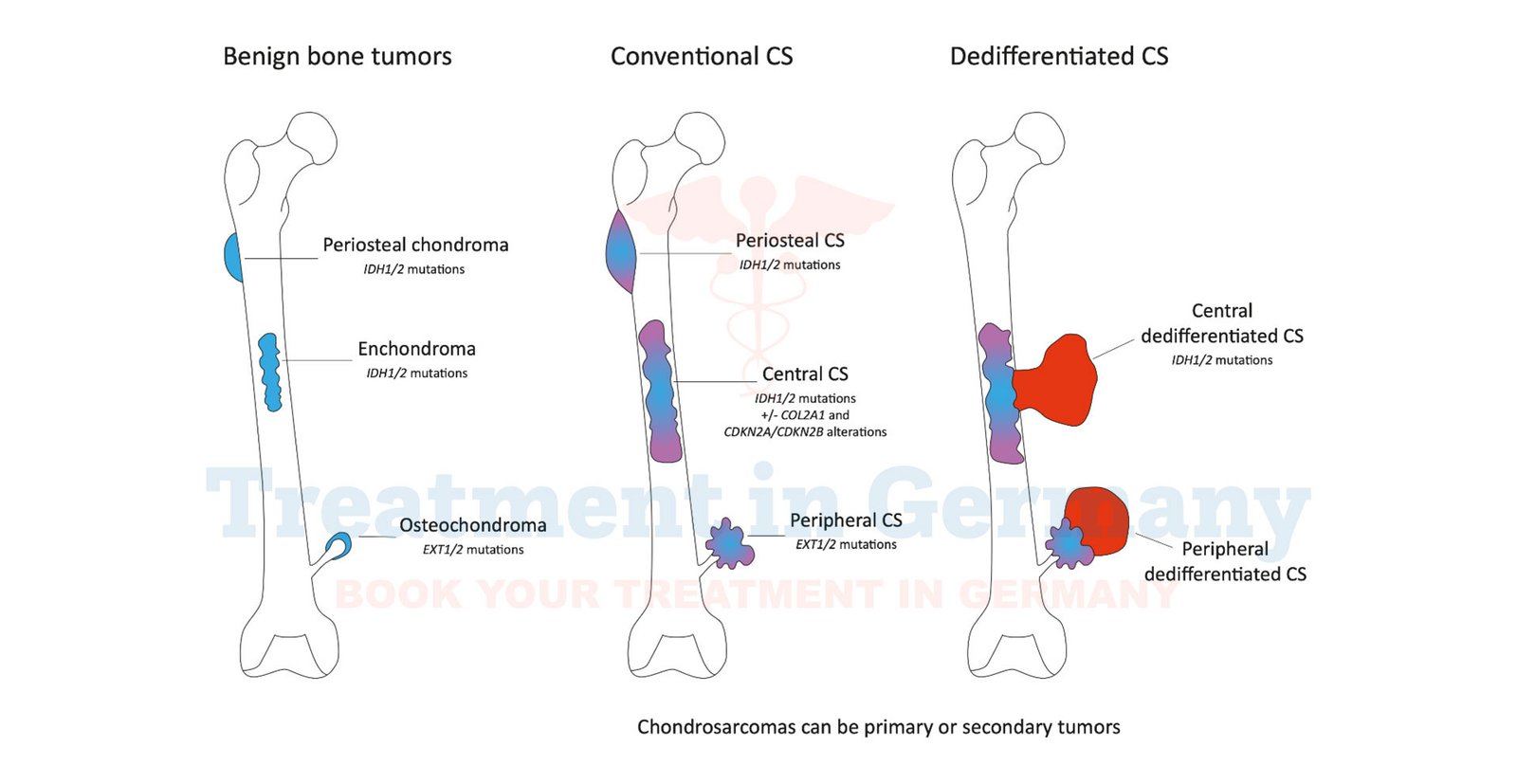
What is Chondrosarcoma?
Chondrosarcoma is a type of cancer that develops in the bones and belongs to a group of cancers known as sarcomas.
It specifically originates in the cells that produce cartilage, which is the tough, flexible tissue found throughout the body, providing cushioning and support to joints.
Side Effects of Chondrosarcoma
The symptoms and side effects of chondrosarcoma can vary depending on its location and size. Common signs may include:
- Pain: Persistent pain in the affected bone or joint.
- Swelling: Swelling around the tumor site.
- Limited Mobility: Difficulty moving the affected limb or joint.
- Fractures: Increased risk of fractures due to weakened bone structure.
- Neurological Symptoms: If the tumor compresses nerves, it can cause neurological symptoms such as numbness or weakness.
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial in managing these symptoms and preventing complications.
How is Chondrosarcoma Diagnosed?
Diagnosing chondrosarcoma typically involves several steps:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Your doctor will review your medical history and conduct a physical exam to assess symptoms and any noticeable abnormalities.
- Imaging Tests: Techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, or PET scans are used to visualize the affected bone and determine the size and location of the tumor.
- Biopsy: A biopsy is often necessary to confirm the diagnosis. During this procedure, a sample of tissue is removed from the tumor and examined under a microscope by a pathologist to determine if it is cancerous and, if so, what type of cancer it is.
Potential Treatments for Chondrosarcoma
The treatment of chondrosarcoma depends on several factors, including the size and location of the tumor, its grade (how abnormal the cells look under a microscope), and your overall health. Treatment options may include:
- Surgery: Surgery is the primary treatment for chondrosarcoma. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible while preserving surrounding healthy tissue and function. In some cases, amputation or limb-sparing surgery may be necessary.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy may be used before or after surgery to kill cancer cells or reduce the size of the tumor.
- Chemotherapy: Although chemotherapy is generally not very effective for treating chondrosarcoma, it may be used in certain cases where the cancer has spread or cannot be removed completely with surgery.
- Targeted Therapy: Newer treatments, such as targeted therapy and immunotherapy, are being studied in clinical trials to determine their effectiveness against chondrosarcoma.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
