Cardiomyopathy is a group of diseases that affect the heart muscle, impacting its ability to pump blood effectively. This condition can lead to serious complications, including heart failure and irregular heartbeats.
Understanding the types, symptoms, causes, and treatment options for cardiomyopathy is crucial for managing this complex heart disorder and improving quality of life for those affected.
Understanding the Types of Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy comes in various forms, each with its own discrete characteristics and challenges. Let's explore the main types of this heart muscle disease:
Dilated Cardiomyopathy: When the Heart Chambers Expand
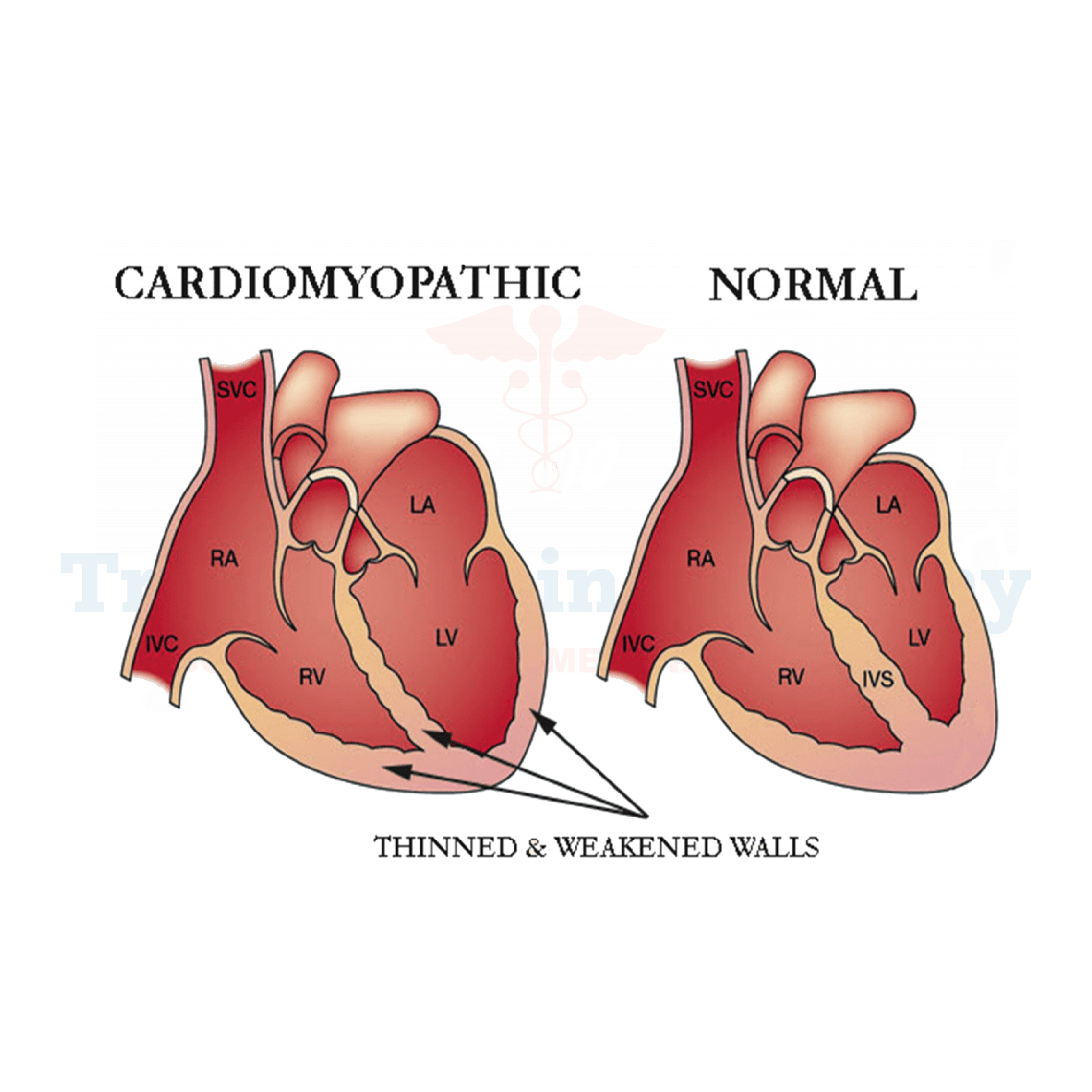
This heart ailment most commonly manifests as dilated cardiomyopathy. This kind causes the heart's chambers to expand and stretch, particularly the ventricles. This expansion weakens the heart muscle, making it harder to pump blood effectively.
Causes of dilated cardiomyopathy can include genetic factors, viral infections, alcohol abuse, and certain medications. People with this condition often experience fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling in their legs and ankles. Treatment in Germany typically involves medications to improve heart function and manage symptoms.
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Thickening of the Heart Muscle
The hallmark of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the left ventricle's increased heart muscular thickness,this thickening may cause blood flow obstructions and other issues.
Key features of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy include its often genetic nature, affecting people of all ages, and the potential to cause sudden cardiac death in young athletes. Symptoms can range from mild to severe, including chest pain, shortness of breath, and fainting spells. Management typically involves medications, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, surgical interventions.
Ischemic Cardiomyopathy: When Blood Flow is Restricted
Ischemic cardiomyopathy, which frequently results from coronary artery disease, is a condition in which the heart muscle weakens as a result of decreased blood flow. Damage to the heart muscle and decreased cardiac function may result from this lack of blood flow.
High blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, and diabetes are risk factors. Treatment focuses on managing underlying heart disease, often through medications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes coronary revascularization procedures.
Recognizing the Symptoms and Causes of Cardiomyopathy
Understanding the symptoms and causes of cardiomyopathy is crucial for early detection and effective management of the condition.
Common Symptoms Across Different Types of Cardiomyopathy
While symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of cardiomyopathy, some common signs include shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling in the extremities, irregular heartbeats, dizziness, and chest pain. It's crucial to remember that in the early phases of the illness, some people could not exhibit any symptoms.
Unraveling the Causes and Risk Factors for Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy can have a variety of reasons, some of which are unknown. However, several risk factors for cardiomyopathy have been identified, including genetic predisposition, high blood pressure, heart valve problems, alcoholism, certain viral infections, metabolic disorders, and pregnancy complications. Early intervention and prevention initiatives can benefit from an understanding of these risk factors.
Diagnosing Cardiomyopathy: Tests and Procedures
Accurate diagnosis of cardiomyopathy is crucial for proper management and treatment. Healthcare providers use a variety of tests and procedures to identify and assess the condition.
Non-Invasive Diagnostic Techniques
Several non-invasive tests can help diagnose cardiomyopathy:
These tests help doctors assess heart function, identify structural abnormalities, and determine the type and severity of cardiomyopathy.
Advanced Diagnostic Procedures
More sophisticated diagnostic techniques can be required in specific situations.
Ambulatory monitoring: Long-term cardiac rhythm tracking is done via devices such as Holter monitors.
These advanced tests provide additional information to guide treatment decisions and help to predict the course of the disease.
Innovative Treatment Approaches for Cardiomyopathy
While there's no cure for cardiomyopathy, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment plans in Germany are tailored to the specific type of cardiomyopathy and individual patient needs.
Medication-Based Treatments in Germany
Medications play a crucial role in managing cardiomyopathy. Common drugs used include beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, diuretics, and anticoagulants. These medications can help improve heart function, manage symptoms, and prevent complications.
Devices to Correct Arrhythmias and Improve Heart Function
For some patients, implantable devices can be life-saving. Devices to correct arrhythmias include implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) that monitor heart rhythm and deliver shocks to correct dangerous arrhythmias. With cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), the ventricles of the heart contract in unison thanks to a specialized pacemaker.
Lifestyle Modifications and Supportive Care
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing cardiomyopathy.
Heart-Healthy Living with Cardiomyopathy
Patients with cardiomyopathy are often advised to follow a heart-healthy diet, engage in regular moderate exercise, quit smoking, limit alcohol consumption, and manage stress. These lifestyle modifications can help reduce the workload on the heart and improve overall health.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Living with a chronic heart condition can be emotionally challenging. Many patients benefit from support groups, counseling, and education programs to better understand and manage their condition. For those with cardiomyopathy, emotional health is a critical component of overall health.
Cutting-Edge Research and Future Directions
The field of cardiomyopathy research is rapidly evolving, with new treatments and diagnostic tools on the horizon.
Emerging Therapies and Clinical Trials
Researchers are exploring several promising avenues, including gene therapy to correct underlying genetic defects, stem cell treatments to regenerate damaged heart tissue, and new medications targeting specific molecular pathways involved in cardiomyopathy. Patients interested in cutting-edge treatments may consider participating in clinical trials to access these innovative therapies.
Innovations in Personalized Medicine
The future of cardiomyopathy treatment lies in personalized medicine, including genetic profiling to predict disease progression and treatment response, tailored treatment plans based on individual characteristics, and advanced imaging techniques for early detection and monitoring of heart changes.
Living with Cardiomyopathy: Coping Strategies and Long-Term Outlook
While cardiomyopathy is a serious condition, many people lead full and active lives with proper management.
Adapting to Life with a Chronic Heart Condition
Living with cardiomyopathy often requires lifestyle adjustments, including regular medical check-ups, symptom monitoring, balancing activity and rest, and planning for the future. A high quality of life is maintained by many individuals with cardiomyopathy when they receive the appropriate care and support.
Transthyretin Amyloidosis Cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM): A Unique Challenge
Transthyretin amyloidosis cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM) is a specific type of cardiomyopathy caused by the buildup of abnormal proteins in the heart. This rare form of the disease presents unique challenges in diagnosis and treatment. Recent advances offer hope for patients with this complex form of cardiomyopathy.
Global Perspectives on Cardiomyopathy Research
Cardiomyopathy research is a global endeavor, with contributions from scientists and clinicians worldwide. For instance, Germany has been at the forefront of developing new diagnostic techniques for early detection of cardiomyopathy.
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia (ARVD): A Rare but Serious Form
The right ventricle is the main organ affected by the uncommon cardiomyopathy known as arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD). It's characterized by the replacement of heart muscle with fatty or fibrous tissue, leading to arrhythmias and potential sudden cardiac death.
The Role of Scar Tissue in Cardiomyopathy
Scar tissue formation in the heart can significantly impact the progression of cardiomyopathy. Understanding the mechanisms of scar formation and developing strategies to prevent or reverse it are active areas of research in the field of cardiology.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
