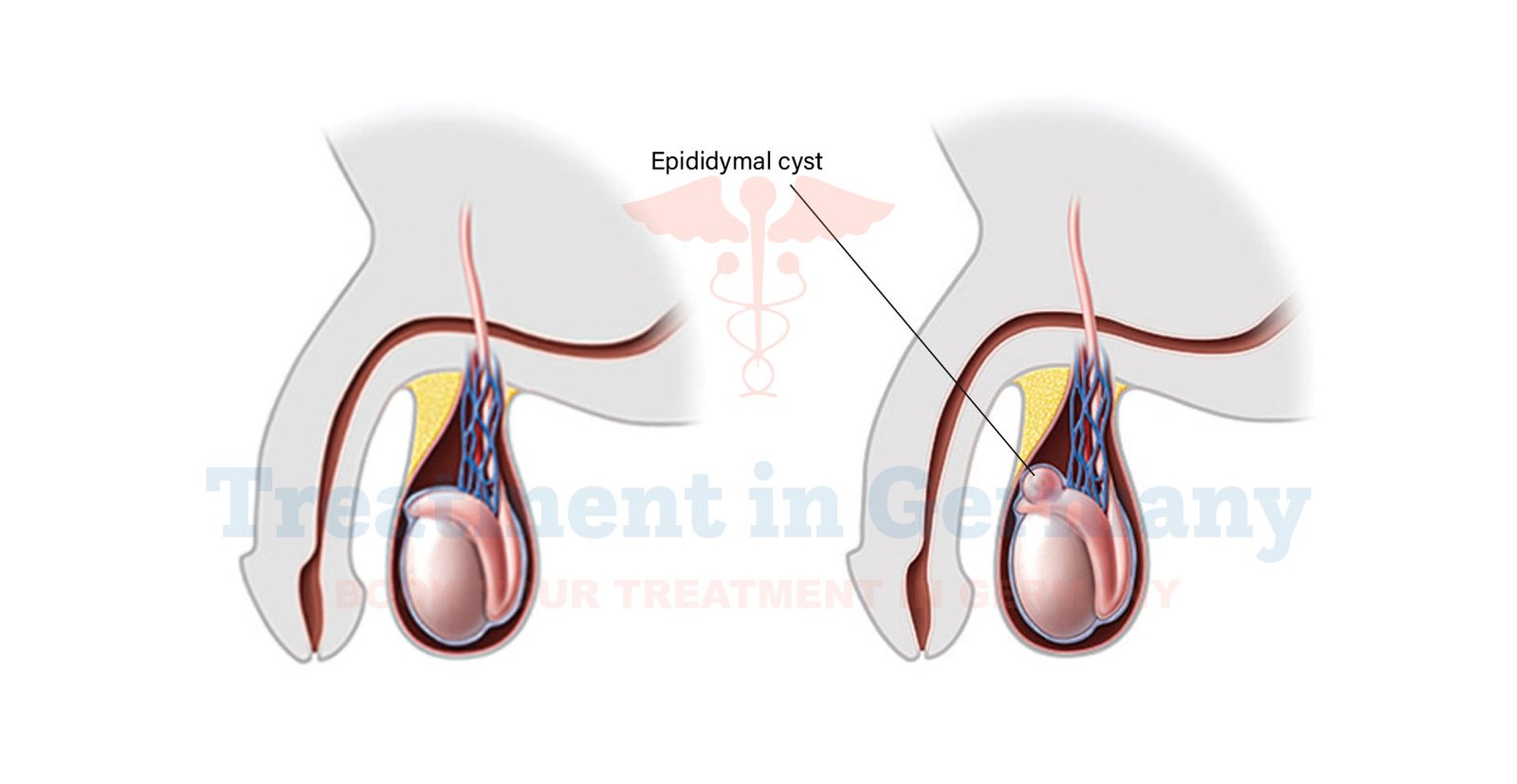
What is an Epididymal Cyst?
An epididymal cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms in the epididymis, a coiled tube located at the back of the testicle. The epididymis is responsible for storing and maturing sperm.
These cysts are usually benign and can vary in size. They are often discovered incidentally during routine medical examinations or imaging studies.
Side Effects of Epididymal Cysts
Epididymal cysts are generally asymptomatic, meaning they don't always cause noticeable symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Swelling: A noticeable lump or swelling in the scrotum.
- Discomfort or Pain: Mild discomfort or pain in the affected area, particularly if the cyst grows larger.
- Feeling of Fullness: A sensation of fullness or heaviness in the scrotum.
It's important to note that while these cysts are typically harmless, any persistent discomfort or changes should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
How is an Epididymal Cyst Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of an epididymal cyst usually involves a combination of:
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will examine the scrotum for lumps or swelling.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound of the scrotum is the primary diagnostic tool. It uses sound waves to create an image of the scrotum and helps differentiate between cysts and other potential conditions.
- Medical History: Providing a detailed medical history and describing any symptoms you may be experiencing can help with the diagnosis.
In some cases, if there is uncertainty about the nature of the cyst, further tests or referrals may be recommended.
Potential Treatment of Epididymal Cysts
Most epididymal cysts do not require treatment unless they cause significant symptoms or discomfort. Treatment options include:
- Observation: For asymptomatic cysts, regular monitoring may be all that's needed. Your doctor will schedule follow-up appointments to check if the cyst changes in size or causes any problems.
- Pain Management: If the cyst causes discomfort, over-the-counter pain relievers may be recommended.
- Surgical Removal: If the cyst becomes large, painful, or problematic, surgical removal may be considered. This procedure is typically done on an outpatient basis and involves removing the cyst while preserving the surrounding structures.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
