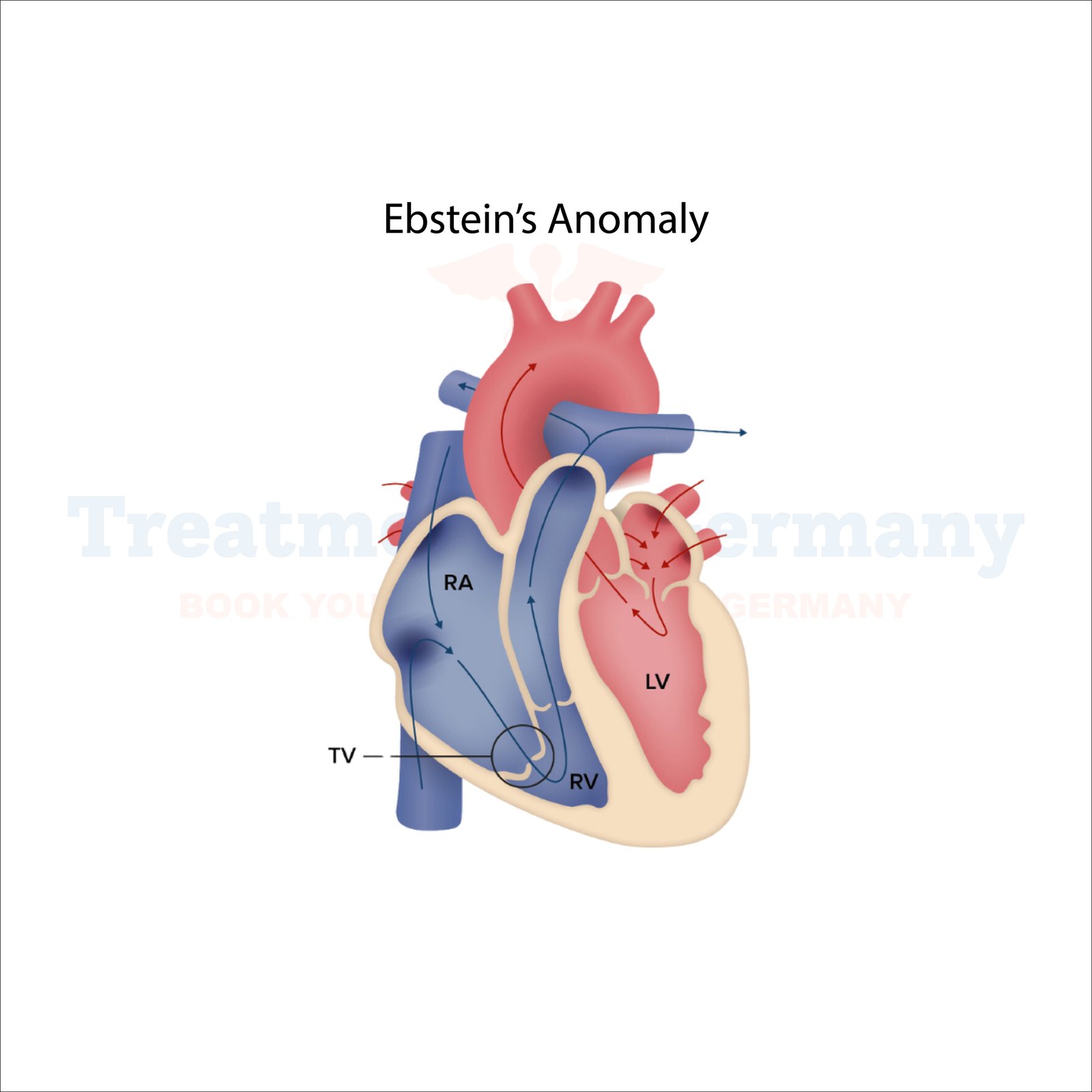
Ebstein's anomaly is one of the rarest congenital heart conditions. This would represent a form of malformation in the tricuspid valve where it fails to properly reach the right ventricle, thereby permitting the leakage of blood from the right atrium. The complications run up to regurgitation, heart enlargement, or even heart failure at the worst extremes.
It is also very often associated with other abnormalities, such as atrial septal defects or patent foramen ovale, and this makes the situation worse. Ebstein's anomaly nowadays can be diagnosed very early and there are novel treatment alternatives that offer new hope for patients suffering from it.
Ebstein's anomaly is a congenital deformity of the tricuspid valve, and it is said that the position of its occurrence in the heart is abnormally held. Its positioning leads backward flow of blood into the right atrium rather than proper flow towards the lungs. It can contribute to extra pressure to the heart, which may result in causing the heart to enlarge or fail eventually if severe.
Ebstein's anomaly Major findings
Most people suffering from Ebstein's anomaly have other birth defects, such as an atrial septal defect or patent foramen ovale. Most of these defects will complicate the normal flow of blood hence exhibiting symptoms such as shortness of breath and fatigue in most patients. Others may never show any signs at all, while in the worst extreme cases, some would be presented.
Common Symptoms of Ebstein's Anomaly
The intensity of each case determines the degree of the symptoms, no matter how severe. In some people, the symptoms are not characterized at all, even by early in life while to others, the symptoms are evident from birth.
Breathlessness
The most typical symptom is the beginning of dyspnea, which usually happens after physical activity. The irregular pulsations of the valve connecting the right atrium and ventricle to each other will generate irregular pumping into the lungs causing the patient difficulty breathing.
Edema and Fluid Retention
Most patients who suffer from this disease often exhibit edema, which refers to abnormal limb swelling brought by fluid accumulation in the legs, abdomen, or around the eyes. This happens as a result of the heart's poor blood pumping performance; fluid builds up and is one of the hallmarks of heart failure.
Irregular Heartbeat
Most patients with Ebstein's anomaly also experience arrhythmia, which is an irregular heart rate. That causes dizziness, fainting or even cannot walk safely if it goes uncoordinated rhythm. It also requires treatments such as catheter ablation so as to correct the abnormal pathways in the heart.
Chest Pain and Physical Fatigue
Most patients suffering from Ebstein's anomaly experience chest pain and weakness. Such symptoms result from the heart failure to pump blood effectively; hence, it reduces the flow of oxygen into the body tissues. All sorts of exercises normally deteriorate the symptoms to an extent that simple activities can no longer be tolerated.
Diagnosis of Ebstein's Anomal
Ebstein's anomaly can be detected and evaluated with a number of diagnostic tools, which becomes critical in measuring the extent of severity and helps in making a treatment decision.
Chest X-ray for Preliminary Examination
Lungs in most cases of Ebstein's anomaly contain one of the first radiographic imaging techniques: chest X-ray, obtained to assess enlargement of the heart. Fluid accumulation in lungs-the chest X-ray also may be used to record-can serve as evidence of heart stress.
More Specific Inventing with Cardiac MRI
The cardiac MRI offers clear images of the heart structures where the existence of the tricuspid valve with its chambers is shown. This will create an almost holistic view of how fluid flow is affected by the placement of the defective valve and thus allow better assessment of heart function.
Echocardiogram for Heart Function
Ultrasound waves are used in an echocardiogram to provide real-time images of how the heart works in real time. It is one of the best tests for valvular assessment, especially identification of defects that are associated with this anomaly, such as an atrial septal defect or patent foramen ovale, that often accompany Ebstein's anomaly.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) for Rhythm Analysis
An ECG is a test that gauges the heart's electrical activity. It has been used in clinical practice for diagnosing arrhythmias in patients. Ebstein's anomaly is one condition whereby such a finding is quite common. Other less common patterns warrant further intervention.
Functional Evaluation with Exercise Stress Test
The exercise stress test is utilized to measure how well the heart operates under exertion. This therefore means most underlying heart rhythm problems would only be noticed if the heart were subjected to greater functional loads than what it usually operates at, such as during exercise.
Holter monitoring on a continuous basis
A holter monitor captures all the electrical activity of the heart in 24 to 48 hours. This is very helpful in diagnosing intermittent arrhythmias that may not be revealed by a routine ECG, so doctors can determine the frequency and severity of erratically beating hearts.
Treatment Options for Ebstein's Anomaly in Germany
As such, the management of Ebstein's anomaly will vary with the severity of symptoms and the overall condition of the patient. Treatment may start as simple as a medication and can go to as invasive as surgery.
Medications to Control Symptoms
Depending on the severity of the symptoms, even the milder types become manageable through the help of medicines that can regulate heart failure and arrhythmias. Diuretics are many times prescribed in an attempt to reduce fluid accumulation as well as edema.
Beta-blockers or anti-arrhythmic drugs might be used to correct heart rhythm.
Surgical Tricuspid Valve Repair
For more serious anomalies, operative repair of the tricuspid valve is done primarily. The tissue used in the reconstruction of the valve should be taken from the patient, and this is the preferred option over replacing it with a valve.
In case the reconstruction cannot be made, then the valve is replaced by either of the biological or mechanical valve.
Arrhythmias through Catheter Ablation
Hospital-based catheter ablation is also a minimally invasive procedure that can correct the rhythm disturbance for most patients with severe cases of arrhythmia. The idea behind this treatment is to try to eliminate the aberrant electrical pathways in the cardiac tissue that are causing the arrhythmia.
Pacemaker implantation for rhythm management.
At times, pacing may be needed if the heart rhythm is not balanced or in its rhythm as a result of faulty working of the tricuspid valve; it helps in the regulation of the heart rate and prevents complications arising due to arrhythmia.
Heart Transplant for Severest Cases
If the failure of the heart has complexed to an extreme stage and other therapies seem to offer little hope, then transplanting a new heart will be considered. Often this is indicated in patients with major Ebstein's anomaly, who do not improve with other forms of treatment.
Innovative Treatment in Germany
It advances the medical science of Ebstein's anomaly, where Germany is considered to be one of the most developed health care systems and leads the world in modern-day treatments for the patient.
Advanced Treatment Options in Germany
Germany is one of the developed countries where any advanced treatment of Ebstein's anomaly will be applied, and most advanced surgical and medical practices will be performed here.
The reputation for vast experience among specialists who are used to working with patients and providing them with access to the newest developments in cardiac care is fantastic.
New Surgical Procedures
This innovation of techniques in the surgical method domain, such as cone procedure will create better tricuspid valve repair with only the usage of the patient's own tissue. These innovative techniques will enhance long-term results and potentially even decrease the strong requirement for surgery in the future.
Living with Ebstein's Anomaly
The care and follow-up needed after Ebstein's anomaly require lifelong management. With time, the degree of the anomaly may change, or even deteriorate; proper follow-up is therefore necessary whenever the degree of the anomaly alters.
Management of Disease
The management on a daily basis of the disease involves monitoring the drugs advised by the physician, attending routine check-ups, and being aware of their physical limitations. Chest pain, shortness of breath, and tiredness are a few of the common symptoms of the disease; if treated properly, most of the patients suffering from it can lead their usual lives.
The long-term prognosis for Ebstein's abnormality varies somewhat. Some patients with mild forms will never undergo surgery in their lifetime, but the other ones with severe features require surgical intervention throughout their life. Early diagnosis and modes of treatments have significantly improved the prognosis for most patients.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
