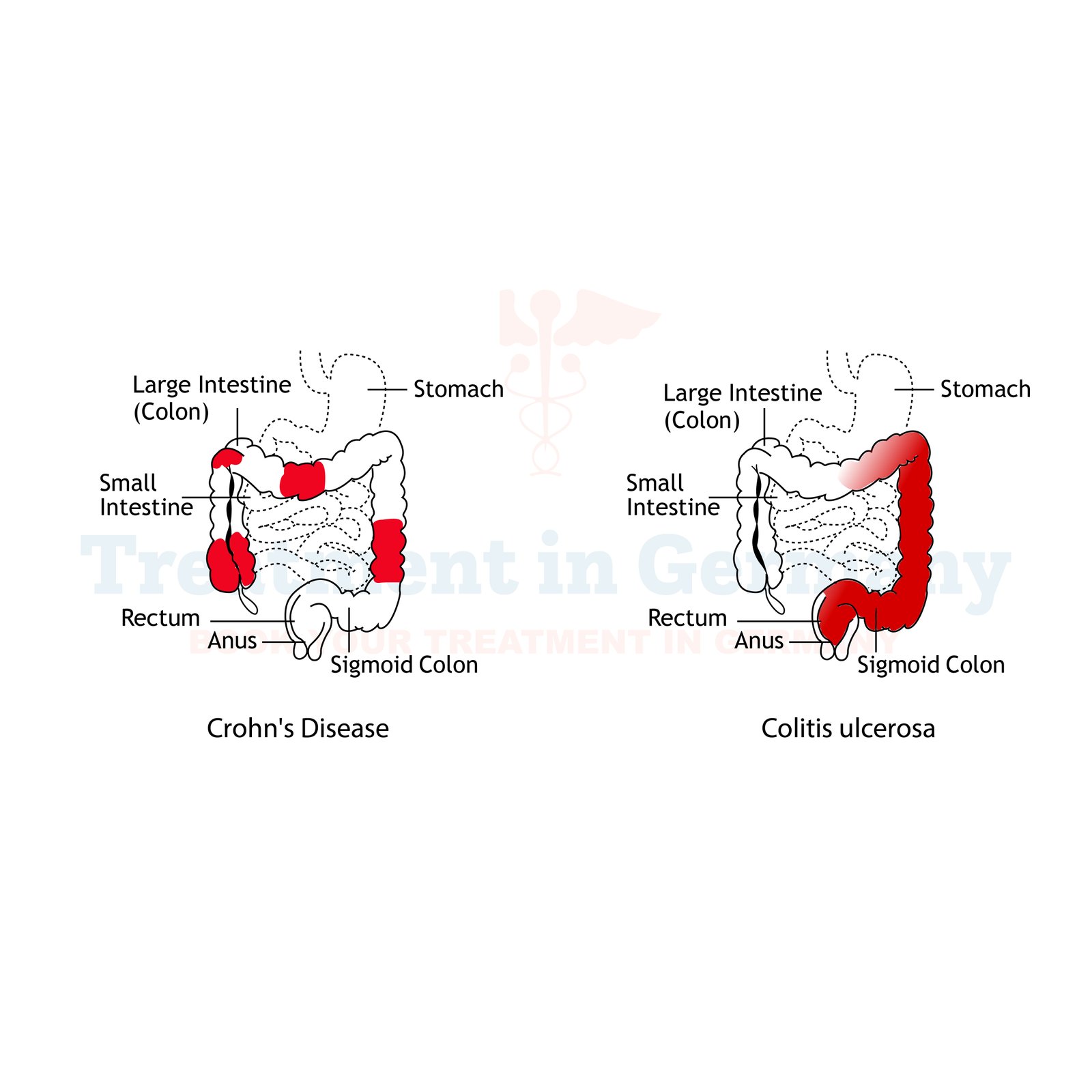
Understanding Crohn's Disease
Crohn's Disease is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the gastrointestinal tract, causing inflammation, ulcers, and discomfort. This condition can affect any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus, but it most commonly impacts the small intestine and the beginning of the large intestine.
Side Effects of Crohn's Disease:
How is Crohn's Disease Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Crohn's Disease typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, including:
Potential Treatments of Crohn's Disease:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
