What is Celiac Disease?
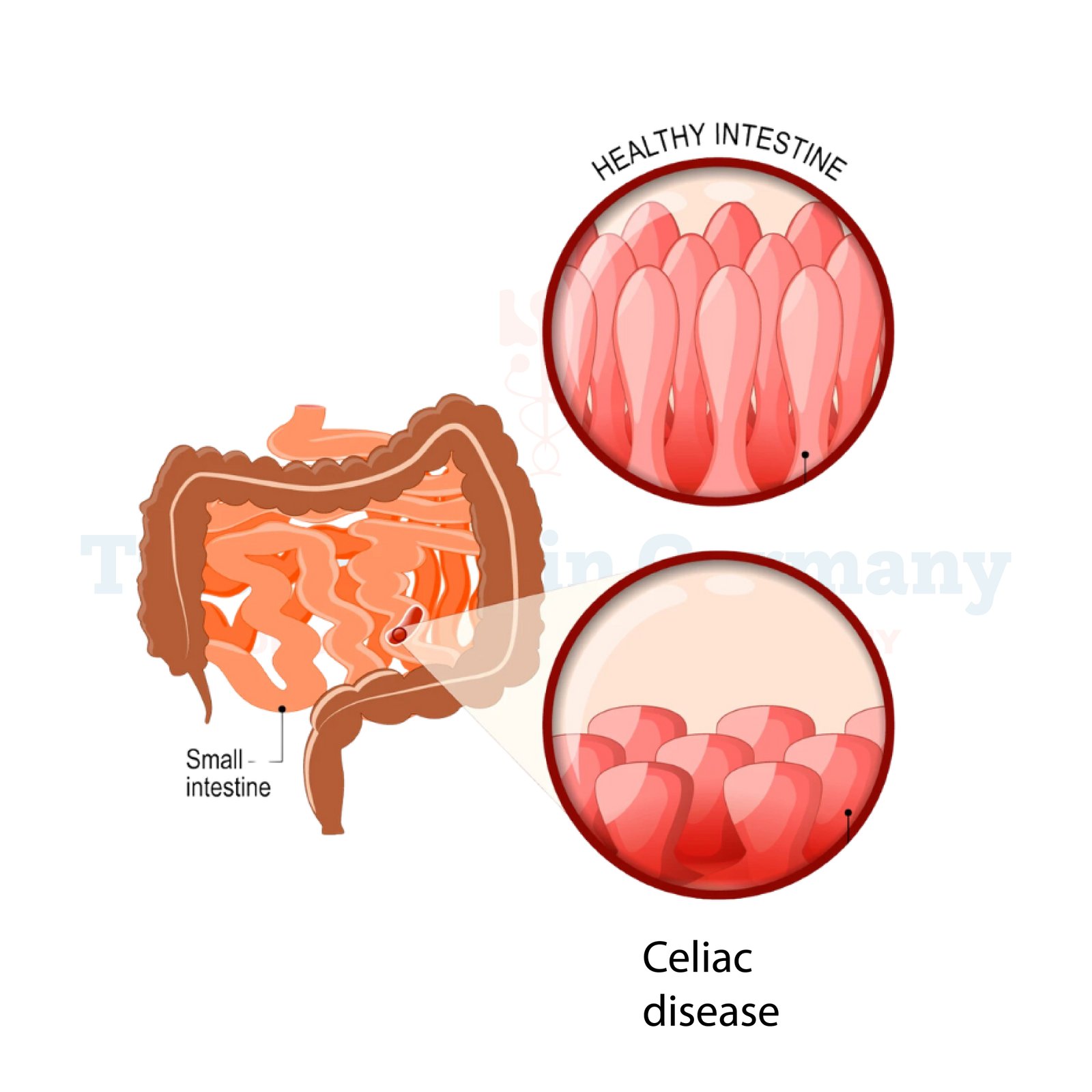
Celiac Disease, also known as Coeliac Disease, is a chronic autoimmune disorder triggered by the ingestion of gluten-containing foods. Gluten is a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye.
When individuals with Celiac Disease consume gluten, their immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the small intestine, leading to inflammation and damage to the intestinal villi.
This damage impairs the absorption of nutrients from food, resulting in various symptoms and complications.
Side Effects of Celiac Disease:
The symptoms of Celiac Disease can vary widely among individuals and may include:
Untreated Celiac Disease can lead to serious complications such as infertility, miscarriage, neurological disorders, and an increased risk of certain cancers, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and management.
How is Celiac Disease Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Celiac Disease typically involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, blood tests, and confirmatory procedures. The primary diagnostic tool is the serologic testing for specific antibodies associated with Celiac Disease, including anti-tissue transglutaminase (tTG) and anti-endomysial antibodies (EMA).
If these tests suggest Celiac Disease, an endoscopic biopsy of the small intestine may be performed to assess the extent of damage to the intestinal villi.
It is crucial for individuals suspected of having Celiac Disease to continue consuming gluten-containing foods prior to testing, as a gluten-free diet can interfere with accurate diagnosis.
Potential Treatments of Celiac Disease:
Currently, the only effective Treatment for Celiac Disease is strict adherence to a lifelong gluten-free diet. This involves avoiding all foods and products containing wheat, barley, and rye. Patients must also be vigilant about cross-contamination in food preparation and be cautious when dining out or purchasing packaged foods.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
