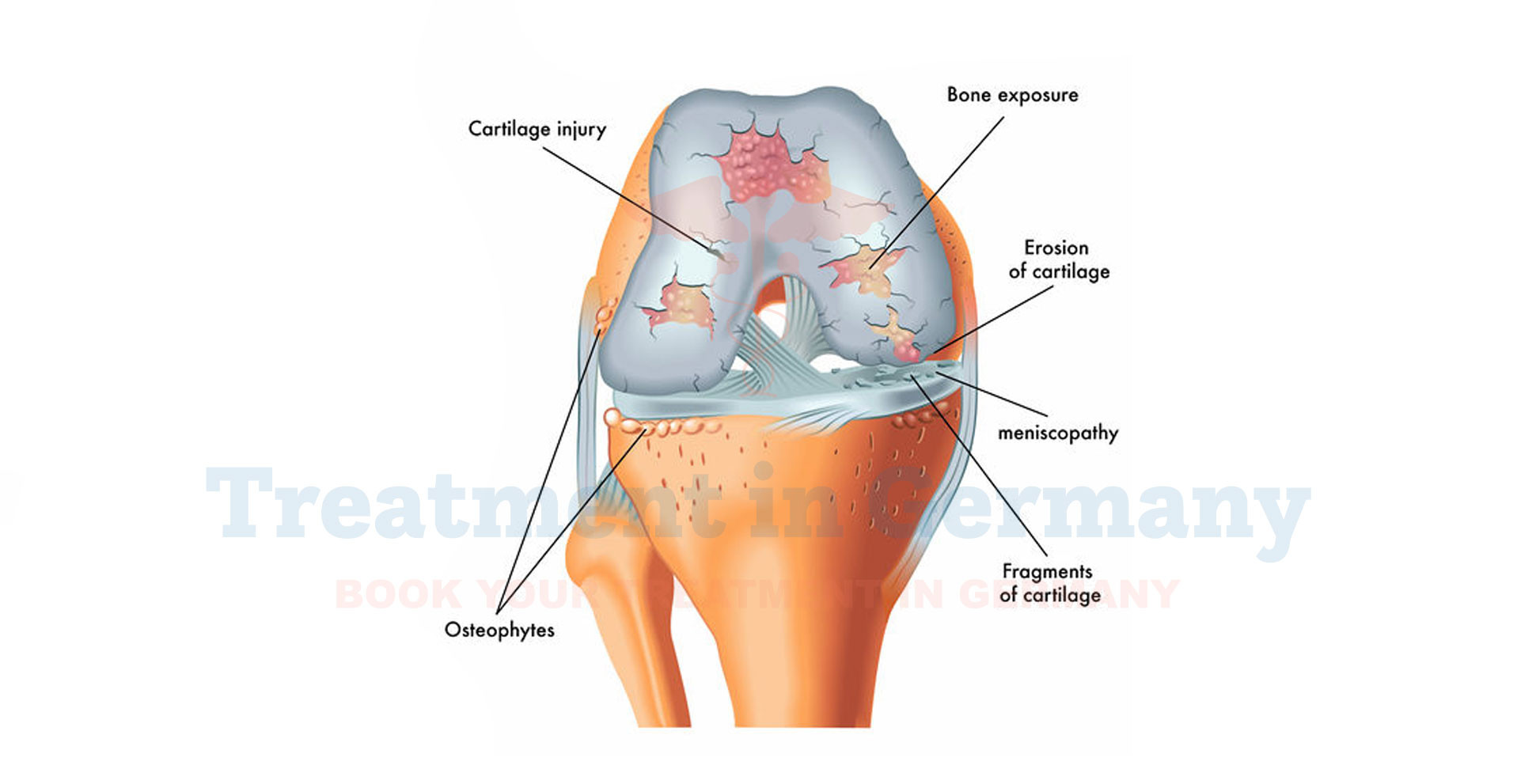
What is Cartilage Damage?
Cartilage damage refers to the deterioration or injury to the cartilage tissue, which is a tough, flexible connective tissue found throughout the body. Cartilage acts as a cushion between bones in joints and helps to absorb shock and prevent friction during movement.
Side Effects of Cartilage Damage
When cartilage is damaged, several symptoms may arise depending on the severity and location of the injury:
- Pain: Especially during movement or weight-bearing activities.
- Stiffness: Difficulty in moving the affected joint.
- Swelling: Inflammation and fluid buildup in and around the joint.
- Joint Instability: Feeling of the joint giving way or being unable to support weight properly.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty in fully bending or straightening the joint.
How is Cartilage Damage Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of cartilage damage typically involves a combination of the following methods:
- Physical Examination: To assess symptoms and joint function.
- Imaging Tests: Such as X-rays, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), or CT (Computed Tomography) scans to visualize the extent and location of the damage.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure where a small camera is inserted into the joint to directly observe the cartilage.
Potential Treatments for Cartilage Damage
Treatment options for cartilage damage vary depending on factors such as the extent of the damage, location, and the patient’s overall health. Some common treatments include:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen muscles around the joint and improve range of motion.
- Injections: Such as corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid to reduce inflammation and provide lubrication.
Surgical Interventions:
- Arthroscopic Debridement: Removal of loose or damaged cartilage.
- Microfracture: Stimulating new cartilage growth by creating tiny fractures in the underlying bone.
- Cartilage Transplantation: Transferring healthy cartilage from another part of the body or using donor tissue.
- Joint Replacement: In severe cases where the damage is extensive and other treatments are ineffective.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
