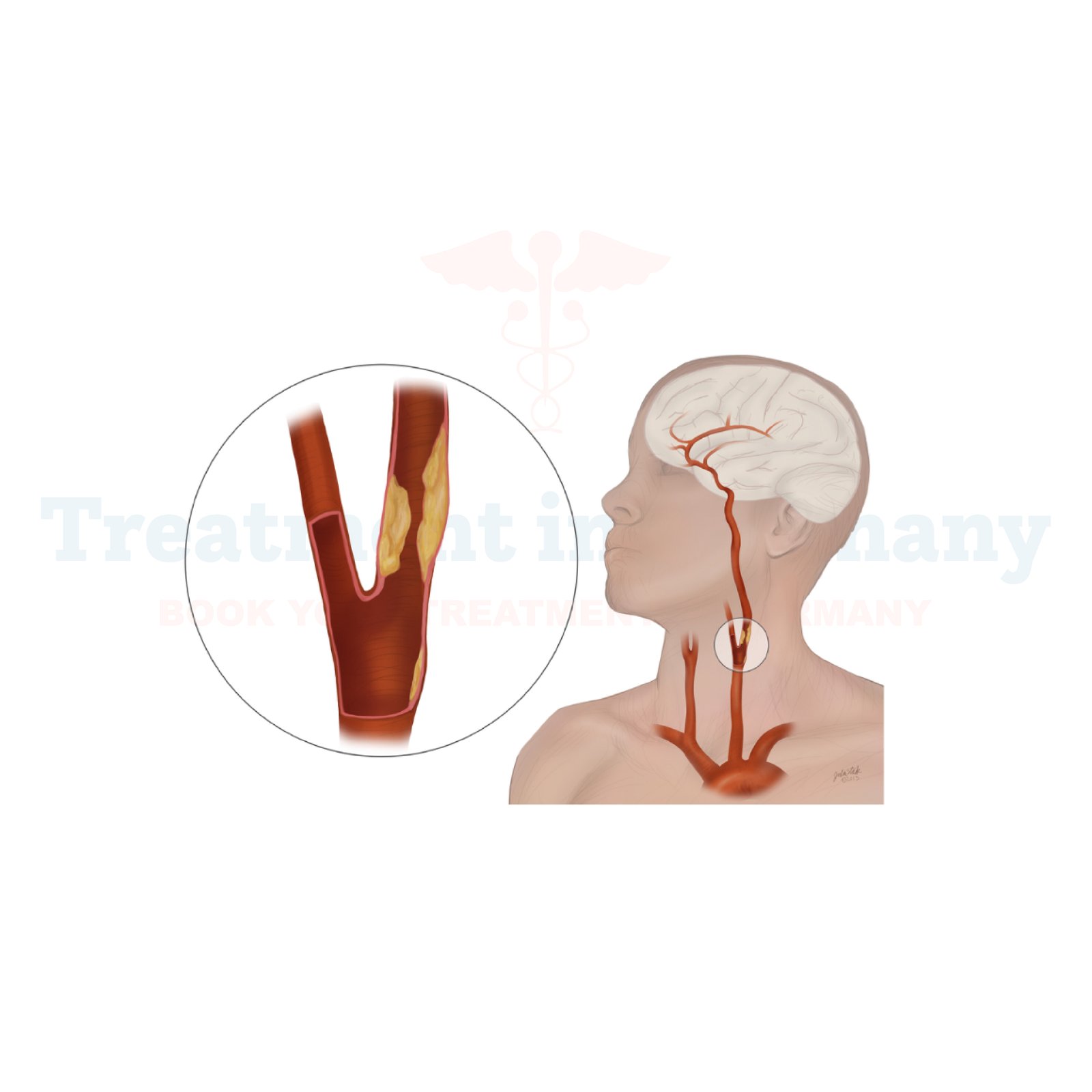
What is Carotid Artery Disease?
Carotid Artery Disease refers to the narrowing or blockage of the carotid arteries, which are major blood vessels located on each side of the neck. These arteries supply oxygen-rich blood to the brain, and when they become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of plaque, it can lead to serious health complications such as stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
Side effects of Carotid Artery Disease:
The narrowing or blockage of the carotid arteries can lead to various side effects, including:
1. Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA): Also known as a "mini-stroke," a TIA occurs when blood flow to the brain is temporarily disrupted, leading to symptoms such as weakness or numbness in the face, arms, or legs, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, and temporary loss of vision.
2. Stroke: If the blockage in the carotid arteries becomes severe, it can result in a stroke, which occurs when blood flow to the brain is completely blocked. Strokes can cause permanent brain damage and may lead to long-term disability or even death.
How is Carotid Artery Disease diagnosed?
Diagnosing Carotid Artery Disease typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, including:
1. Carotid Ultrasound: This non-invasive imaging test uses sound waves to create detailed images of the carotid arteries, allowing healthcare providers to assess the degree of narrowing or blockage.
2. Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) or Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA): These imaging tests provide detailed images of the blood vessels in the neck and brain, helping to identify any blockages or abnormalities in the carotid arteries.
3. Angiography: In this procedure, a special dye is injected into the bloodstream, and X-ray images are taken to visualize the flow of blood through the carotid arteries.
Potential treatments of Carotid Artery Disease:
The appropriate treatment for Carotid Artery Disease depends on the severity of the blockage and the patient's overall health. Treatment options may include:
1. Lifestyle Changes: Making lifestyle modifications such as quitting smoking, adopting a healthy diet low in saturated fat and cholesterol, exercising regularly, and managing conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes can help slow the progression of Carotid Artery Disease and reduce the risk of complications.
2. Medications: Certain medications may be prescribed to lower cholesterol levels, reduce blood pressure, prevent blood clots, and control other risk factors associated with Carotid Artery Disease.
3. Carotid Endarterectomy: This surgical procedure involves removing the plaque buildup from the carotid arteries to restore normal blood flow to the brain. It is typically recommended for patients with severe blockages or those who have already experienced a TIA or stroke.
4. Carotid Artery Stenting: In this minimally invasive procedure, a small mesh tube called a stent is inserted into the narrowed or blocked carotid artery to help keep it open and improve blood flow to the brain.
5. Transcarotid Artery Revascularization (TCAR): TCAR is a newer, less invasive procedure that combines elements of carotid endarterectomy and carotid artery stenting. It involves making a small incision in the neck to access the carotid artery and temporarily redirecting blood flow away from the brain to protect against stroke while the blockage is treated.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
