Epilepsy Treatment in Germany
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent, unprovoked seizures caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It is one of the most common neurological conditions, affecting people of all ages worldwide. Germany, renowned for its advanced healthcare system, offers cutting-edge diagnostic tools and treatment options for epilepsy, ensuring patients receive comprehensive and effective care.
Epilepsy is a disorder of the central nervous system in which brain activity becomes abnormal, causing seizures or periods of unusual behavior, sensations, and sometimes loss of awareness. While the condition can affect anyone, it is most commonly diagnosed in children, adolescents, and older adults.
Causes of Epilepsy
The causes of epilepsy vary and can be grouped into the following categories:
- Genetic Factors: Certain types of epilepsy run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
- Structural Abnormalities: Brain malformations, strokes, or tumors can disrupt normal brain activity.
- Infections: Conditions such as meningitis, encephalitis, or neurocysticercosis can lead to epilepsy
- Head Injury: Trauma to the brain may result in seizures
Metabolic Disorders: Imbalances in electrolytes or glucose levels can trigger seizures.
- Unknown Causes: In many cases, the exact cause remains unidentified.
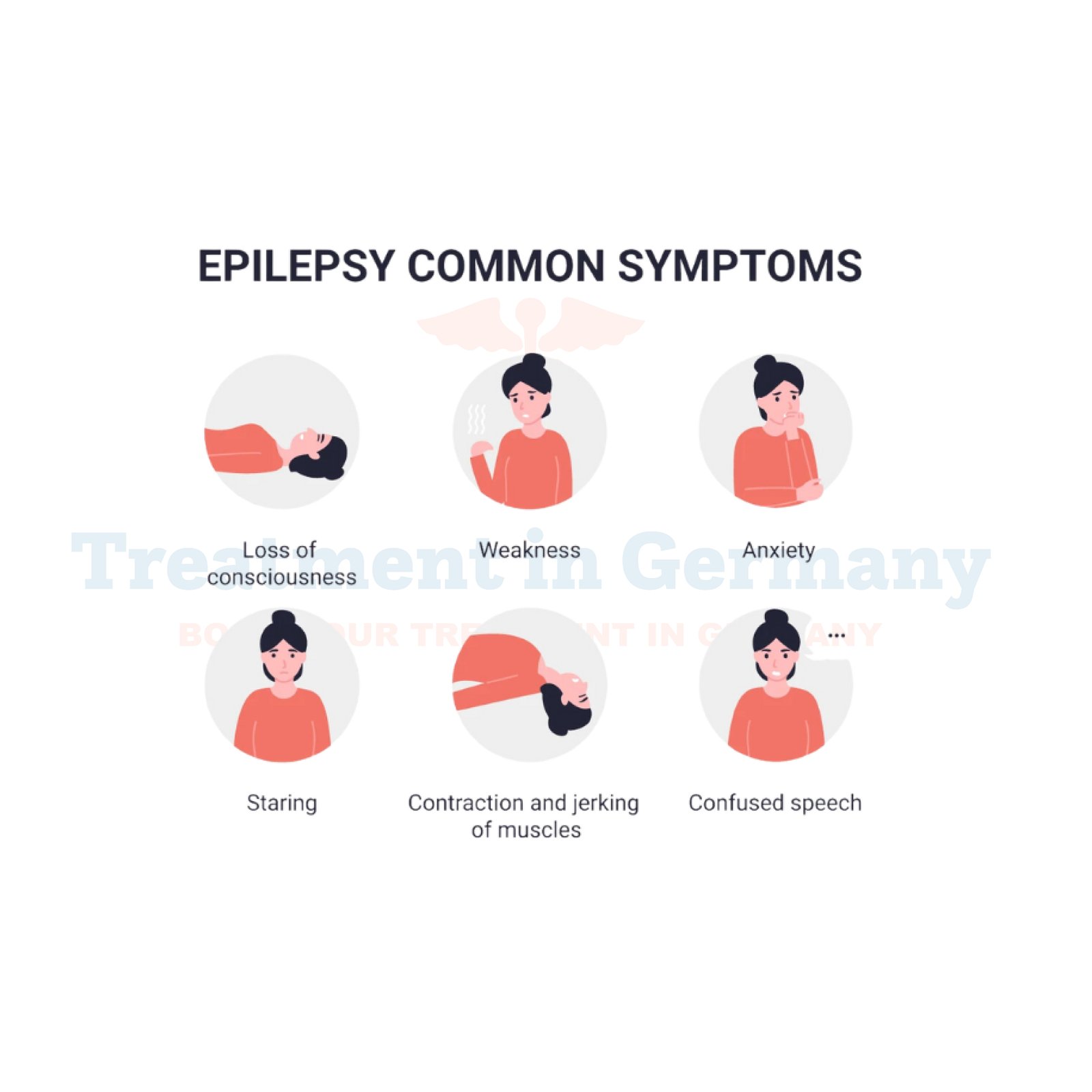
Symptoms of Epilepsy
Epileptic seizures can vary significantly depending on the type of epilepsy and the areas of the brain affected. Common symptoms include:
- Temporary confusion or cognitive disruption.
- Staring spells.
- Uncontrollable jerking movements of the arms and legs.
- Loss of consciousness or awareness.
- Psychological symptoms such as fear or anxiety.
Seizures are classified into two main types:
- Focal Seizures: Originate in one part of the brain and can be simple (no loss of consciousness) or complex (altered awareness).
- Generalized Seizures: Involve both hemispheres of the brain and include subtypes such as tonic-clonic, absence, myoclonic, and atonic seizures
Diagnosis and Diagnostic Tools
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Germany offers advanced diagnostic techniques, including:
- Electroencephalogram (EEG): Records electrical activity in the brain and identifies abnormal patterns.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Detects structural abnormalities in the brain.
- CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: Useful for identifying tumors or bleeding in the brain.
- Blood Tests: Rule out infections, metabolic disorders, or genetic conditions.
- Neuropsychological Tests: Assess cognitive function and identify areas of brain impairment.
Treatment Options for Epilepsy in Germany
Germany’s healthcare system provides a wide array of treatment options for epilepsy, ranging from medication to advanced surgical interventions. These include:
Medications
- Antiepileptic Drugs (AEDs): First-line treatment to control seizures. Common AEDs include lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and valproate.
- Newer Medications: Germany’s innovative research allows access to cutting-edge drugs with fewer side effects.
Surgical Treatments
- Resective Surgery: Removal of the brain tissue causing seizures.
- Laser Ablation Therapy: Minimally invasive surgery to target seizure-causing areas.
- Corpus Callosotomy: Disconnects neural connections between brain hemispheres to prevent seizure spread.
Neuromodulation Therapies
- Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS): A device implanted under the skin stimulates the vagus nerve to reduce seizure frequency.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): Electrodes implanted in specific brain areas regulate abnormal activity.
- Responsive Neurostimulation (RNS): Monitors brain activity and delivers electrical pulses to prevent seizures.
Innovative Therapies in Germany
- Dendritic Cell Therapy: While primarily used for immune modulation, ongoing research explores its potential role in managing epilepsy linked to autoimmune conditions.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Investigated for repairing brain tissue and reducing seizure susceptibility.
- Ketogenic Diet: A high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet effective in managing drug-resistant epilepsy, often supervised in specialized clinics.
Why Choose Treatment in Germany?
Germany is a global leader in epilepsy care due to:
- World-Class Hospitals: Equipped with the latest diagnostic and therapeutic technologies.
- Expert Specialists: Neurologists, neurosurgeons, and epileptologists with extensive experience.
- Innovative Research: Pioneering advancements in neuromodulation and regenerative medicine.
- Comprehensive Care: Multidisciplinary teams offering personalized treatment plans.
- Cutting-Edge Rehabilitation Programs: Focused on improving quality of life and minimizing seizure impact.
Prevention and Management
While epilepsy cannot always be prevented, proactive measures can help manage the condition and reduce seizure frequency:
- Adherence to Medications: Taking prescribed antiepileptic drugs regularly.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Adequate sleep, balanced nutrition, and stress management.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding factors like flashing lights, stress, or lack of sleep.
- Regular Monitoring: Routine check-ups to assess treatment effectiveness and adjust medications if needed.
Conclusion
Epilepsy is a complex neurological disorder, but with early diagnosis and advanced treatment options, patients can achieve significant seizure control and improved quality of life. Germany’s world-class medical facilities, expert specialists, and innovative therapies make it a premier destination for epilepsy care. A multidisciplinary approach, combining medications, surgical interventions, and lifestyle management, ensures the best outcomes for individuals living with epilepsy.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
