Germany is considered one of the world leaders in advanced treatments for chronic myeloid leukemia, or a type of blood cancer caused by bone marrow. Advanced treatments for CML include tyrosine kinase inhibitors and allogeneic stem cell transplantation, among others, for which Germany is widely acclaimed, offering unique and personalized care with high survival rates and quality of life.
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia is a type of blood malignancy that originates in the bone marrow due to a genetic mutation that leads to an elevated amount of abnormal white blood cells. This can eliminate proper red leukemia and platelet production, potentially leading to anemia and splenomegaly.
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia progresses slowly and can result in death if left untreated at the first signs of the condition. The latest advancements in medical technology ensure proper diagnosis and effective management of the disease in Germany.
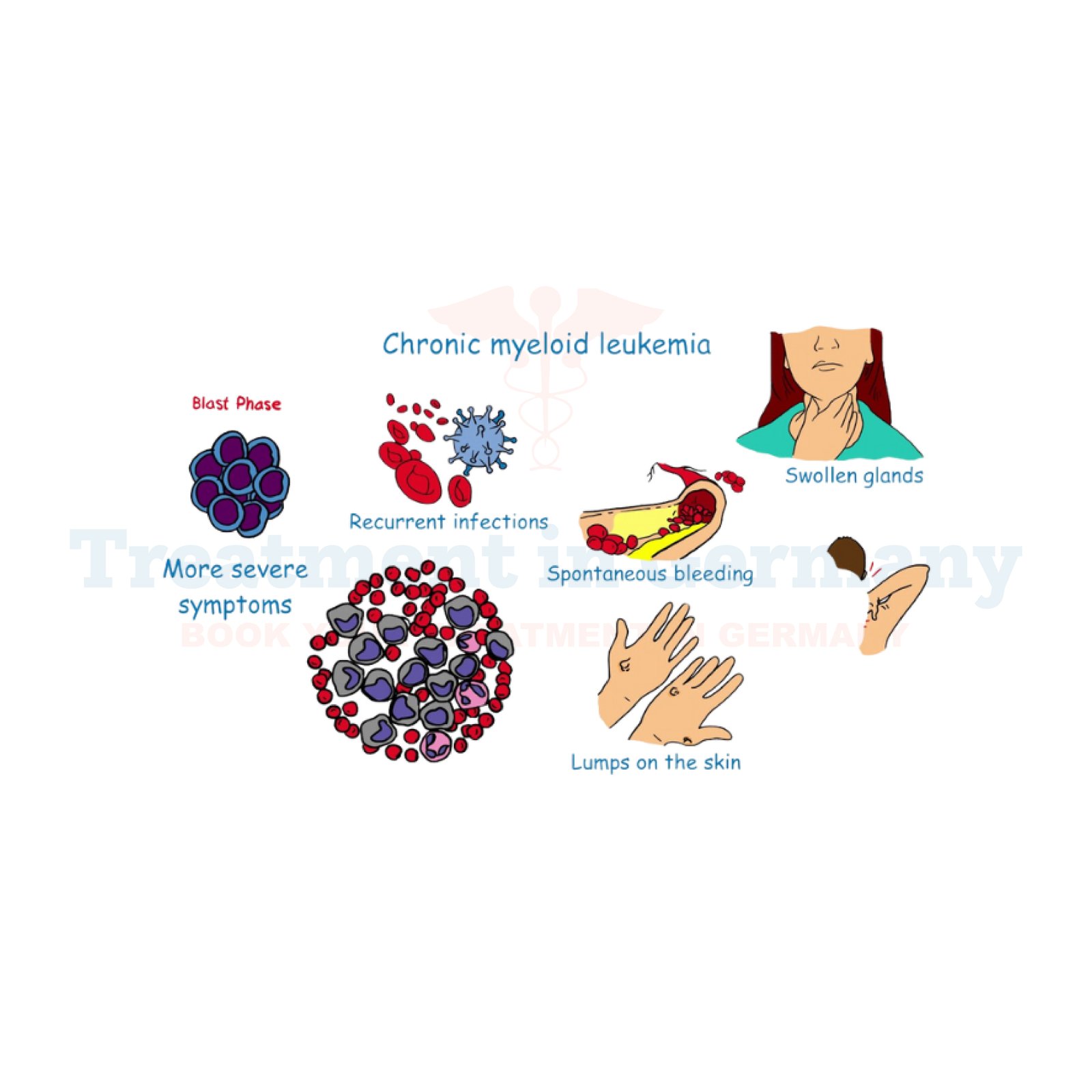
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Symptoms
The early stages may not exhibit symptoms. However, the symptoms begin to manifest with the advancement of the disease as follows:
Early detection of such symptoms through routine checkups in Germany will most likely increase the chances of proper treatment.
Diagnosis of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Germany
Germany uses state of the art diagnostic tools and competent professionals to properly diagnose CML. The most often used techniques for diagnosis are:
The German centers are well armed with all modern facilities so that the diagnosis done will be correct. So, treatment will be proper and fruitful.
Stages of CML
There are three basic stages of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia .
The German doctors are highly skilled at identifying the disease phase. It is probably one of the main justifications for the adoption of various treatment protocols for different patients.
New Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Treatments in Germany
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors are currently the first-line treatment for CML. These drugs act by suppressing the abnormally produced kinase due to the BCRABL gene, which decreases the multiplication of leukemic cells. The TKIs available are:
TKIs are good medications that cause remission and also improve quality of life. These medicines are being handed out very liberally in Germany with close monitoring by professionals. Side effects include diarrhea, muscle spasms, fluid retention, pleural effusion, pancreatitis, and liver inflammation.
Chemotherapy of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Chemotherapy is recommended if the TKIs fail. Chemotherapy decreases the amount of abnormal cells that are present, and it also decreases symptoms. Advanced chemotherapy regimens are provided in Germany and are individualized to specific patient needs.
Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation
For refractory CML patients, allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation stands as a potential curative treatment. It involves an invasive process where the disease-causing bone marrow is replaced with healthy donor stem cells but applies only to the advanced stages. Some of the best hospitals at sea in Germany have top-notch services in performing successful transplants coupled with advanced care protocols.
Prognosis and Survival Rate in Germany
The advance of treatment in CML has dramatically improved survival rates. Now, more than 90% of patients attain long-term remission with TKIs. Some patients are now able to discontinue treatment and stay within treatment-free remission. Germany boasts a magnificent care system and the latest research, which guarantees these patients the best in worldwide treatment with great survival outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the cause of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia?
CML is provoked by a chromosomal mutation called the Philadelphia chromosome, which has an abnormality resulting in the overproduction of blood cells. This mutation can be confirmed in some expert genetic testing conducted in Germany.
What are the early warning signs of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia?
The early symptoms are fatigue, fever, shortness of breath, and night sweats, but they are mostly found during routine blood testing; early detection is highly encouraged. Early detection is a prominent interest in the German healthcare system.
How is Chronic Myeloid Leukemia treated in Germany?
Germany provides complete care, including TKIs, chemotherapy, and allogeneic stem cell transplantation, for the treatment and potential cure of the disease.
Is it possible to fully cure Chronic Myeloid Leukemia?
It can be cured by allogeneic stem cell transplantation, but most of the patients achieve long-term remission with target therapy. Any proper case will be provided with curative treatment in the specialized facilities in Germany.
Are TKIs safe?
In general, yes, TKIs are effective and relatively well-tolerated but may be accompanied by side effects such as muscle spasms, stomach pains, and edema. Germany’s health system would make sure that patients on TKIs are monitored regularly to establish effective management of their side effects.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
