Understanding Cholecystitis:
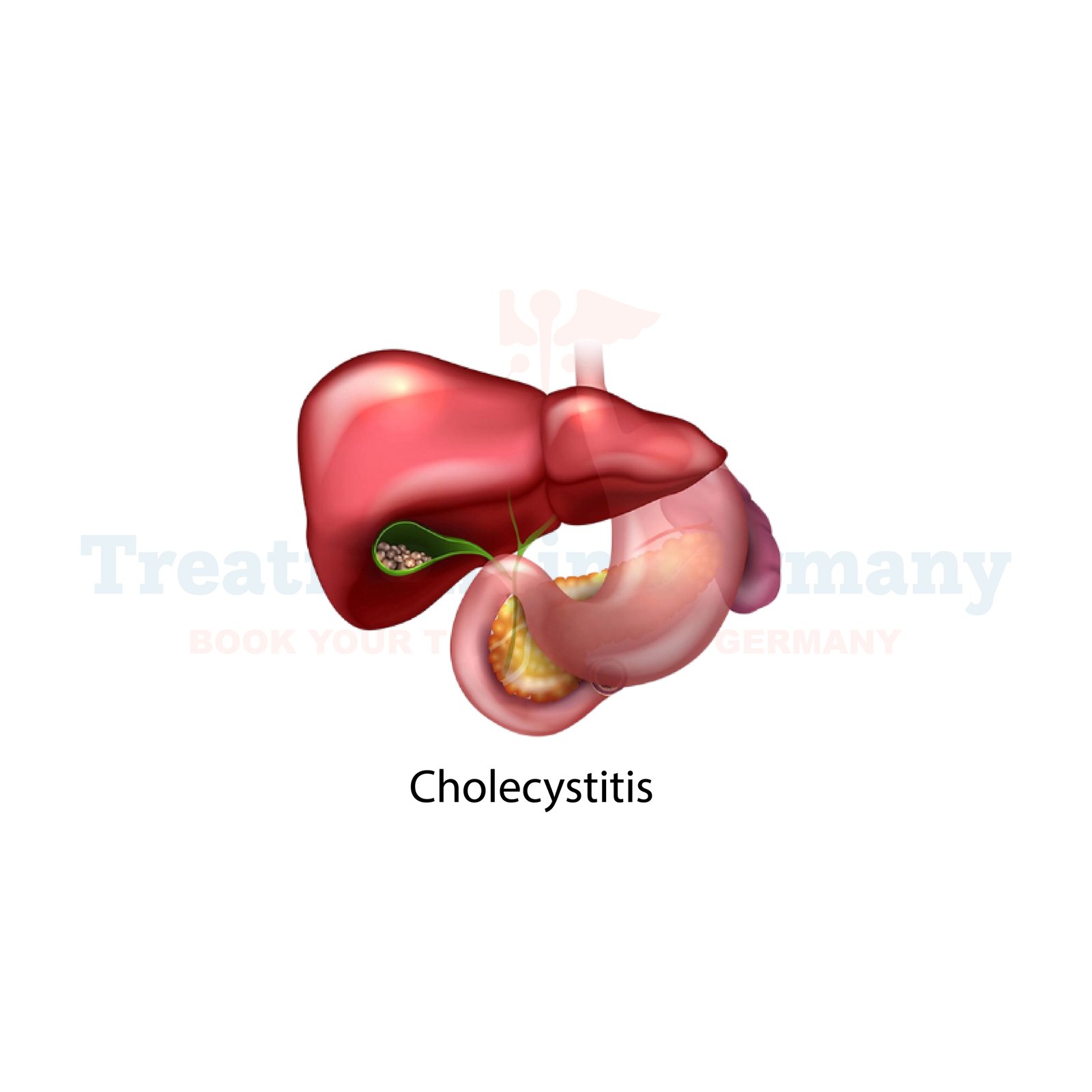
Cholecystitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the gallbladder, which is a small organ located beneath the liver. The gallbladder plays a crucial role in storing bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver.
Cholecystitis often occurs when bile becomes trapped in the gallbladder due to the presence of gallstones or other blockages.
Side Effects of Cholecystitis:
The inflammation associated with cholecystitis can lead to a range of symptoms, including:
- Abdominal Pain: Patients with cholecystitis often experience sudden and intense pain in the upper right abdomen, which may radiate to the back or shoulder.
- Nausea and Vomiting: The inflammation can cause nausea and vomiting, especially after consuming fatty or greasy foods.
- Fever: Some individuals may develop a fever as a result of the body's immune response to the inflammation.
- Jaundice: In severe cases, cholecystitis can lead to jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes due to the buildup of bilirubin in the bloodstream.
How is Cholecystitis Diagnosed?
To Diagnose Cholecystitis, healthcare providers may perform a combination of the following tests:
- Physical Examination: A doctor will examine the abdomen for tenderness and swelling, and inquire about the patient's symptoms.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can help identify signs of inflammation and assess liver function.
- Imaging Tests:Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans may be used to visualize the gallbladder and identify any signs of inflammation or blockages.
- HIDA Scan: A hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan involves injecting a radioactive tracer into the bloodstream to evaluate the function of the gallbladder and detect any obstruction in the bile ducts.
Potential Treatments of Cholecystitis:
The treatment approach for cholecystitis depends on the severity of the condition and the patient's overall health. Options may include:
- Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs may help alleviate symptoms during mild cases of cholecystitis.
- Antibiotics: If cholecystitis is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to help clear the infection.
- Gallbladder Removal Surgery (Cholecystectomy): For recurrent or severe cases of cholecystitis, surgical removal of the gallbladder may be recommended. This procedure can be performed laparoscopically, with small incisions and a shorter recovery time.
- Percutaneous Cholecystostomy: In cases where surgery is not immediately possible, a tube may be inserted through the skin into the gallbladder to drain excess bile and relieve symptoms temporarily.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a
complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
