What is Diabetes Mellitus?
Diabetes Mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood sugar levels resulting from either insufficient insulin production (Type 1) or the body's inability to effectively use insulin (Type 2).
Side Effects of Diabetes Mellitus
Both Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus can lead to various complications if not managed properly. These include cardiovascular diseases, nerve damage, kidney problems, vision impairment, and even amputation in severe cases. Additionally, uncontrolled diabetes can affect other organs such as the skin, leading to conditions like diabetic dermopathy and diabetic foot ulcers.
Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus
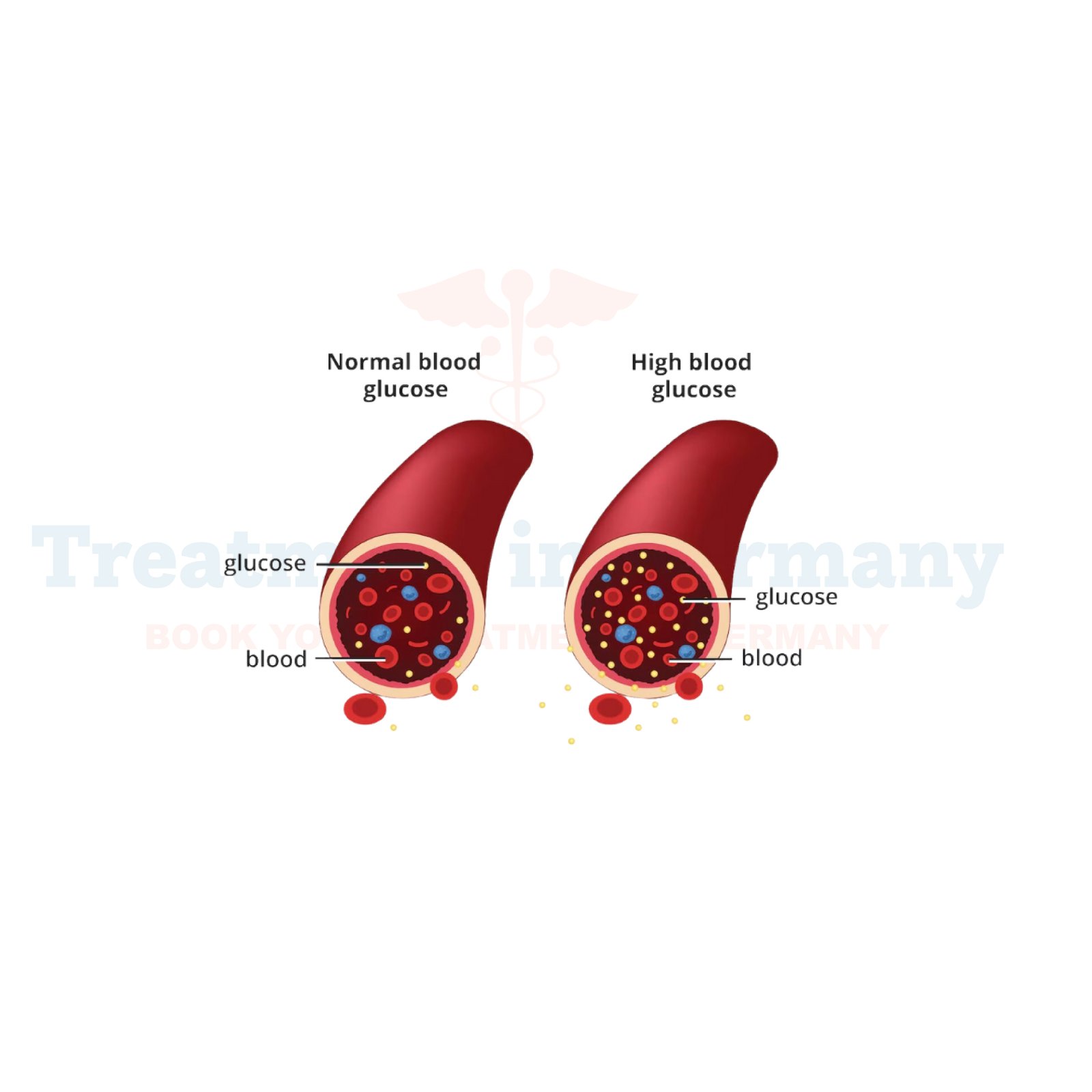
Diagnosing Diabetes Mellitus typically involves blood tests to measure blood glucose levels. For Type 1 Diabetes, tests for autoantibodies associated with the destruction of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas may also be conducted. For Type 2 Diabetes, additional tests to assess insulin resistance and pancreatic function may be recommended.
Potential Treatments of Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1 Diabetes:
Type 2 Diabetes:
1. Lifestyle Modifications: Healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, and weight management are essential in managing Type 2 Diabetes.
2. Oral Medications: Several classes of oral medications, such as metformin, sulfonylureas, and DPP-4 inhibitors, are available to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
3. Injectable Medications: In cases where oral medications are not sufficient, injectable medications like GLP-1 receptor agonists and insulin may be prescribed to help regulate blood sugar levels.
4. Bariatric Surgery: For individuals with severe obesity and Type 2 Diabetes, bariatric surgery may be recommended to achieve significant weight loss and improve insulin sensitivity.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
