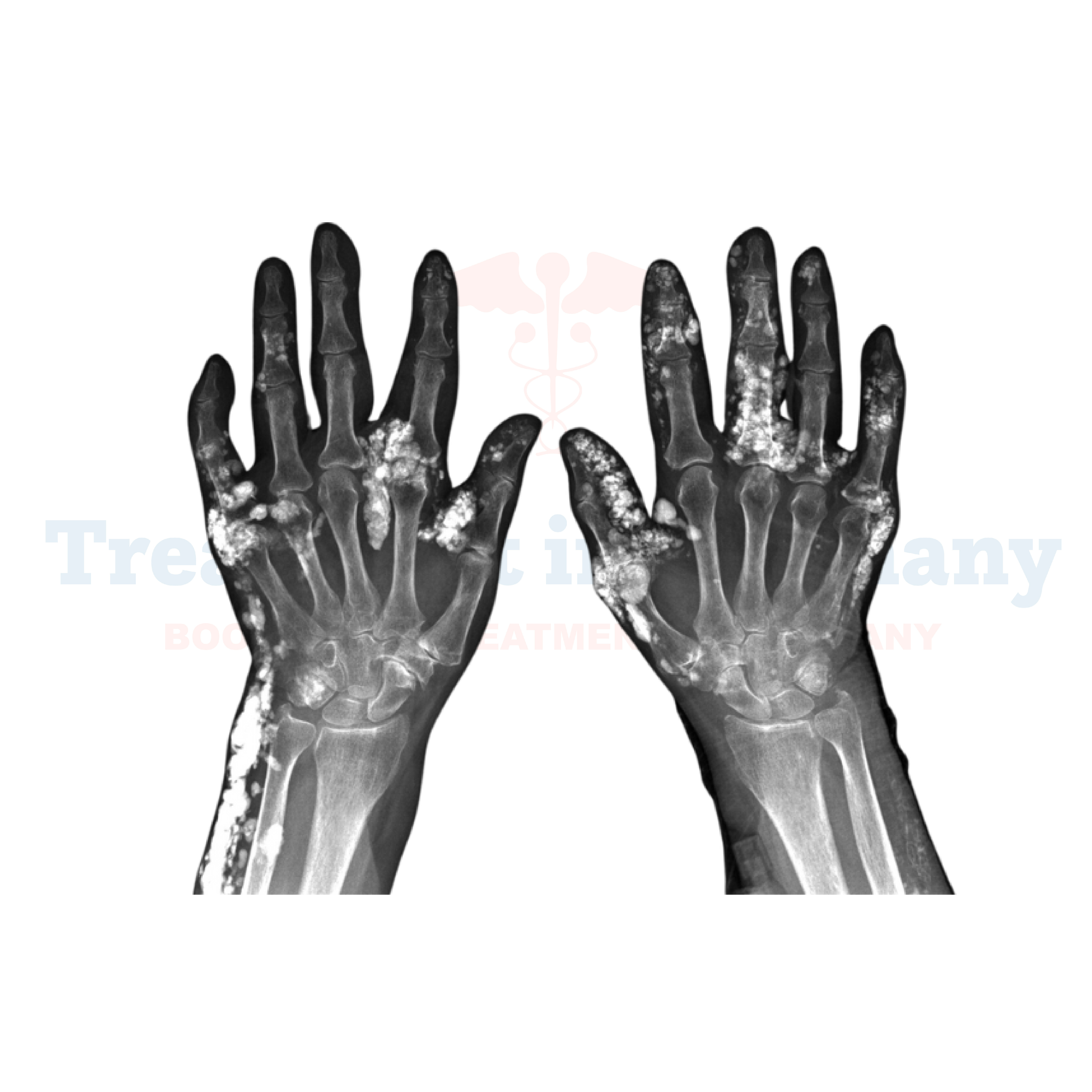
Diagnosing calcinosis typically involves a combination of clinical assessment, imaging studies such as X-rays and CT scans to visualize the calcium deposits, and sometimes blood tests to assess calcium and phosphate levels.
A thorough medical history and physical examination are crucial for understanding the extent and impact of calcinosis on the patient's health.
Potential Treatment of Calcinosis
Treatment of calcinosis focuses on managing symptoms and reducing the burden of calcium deposits. In Germany, treatment approaches may include:

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
