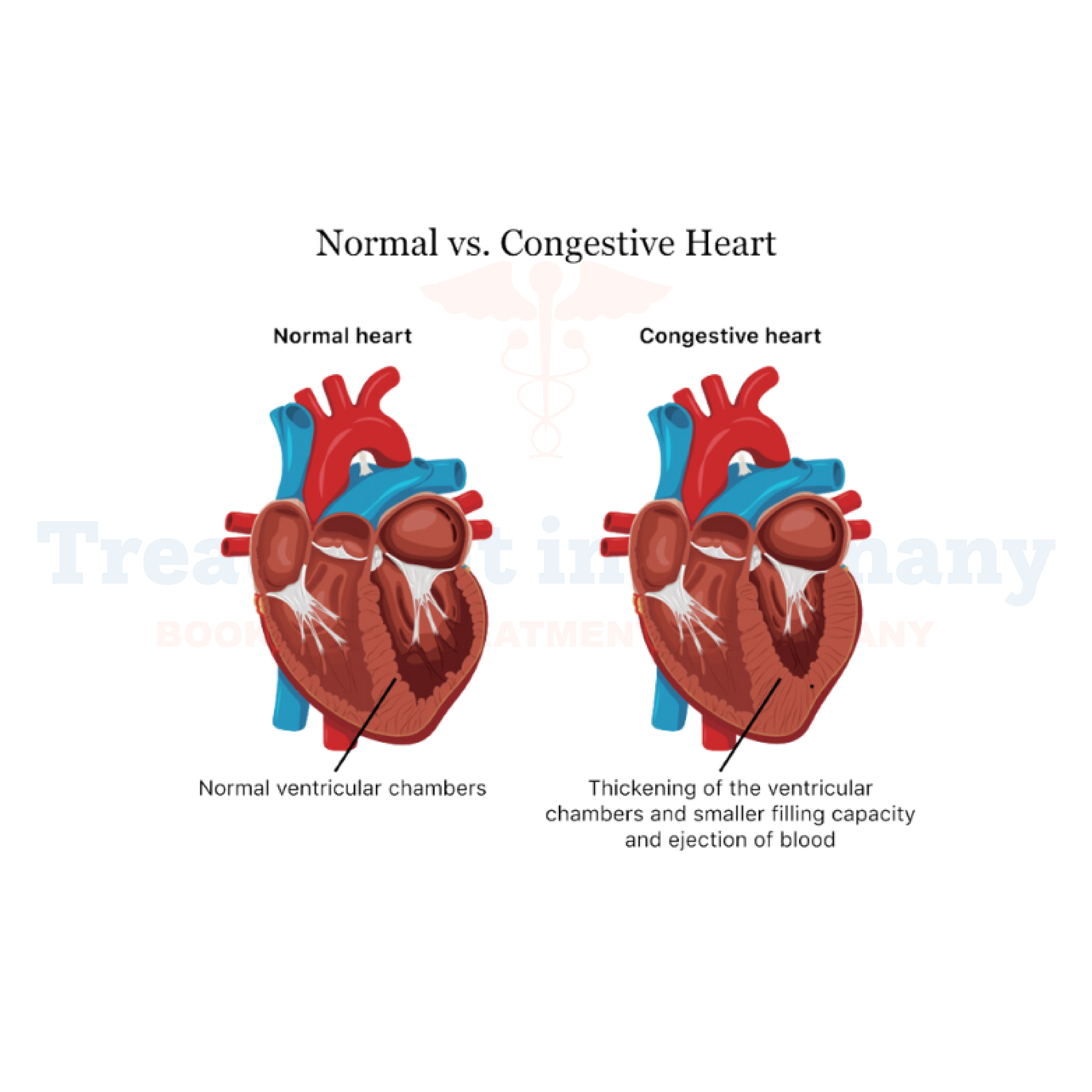
Understanding Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
Congestive Heart Failure(CHF) is a serious medical condition where the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's demands. This results in fluid buildup (congestion) in various parts of the body, particularly in the lungs, liver, and lower extremities.
Side Effects of Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
The symptoms of Congestive Heart Failure can vary but commonly include:
- Shortness of breath: Especially during physical exertion or when lying down.
- Fatigue and weakness: Feeling tired and lacking energy.
- Swelling: Edema in the legs, ankles, and feet.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat: Palpitations or a sensation of fluttering in the chest.
- Persistent cough: Often with pinkish or blood-tinged phlegm.
- Reduced ability to exercise: Feeling easily fatigued during physical activity.
How is Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Congestive Heart Failure typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as:
- Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to create images of the heart's structure and function.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Records the heart's electrical activity to detect any abnormalities.
- Blood tests: To assess kidney function and check for markers of heart failure.
- Chest X-ray: Helps visualize the heart, lungs, and fluid buildup.
- Cardiac catheterization: Measures pressures within the heart and blood vessels.
Potential Treatments for Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
Treatment for CHF aims to relieve symptoms, improve quality of life, and slow the progression of the condition. Depending on the severity and underlying causes, treatment options may include:
- Medications: Such as ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, diuretics, and in some cases, medications to strengthen the heart muscle (e.g., aldosterone antagonists).
- Lifestyle changes: Including dietary adjustments (low-sodium diet), regular exercise within recommended limits, smoking cessation, and weight management.
- Device therapy: Such as implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) or cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) devices.
- Surgical procedures: In advanced cases, options like coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or heart transplantation may be considered.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
