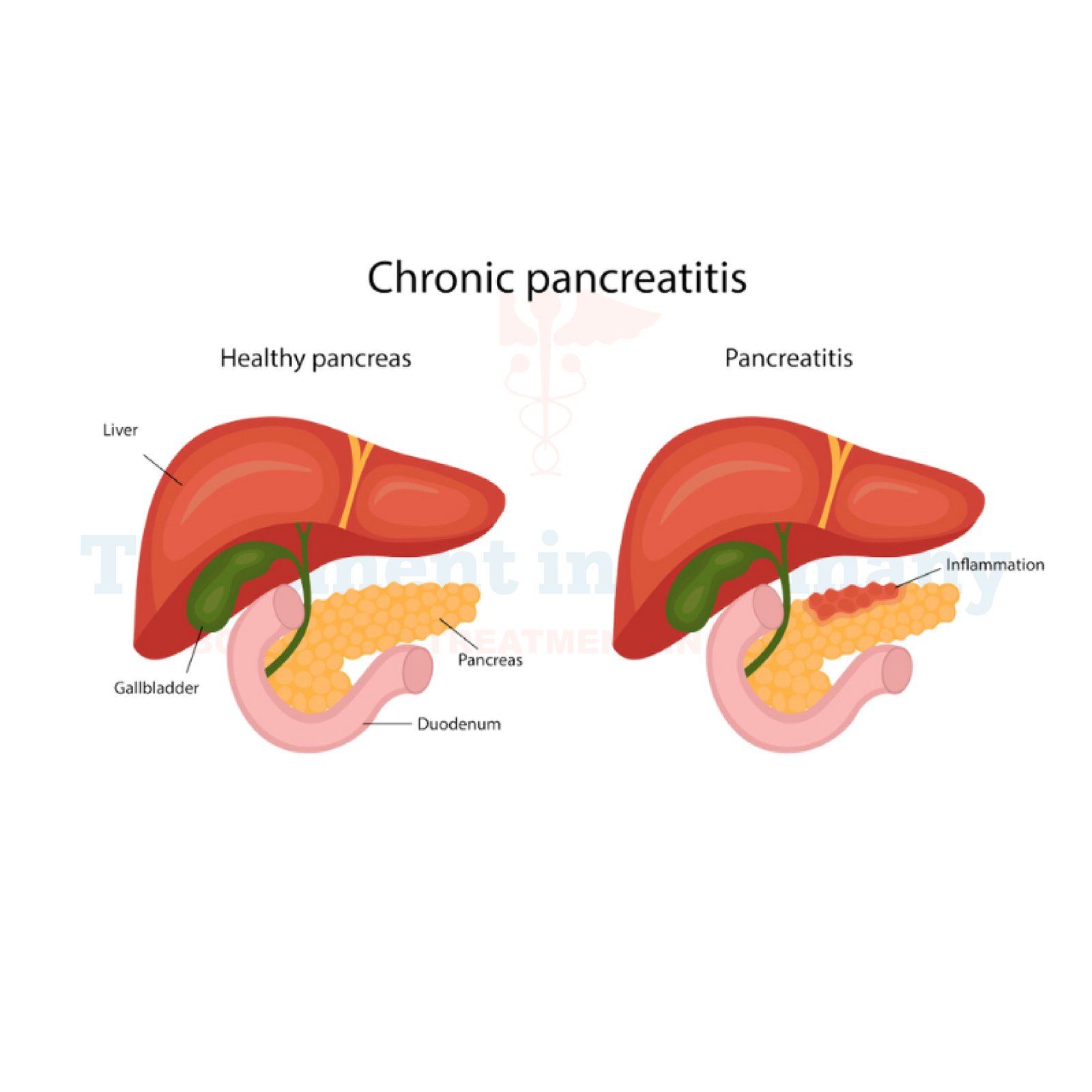
What is Chronic Pancreatitis?
Chronic Pancreatitis is a debilitating condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas, a vital organ responsible for producing digestive enzymes and insulin. Over time, this inflammation can cause irreversible damage to the pancreas, leading to persistent pain, digestive problems, and potential complications.
Side Effects of Chronic Pancreatitis:
The symptoms of Chronic Pancreatitis can vary from mild discomfort to severe pain and can include:
- Abdominal pain: Persistent, severe pain in the upper abdomen, which may worsen after eating or drinking alcohol.
- Digestive issues: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and unintended weight loss due to poor absorption of nutrients.
- Diabetes: Damage to the pancreas can impair insulin production, leading to diabetes.
- Malnutrition: Poor digestion can lead to malnutrition and vitamin deficiencies.
- Pancreatic pseudocysts: Fluid-filled sacs that can develop within or around the pancreas, causing further complications.
How is Chronic Pancreatitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Chronic Pancreatitis involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, including:
- Imaging tests: CT scans, MRI, or endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) to visualize the pancreas and assess for inflammation or structural abnormalities.
- Blood tests: Checking for elevated levels of pancreatic enzymes, such as amylase and lipase, which indicate pancreatic inflammation.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): A specialized procedure to examine the pancreatic and bile ducts for blockages or abnormalities.
- Fecal elastase test: Assessing fecal elastase levels to evaluate pancreatic enzyme function.
Potential Treatments of Chronic Pancreatitis:
The treatment approach for Chronic Pancreatitis aims to relieve symptoms, manage complications, and preserve pancreatic function. Depending on the severity of the condition, treatment options may include:
- Pain management: Over-the-counter or prescription pain medications, pancreatic enzyme supplements, or nerve block injections to alleviate abdominal pain.
- Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding alcohol, quitting smoking, adopting a low-fat diet, and maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pancreatic stress.
- Endoscopic interventions: Endoscopic therapy to remove blockages, drain pseudocysts, or widen narrowed pancreatic ducts.
- Surgical options: In severe cases or when other treatments fail, surgical procedures such as pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple procedure) or total pancreatectomy may be considered.
- Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT): Oral enzyme supplements to aid digestion and alleviate malabsorption-related symptoms.
- Diabetes management: Insulin therapy or oral medications to control blood sugar levels in patients who develop diabetes due to pancreatic damage.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a
complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
