What is Coagulation Disorders (e.g., Hemophilia)?
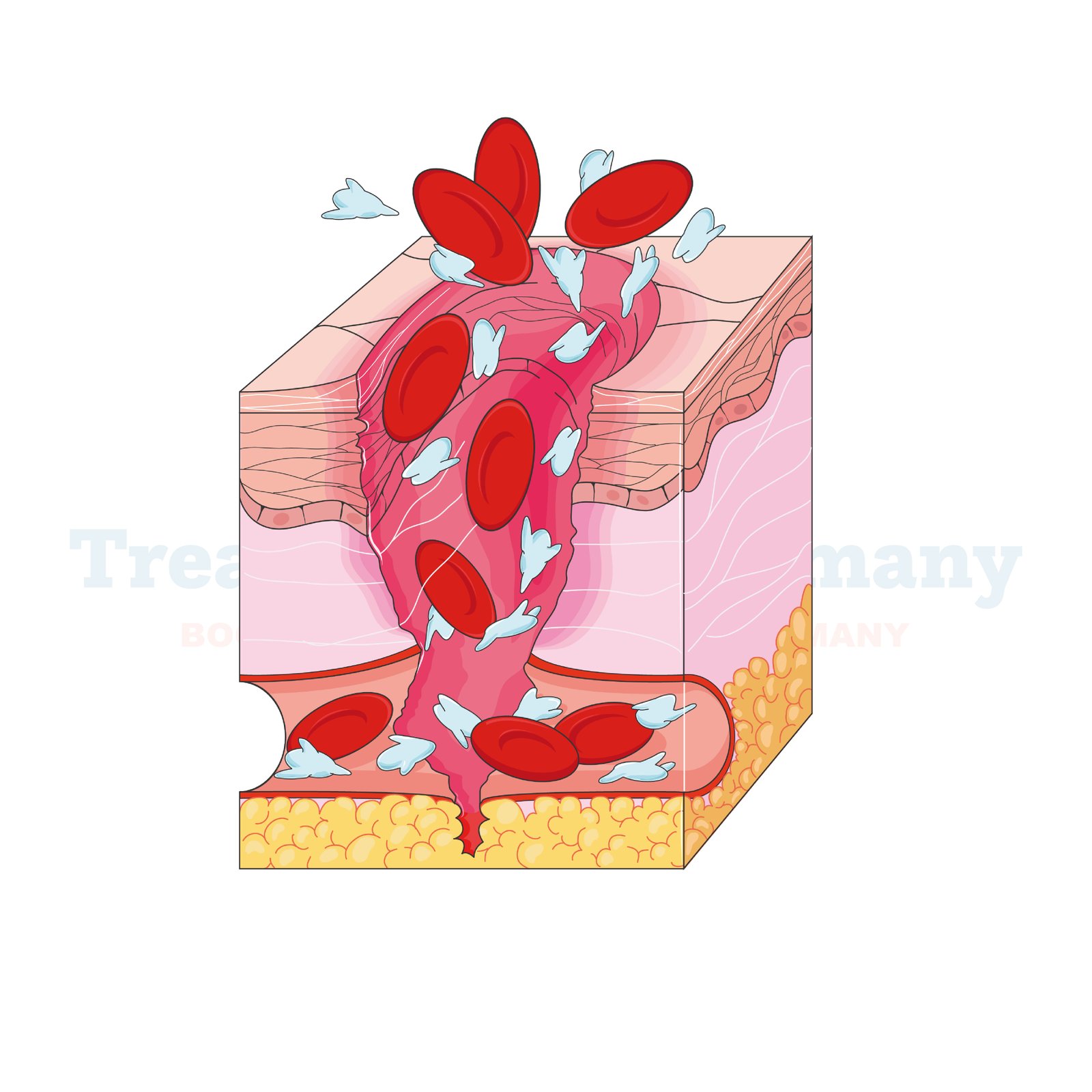
Coagulation Disorders are conditions characterized by abnormalities in the blood clotting process. Hemophilia, for instance, is a genetic disorder that affects the blood's ability to clot properly. It results in prolonged bleeding even from minor injuries or spontaneous bleeding into muscles and joints.
Side effects of Coagulation Disorders (e.g., Hemophilia):
The primary side effect of coagulation disorders, such as hemophilia, is excessive bleeding. This can lead to complications such as:
- Hemarthrosis: Bleeding into joints, causing pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
- Muscle Hematomas: Bleeding into muscles, resulting in pain, stiffness, and potential nerve damage.
- Excessive Bruising: Easy bruising due to minor trauma or even without apparent cause.
- Prolonged Bleeding: Difficulty in stopping bleeding from wounds, cuts, or dental procedures.
- Internal Bleeding: Bleeding into organs or tissues, which can be life-threatening if not promptly treated.
How is Coagulation Disorders (e.g., Hemophilia) diagnosed?
Diagnosing Coagulation Disorders typically involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and specialized laboratory tests. Doctors may perform the following:
- Blood tests to assess clotting factors and detect abnormalities.
- Genetic testing to identify specific genetic mutations associated with hemophilia or other coagulation disorders.
- Joint and muscle evaluations to detect signs of bleeding.
Potential treatments of Coagulation Disorders (e.g., Hemophilia):
Treatment for coagulation disorders aims to control bleeding episodes, prevent complications, and improve quality of life. In Germany, patients with hemophilia may receive the following treatments:
- Clotting Factor Replacement Therapy: Infusions of clotting factors to replace those deficient in the blood.
- Desmopressin (DDAVP): A medication that stimulates the release of stored clotting factors in certain types of hemophilia.
- Antifibrinolytic Agents: Drugs that help stabilize blood clots and prevent their breakdown.
- Gene Therapy: Emerging treatment option involving the introduction of functional genes to correct genetic mutations.
- Joint Protection Strategies: Physiotherapy, joint exercises, and orthopedic interventions to prevent and manage joint damage.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
