Cartilage Injuries Treatment in Germany
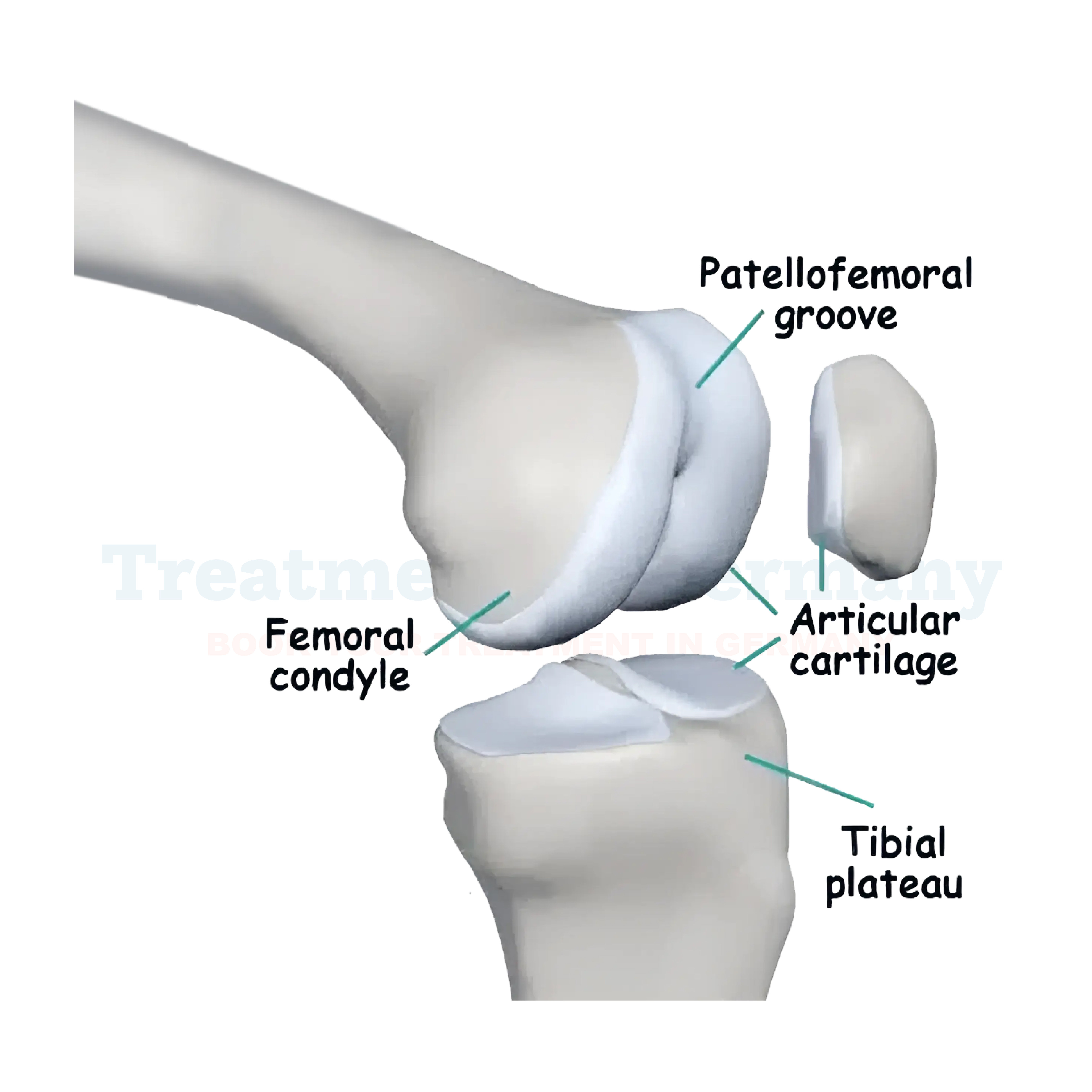
Cartilage injuries occur when the smooth, flexible connective tissue that cushions joints and enables smooth movement is damaged. These injuries can result from trauma, repetitive stress, aging, or underlying medical conditions. Cartilage does not have a direct blood supply, making it difficult to heal naturally. This makes professional medical intervention essential for recovery. Germany is known for its cutting-edge treatments for cartilage injuries, including minimally invasive surgery, regenerative medicine, and innovative therapies like stem cell and PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) therapy.
Causes of Cartilage Injuries
Cartilage injuries can occur due to several factors, including:
Trauma: Sudden impact from accidents, falls, or sports injuries.
- Repetitive Strain: Continuous pressure on joints from activities like running or heavy lifting.
- Aging & Degeneration: Cartilage naturally wears down over time, leading to osteoarthritis.
- Obesity & High BMI: Excess weight puts stress on joints, increasing the risk of cartilage damage.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can trigger cartilage deterioration.
- Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes and high cholesterol (hyperlipidemia) can contribute to joint damage.
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals are predisposed to cartilage-related disorders.
Risk Factors of Cartilage Injuries
Certain factors make individuals more susceptible to cartilage injuries:
- Athletes & Active Individuals: High-impact sports like football, basketball, and skiing increase the risk.
- Age: Older adults are more prone to cartilage degeneration.
- Previous Joint Injuries: Past injuries weaken joint structures, making them vulnerable.
- Poor Posture & Joint Overuse: Incorrect movement patterns can accelerate cartilage wear.
- Occupational Hazards: Jobs requiring frequent kneeling, squatting, or lifting can strain cartilage.
Symptoms of Cartilage Injuries
- Joint Pain: Mild to severe pain that worsens with movement.
- Swelling & Inflammation: The affected area may become swollen and tender.
- Stiffness & Reduced Mobility: Difficulty bending or straightening the joint.
- Clicking or Locking Sensation: The joint may catch or lock due to loose cartilage fragments.
- Weakness & Instability: Difficulty bearing weight on the affected joint.
Diagnosis & Diagnostic Tools
Germany’s top medical centers use advanced imaging and diagnostic tools for precise evaluation:
- X-rays: Identify bone-related abnormalities but may not detect cartilage damage.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides a detailed view of soft tissues, including cartilage.
- CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: Helps visualize cartilage damage in complex joint structures.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure using a camera to examine and treat cartilage damage.
- Blood Tests: Identify underlying autoimmune or metabolic conditions contributing to cartilage deterioration.
Cartilage Injury Treatment in Germany
Germany is renowned for its advanced orthopedic care, offering conservative treatments, minimally invasive procedures, and regenerative therapies for cartilage injuries.
Conservative (Non-Surgical) Treatments
- Pain Relievers (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen help manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening exercises improve joint mobility and stability.
- Orthopedic Braces & Supports: Help reduce stress on injured joints.
- Hyaluronic Acid Injections: Lubricates joints to ease movement and reduce pain.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Weight management and proper ergonomics prevent further damage.
Minimally Invasive & Surgical Treatments
For severe cartilage damage, Germany offers state-of-the-art procedures:
- Arthroscopic Debridement: Removes loose cartilage fragments to relieve pain and improve function.
- Microfracture Surgery: Stimulates new cartilage growth by creating small holes in the bone.
- Osteochondral Autograft Transplantation (OATS): Replaces damaged cartilage with healthy tissue from another part of the body.
- Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (ACI): Cultivates and implants the patient’s own cartilage cells to regenerate damaged areas.
- Joint Replacement Surgery: In extreme cases, artificial joints may be used to restore mobility.
Innovative Therapies in Germany
Germany is at the forefront of regenerative medicine, offering cutting-edge treatments:
- Stem Cell Therapy: Uses regenerative cells to repair damaged cartilage and promote healing.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Enhances tissue repair by injecting platelets from the patient’s own blood.
- Dendritic Cell Therapy: A novel immune-based treatment for inflammation control.
- Shockwave Therapy: Stimulates tissue regeneration using high-energy sound waves.
- Laser Therapy: Reduces inflammation and accelerates tissue healing.
- TACE (Transarterial Chemoembolization): A targeted treatment for chronic joint inflammation.
Why Choose Germany for Cartilage Injury Treatment?
Germany is a leading destination for orthopedic and regenerative medicine due to:
- World-Class Hospitals & Clinics: Equipped with state-of-the-art technology.
- Highly Skilled Specialists: Renowned orthopedic surgeons and sports medicine experts.
- Innovative & Minimally Invasive Techniques: Faster recovery and reduced complications.
- Comprehensive Rehabilitation Programs: Personalized therapy for long-term recovery.
- Medical Tourism Support: Assistance with visas, accommodation, and language services.
Solutions & Prevention of Cartilage Injuries
Preventive Measures
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Reduces joint stress and cartilage wear.
- Strength Training & Exercise: Strengthens muscles around joints to improve stability.
- Use Proper Footwear & Equipment: Supports joint health and reduces impact.
- Avoid Overuse & High-Impact Activities: Take breaks and use correct techniques to prevent injury.
- Manage Underlying Conditions: Control diabetes, arthritis, and metabolic disorders.
Complementary Therapies
- Acupuncture & Massage Therapy: Helps alleviate pain and improve circulation.
- Hydrotherapy: Water-based therapy reduces joint strain and enhances mobility.
- Herbal Supplements: Natural remedies support joint and cartilage health.
- Mind-Body Techniques: Meditation and stress management aid in pain relief.
Conclusion
Cartilage injuries can significantly impact mobility and quality of life, but Germany offers world-class diagnostic tools, minimally invasive treatments, and regenerative therapies to promote recovery. With top-tier orthopedic specialists, state-of-the-art hospitals, and personalized rehabilitation programs, Germany remains a preferred destination for cartilage injury treatment. Seeking expert care and implementing preventive strategies can help individuals achieve long-term joint health and mobility.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
