What is Dysmenorrhea?
Dysmenorrhea, often referred to as painful periods or menstrual cramps, is a common gynecological condition characterized by severe and sometimes debilitating pain during menstruation.
It affects women of reproductive age and can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life.
Side Effects of Dysmenorrhea:
Aside from intense pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea can manifest with various side effects, including:
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some women experience nausea and even vomiting due to the severity of the pain.
- Headaches: Headaches, including migraines, may accompany dysmenorrhea, further exacerbating discomfort.
- Fatigue: The pain and other symptoms of dysmenorrhea can lead to fatigue and exhaustion, affecting daily productivity and mood.
- Diarrhea or Constipation: Gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea or constipation can occur alongside menstrual cramps.
- Emotional Distress: Dysmenorrhea can cause emotional distress, including irritability, anxiety, or depression, particularly if the pain is chronic or severe.
How is Dysmenorrhea Diagnosed?
Diagnosing dysmenorrhea typically involves a comprehensive medical evaluation, which may include:
- Medical History: Your healthcare provider will inquire about your menstrual history, including the onset, duration, and severity of pain, as well as any associated symptoms.
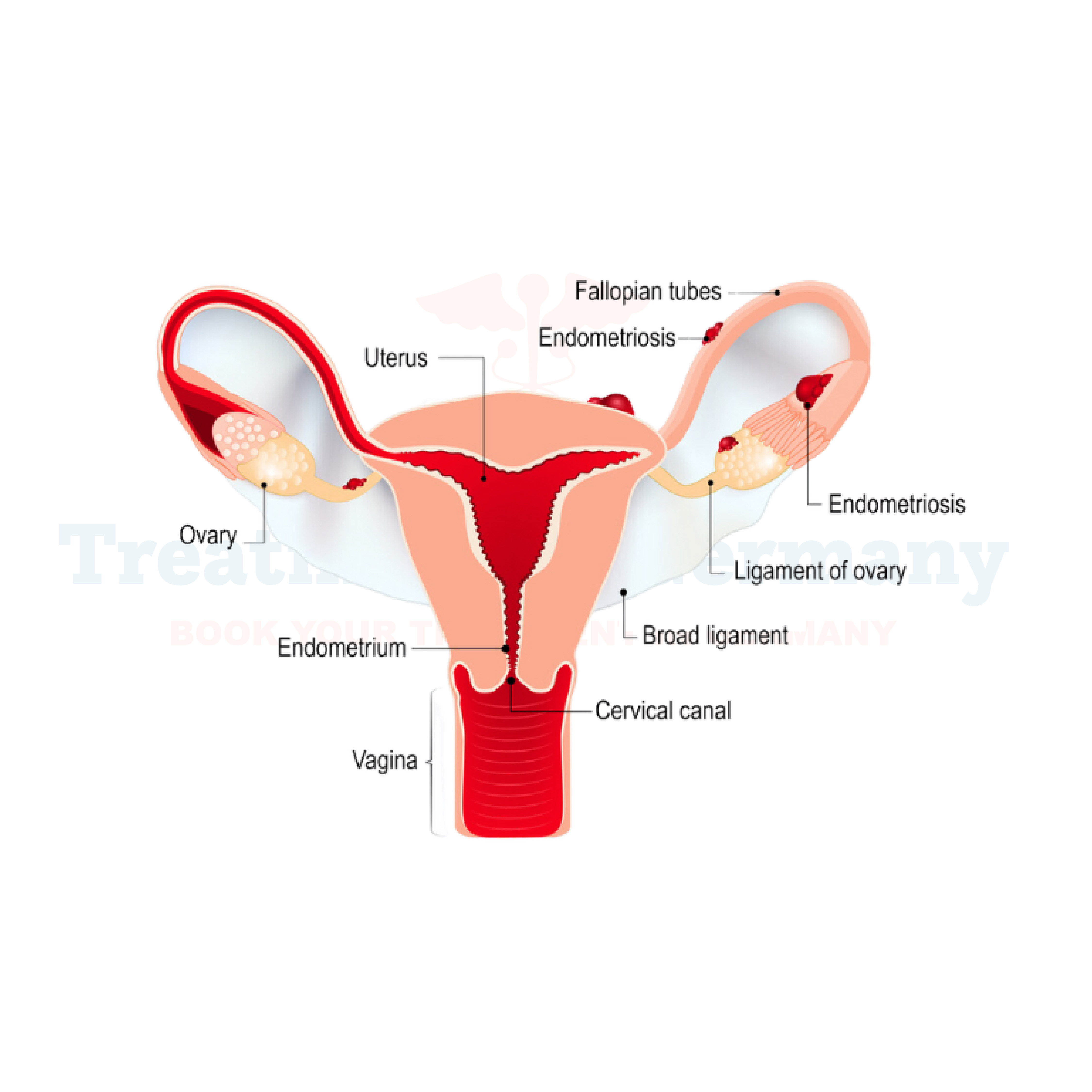
- Physical Examination: A pelvic examination may be conducted to assess for any abnormalities or signs of pelvic inflammatory disease or endometriosis.
- Imaging Tests: In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI may be recommended to rule out underlying conditions.
- Laparoscopy: In severe or refractory cases, a minimally invasive procedure called laparoscopy may be performed to visualize the pelvic organs and identify any abnormalities.
Potential Treatments of Dysmenorrhea:
Treatment for dysmenorrhea aims to alleviate pain and improve quality of life. Depending on the severity of symptoms and underlying causes, treatment options may include:
- Pain Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or naproxen sodium can help alleviate menstrual cramps. For severe pain, prescription-strength medications may be recommended.
- Hormonal Therapies: Hormonal contraceptives, including birth control pills, patches, or hormonal intrauterine devices (IUDs), can help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce the severity of dysmenorrhea.
- Non-Hormonal Therapies: Non-hormonal options such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), acupuncture, heat therapy (using heating pads or warm baths), or dietary supplements like omega-3 fatty acids or magnesium may provide relief.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting healthy lifestyle habits such as regular exercise, stress management techniques (e.g., yoga, meditation), and dietary changes (e.g., reducing caffeine and alcohol intake, increasing intake of fruits and vegetables) may help alleviate symptoms.
- Surgical Interventions: In cases where dysmenorrhea is caused by underlying conditions such as endometriosis or uterine fibroids, surgical interventions such as laparoscopic excision of endometrial tissue or myomectomy may be necessary.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
