Understanding Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS)
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS) is a group of genetic disorders that affect the body's connective tissues, primarily collagen.
Connective tissues provide support to the skin, bones, blood vessels, and other organs. In individuals with EDS, there is a defect in the production of collagen or its structure, leading to various symptoms that can range from mild to severe.
Side Effects of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
The symptoms of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome can vary widely depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common side effects include:
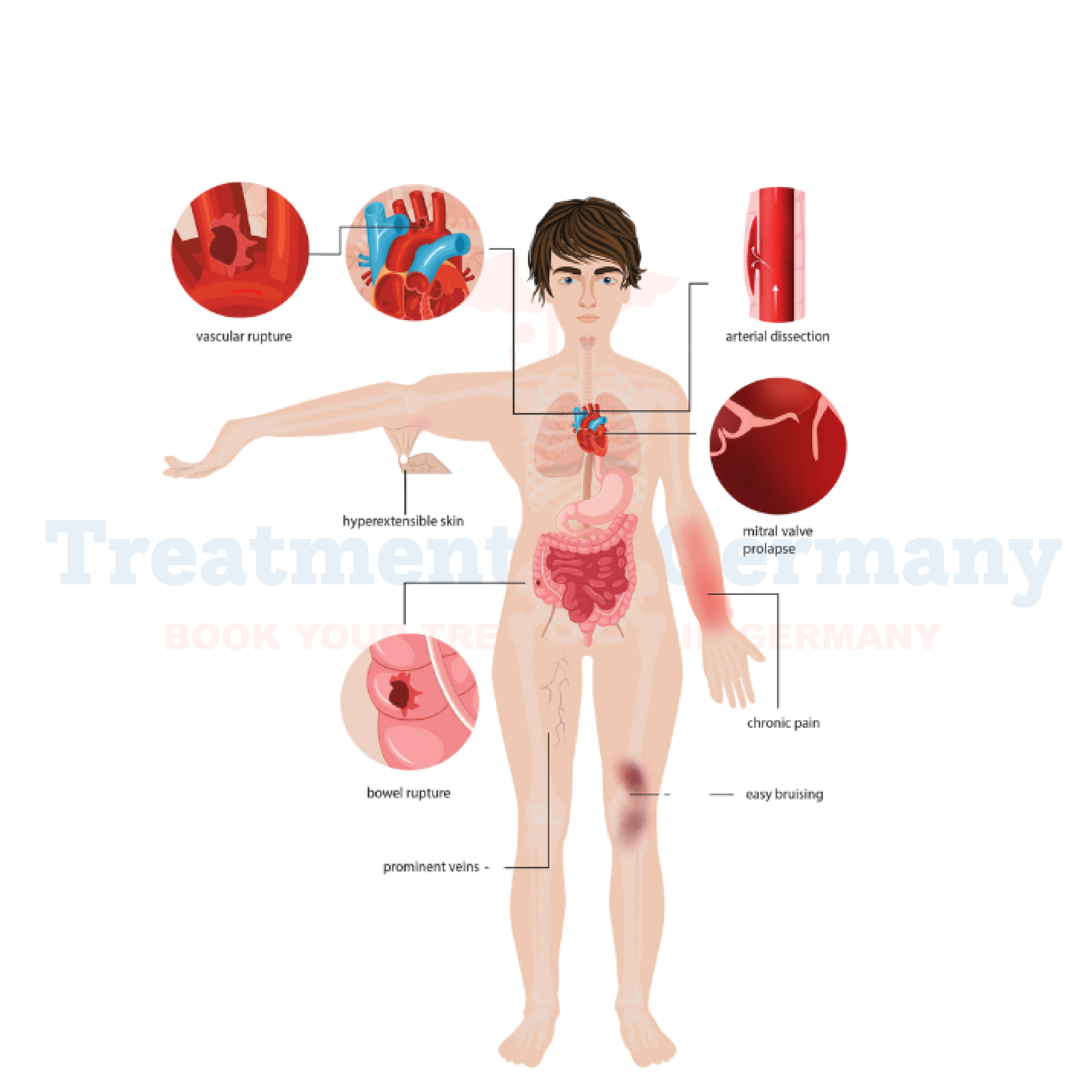
- Joint hypermobility: Joints that are more flexible than usual, which can lead to frequent dislocations and chronic joint pain.
- Skin problems: Fragile, stretchy skin that bruises easily and may be prone to tearing.
- Cardiovascular issues: Weakness in blood vessels that can cause them to rupture or lead to problems with circulation.
- Gastrointestinal issues: Digestive problems such as constipation, acid reflux, and abdominal pain.
- Chronic pain: Persistent pain, often in the joints and muscles, due to the instability of connective tissues.
Diagnosis of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
Diagnosing Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome can be challenging due to its variability and the overlap of symptoms with other conditions. The process typically involves:
- Clinical evaluation: A thorough examination by a healthcare professional to assess joint hypermobility, skin texture, and other physical signs.
- Family history: Since EDS is genetic, information about family members with similar symptoms is crucial.
- Genetic testing: To identify specific genetic mutations associated with EDS in some cases.
- Collagen testing: Assessing the structure and function of collagen through skin biopsy or specialized imaging techniques.
Potential Treatment of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
Currently, there is no cure for Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, so treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. The approach may include:
- Physical therapy: Strengthening muscles around unstable joints to improve stability and reduce pain.
- Pain management: Using medications or therapies to alleviate chronic pain.
- Orthopedic supports: Braces or splints to support joints and prevent dislocations.
- Cardiovascular monitoring: Regular check-ups to detect and manage potential vascular complications.
- Nutritional counseling: Ensuring a diet rich in nutrients that support connective tissue health.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
