What is Epistaxis (Nosebleeds):
Epistaxis, commonly known as nosebleeds, occurs when blood flows from one or both nostrils. While often not serious, recurrent or severe nosebleeds may indicate an underlying health issue that requires attention.
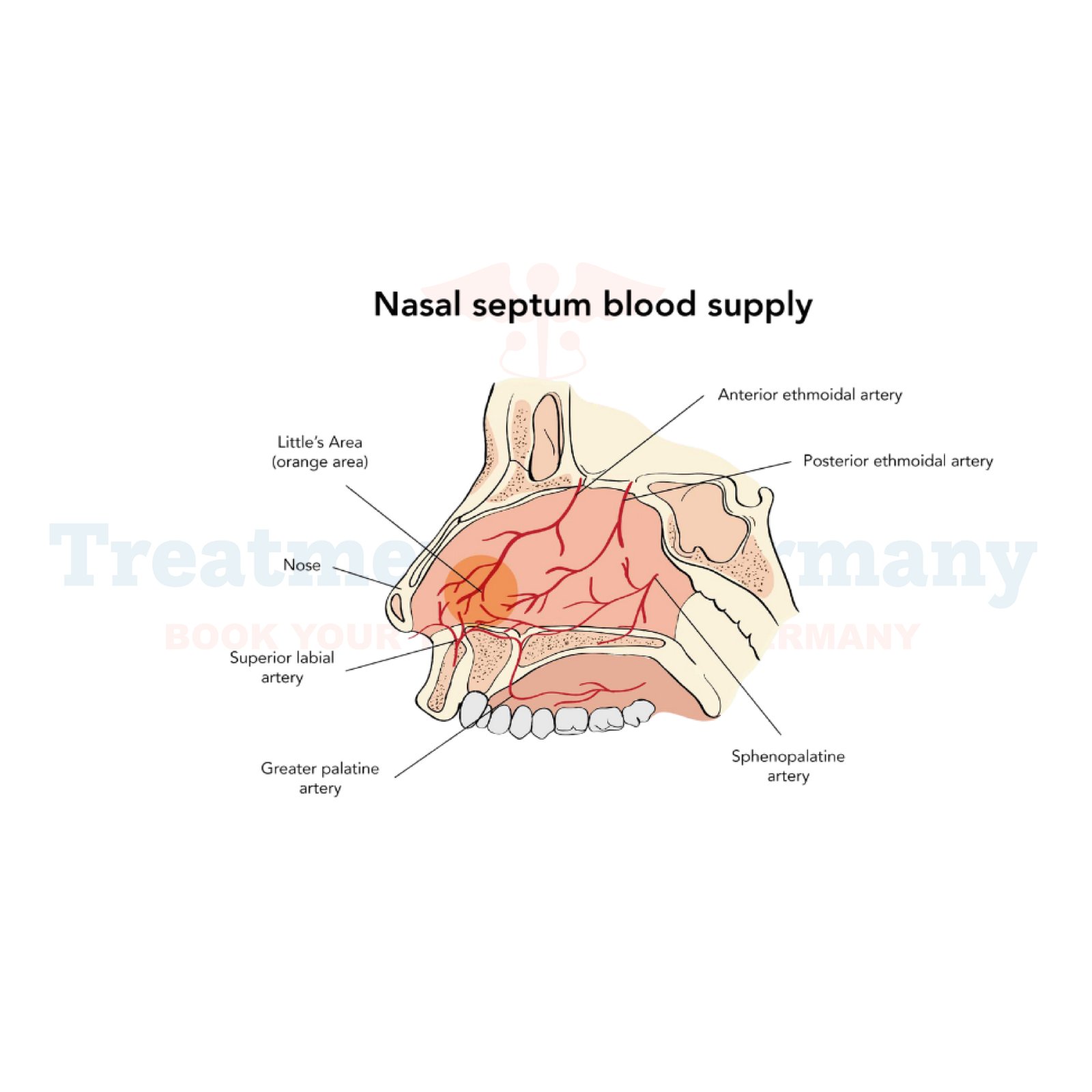
Most nosebleeds originate from blood vessels in the front part of the nose (anterior epistaxis), but in some cases, they can stem from deeper vessels in the back of the nose (posterior epistaxis).
Side Effects of Epistaxis (Nosebleeds):
Epistaxis can cause discomfort, inconvenience, and anxiety for patients. It may lead to blood loss, anemia in severe cases, and may interfere with daily activities. Chronic nosebleeds can also affect one's quality of life and may signal an underlying health condition that needs addressing.
How is Epistaxis (Nosebleeds) Diagnosed?:
Diagnosing the cause of Nosebleeds typically involves a thorough medical history review and a physical examination by a healthcare professional.
In some cases, additional tests such as blood tests, nasal endoscopy, or imaging studies like CT scans may be recommended to identify any underlying conditions contributing to the nosebleeds.
Potential Treatments of Epistaxis (Nosebleeds):
Treatment options for nosebleeds vary depending on the underlying cause, severity, and frequency of the episodes. Some common treatments include:
1. First-Aid Measures: Applying pressure to the nostrils by pinching the soft part of the nose, leaning forward to prevent swallowing blood, and applying a cold compress to the bridge of the nose can help stop bleeding during an episode.
2. Topical Medications: Nasal sprays or ointments containing vasoconstrictors or clotting agents may be prescribed to help control bleeding and promote healing of nasal blood vessels.
3. Cauterization: In cases of recurrent nosebleeds or when conservative measures fail, cauterization may be performed. This involves using heat or chemicals to seal off the bleeding blood vessels in the nose.
4. Nasal Packing: Gauze or special nasal packing materials may be inserted into the nose to apply pressure to the bleeding vessels and promote clotting. This is often used in cases of severe or posterior epistaxis.
5. Surgery: In rare cases where other treatments are ineffective or when a structural abnormality is identified, surgical intervention may be necessary to address the underlying cause of nosebleeds.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
