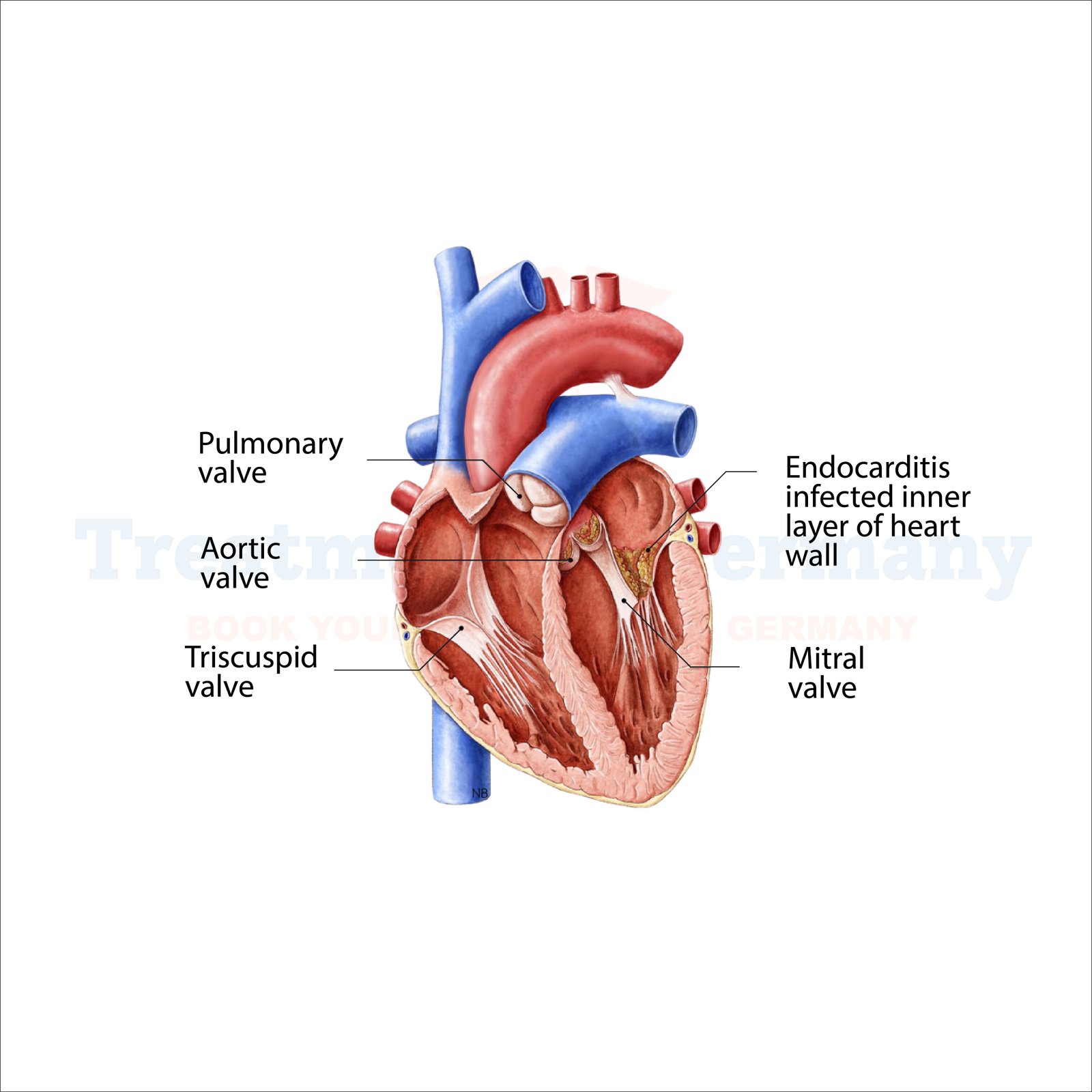
Endocarditis refers to an infection that affects the innermost lining of your heart chambers and valves, known as the endocardium. Normally, it is caused by a bacterial infection that results in the entry into your bloodstream and thereafter its entrance into your heart. It is, however fundamental to offer immediate treatment to prevent life-threatening complications.
This article explores the causes, symptoms, diagnostic approaches, treatment options, and complications brought about by endocarditis. We also touch on other associated conditions; some of which include heart block, sepsis, and heart valve disease.
Risk Factors that Lead to Endocarditis
Endocarditis occurs when there are microscopic germs, mostly bacteria, that enter your blood and attach to different injured parts of your heart. The germs could come from different body parts, mainly the mouth, or even your skin.
Risk Factors for Endocarditis
Congenital heart disease: People who are born with heart defects are at higher risk of getting endocarditis.
Rheumatic heart disease: Untreated rheumatic fever can cause scarring of the heart, which in turn makes it highly susceptible to infection.
Pacemaker: As a matter of general principle, any implanted device in the human body is thought to increase susceptibility to infection since it acts as a breeding ground to such bacteria
The hallmark of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is an enlargement of the heart muscle's thickness. The abnormal movement of blood will then interfere with the pressure applied on the valves and therefore aggravate the risk of endocarditis.
Other people at risk include those with a weakened immune system, artificial heart valves, or intravenous drug users.
Symptoms of Endocarditis
The symptoms of endocarditis can be minor or grave and may mimic any other simple infection. However in most cases, they must be identified early, especially in those at a heightened risk.
Key Symptoms to Watch For
Heart block: The infection can interfere with the heart's electrical system, causing rhythms that are abnormal and irregular.
Shortness of breath: The infection could affect the heart, making one's breathing even more difficult.
Pain from muscles and joints: Unceasing aching may be because of inflammation due to the infection.
Poor appetite and weight loss: Infection for a long time will lead to enormous loss of weight and weakness.
Blood clots: Accumulation of bacteria and cells lead to blood clots that can cause strokes and other complications.
The symptoms may be accompanied by high fever, night sweats, and general fatigue.
Diagnosis of Endocarditis
Early diagnosis is the only way through which this endocarditis can be managed appropriately. Your health provider will carry out a number of tests to confirm the condition.
Diagnostic Tests of Endocarditis
Complete blood count: It checks whether there is a raised white blood cell count, which might be suggestive of an ongoing infection.
Echocardiogram: It's the ultrasound imaging of the heart. On echocardiography, any abnormal mass or vegetation on the heart valves can be ruled out.
Positron emission tomography: With a PET scan, it is easier to pinpoint the exact place of infection in the body as well as a clearer view of how the infection has progressed.
These are diagnostic tools that would be very important in determining the severity of the infection as well as what the right course of treatment is.
Treatment of Endocarditis
Once diagnosed, endocarditis treatment needs to be initiated quickly to avert further complications. The treatment plan is usually oriented for the individual case, starting with antibiotics as the first line of defense.
Antibiotic Therapy
Treatment involves antibiotic therapy to clear the bacterial infection in the bloodstream. It therefore entails:
Intravenous antibiotics: You will have to spend some time in the hospital because antibiotics are given intravenously, depending on the severity of the infection
Change of antibiotics: Your physician will change the course of antibiotics once your infecting bacteria is recognized and target the infection better
The overall goal of antibiotic therapy is to clear the infection with minimal possible damage to the heart valves
When Surgery is Required
Sometimes, even antibiotics cannot help; surgery is required in such cases. Surgery may also be required in the case of serious damage to the valves-the repair or replacement may be done during surgery.
It may involve the removal of infected tissue, dead tissue, and abnormal cells that might have developed within the valves or within the heart to prevent future complications.
It can also lead to surgery if the infection has caused heart failure or if the infection continues despite antibiotics treatment.
Complications of Endocarditis
Prompt and proper medical treatment of endocarditis can prevent deadly complications. Usually, the complications are not only limited to the heart since they involve other organs as well.
Common Complications
Heart failure: Long term infection may cause significant damage to the heart valves and it may lead to heart failure, where the heart would be unable to pump the blood in the body.
Sepsis: The causative bacteria of endocarditis can spread to other parts of the body and may lead to sepsis that is a life-threatening condition due to failure of the organs.
A cardiac arrhythmia: Endocarditis may disrupt electrical activities within the heart and this may result in an abnormal cardiac rhythm that may require medical intervention.
Other complications include embolism (where parts of the infection break off and travel to other parts of the body), kidney damage, and strokes.
Prevention of Endocarditis
A primary concern is the prevention of endocarditis; people with heart problems should pay particular attention to maintaining their dental health to minimize the risk of bacterial entry into the bloodstream.
The Importance of Good Oral Hygiene
Maintaining good dental hygiene can stop oral bacteria from getting into your bloodstream. This is achieved through brushing and flossing daily and scheduled dental appointments every six months. For high-risk patients, this is very important because any dental procedure can introduce bacteria causing endocarditis.
Innovative Treatment Options in Germany
Germany is the leader in the medical front when it comes to curing heart diseases, among others, such as endocarditis. The best of facilities and advanced technology exist in Germany, and this is how patients seeking the most complex heart issues are cured.
High-Quality Care in Germany
Innovations in surgical procedures: The surgeons in Germany have been rated on numerous occasions for expertise in performing minimally invasive heart surgery, and they bring shortened times to recovery and better quality outcomes on the part of the patient.
Treatment in Germany: There, patients can get all forms of heart care, from special treatments to be adhered to during the repair and replacement of the valves of the heart to advanced diagnostic techniques.
For Endocarditis patients, Germany has some of the most innovative solutions for specialized treatment options, thus ensuring superior quality treatment.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
