What is Eosinophilia:
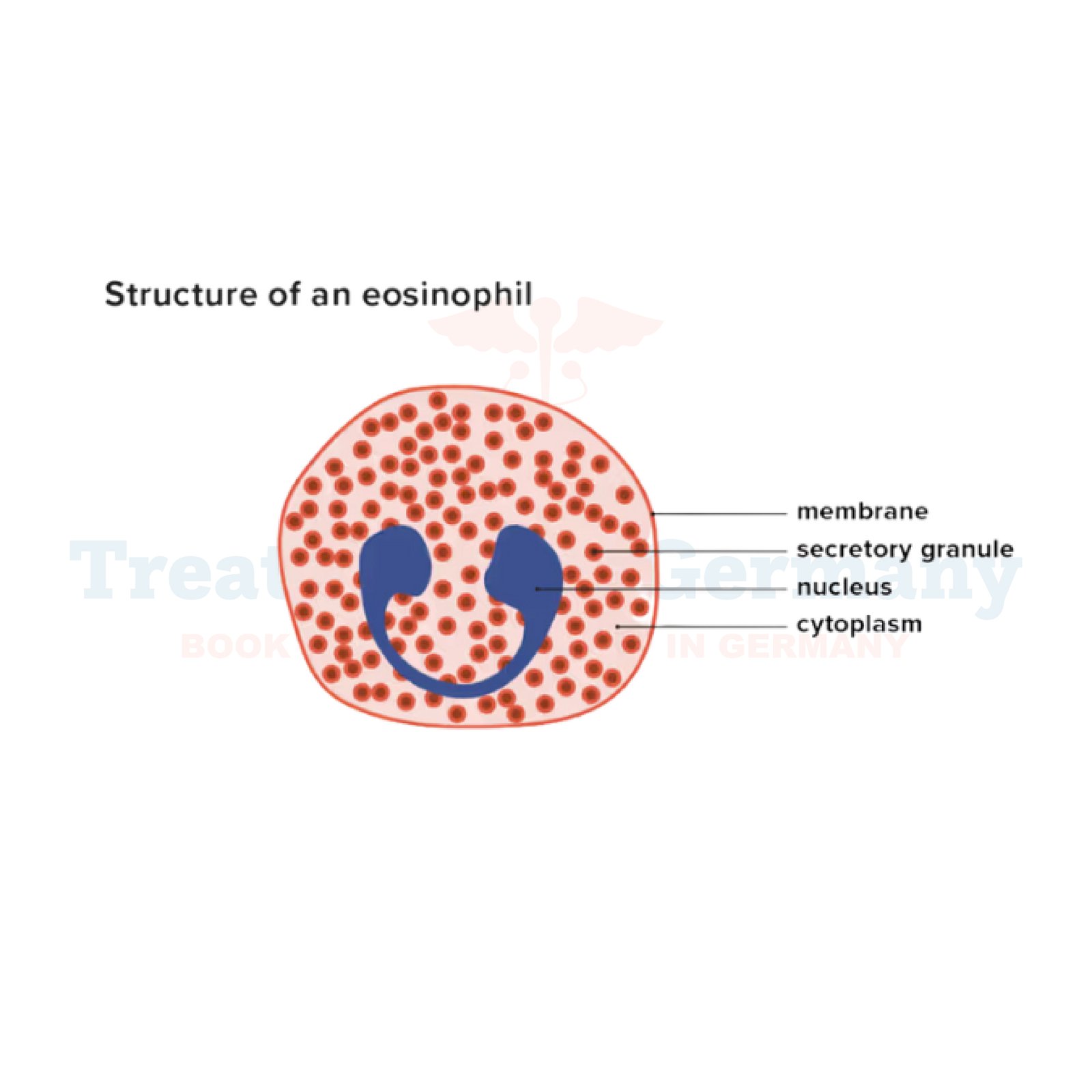
Eosinophilia is a medical condition characterized by an unusually high number of eosinophils in the blood. Eosinophils are a type of white blood cell that play a crucial role in the immune system's response to parasitic infections,
allergies, and other inflammatory conditions. While a small number of eosinophils in the blood is normal, abnormally high levels can indicate an underlying health issue.
Side effects of Eosinophilia:
The presence of eosinophilia in the blood may not always cause noticeable symptoms. However, depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition, patients may experience symptoms such as:
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Weakness
- Skin rashes or itchiness
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Swelling, particularly in the hands, feet, or face
- Persistent cough
It's important to note that the symptoms of eosinophilia can vary widely depending on the underlying cause and individual health factors. Therefore, seeking medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment is essential.
How is Eosinophilia diagnosed?:
Diagnosing Eosinophilia typically involves a combination of medical history assessment, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Your healthcare provider may:
- Ask about your symptoms and medical history to understand potential triggers or underlying conditions.
- Perform a physical examination to check for signs of inflammation or other related symptoms.
- Order blood tests to measure eosinophil levels and identify any other abnormalities in the blood.
- Conduct additional tests such as imaging studies (X-rays, CT scans) or tissue biopsies if necessary to determine the underlying cause of eosinophilia.
Potential treatments of Eosinophilia:
Treatment for Eosinophilia focuses on addressing the underlying cause and managing symptoms. Depending on the specific diagnosis and severity of the condition, treatment options may include:
- Medications: Your healthcare provider may prescribe medications such as corticosteroids, antihistamines, or immunosuppressants to reduce inflammation and control eosinophil levels.
- Allergy management: If allergies are identified as a trigger for eosinophilia, allergy management strategies such as avoiding allergens, using allergy medications, or undergoing allergy desensitization therapy may be recommended.
- Treatment for underlying conditions: If eosinophilia is secondary to an underlying health issue such as parasitic infections, autoimmune diseases, or certain cancers, treatment will focus on managing the primary condition.
- Regular monitoring: Patients with chronic eosinophilia may require regular monitoring of eosinophil levels and overall health status to assess treatment effectiveness and detect any complications early on.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
