What is Fanconi Anemia?
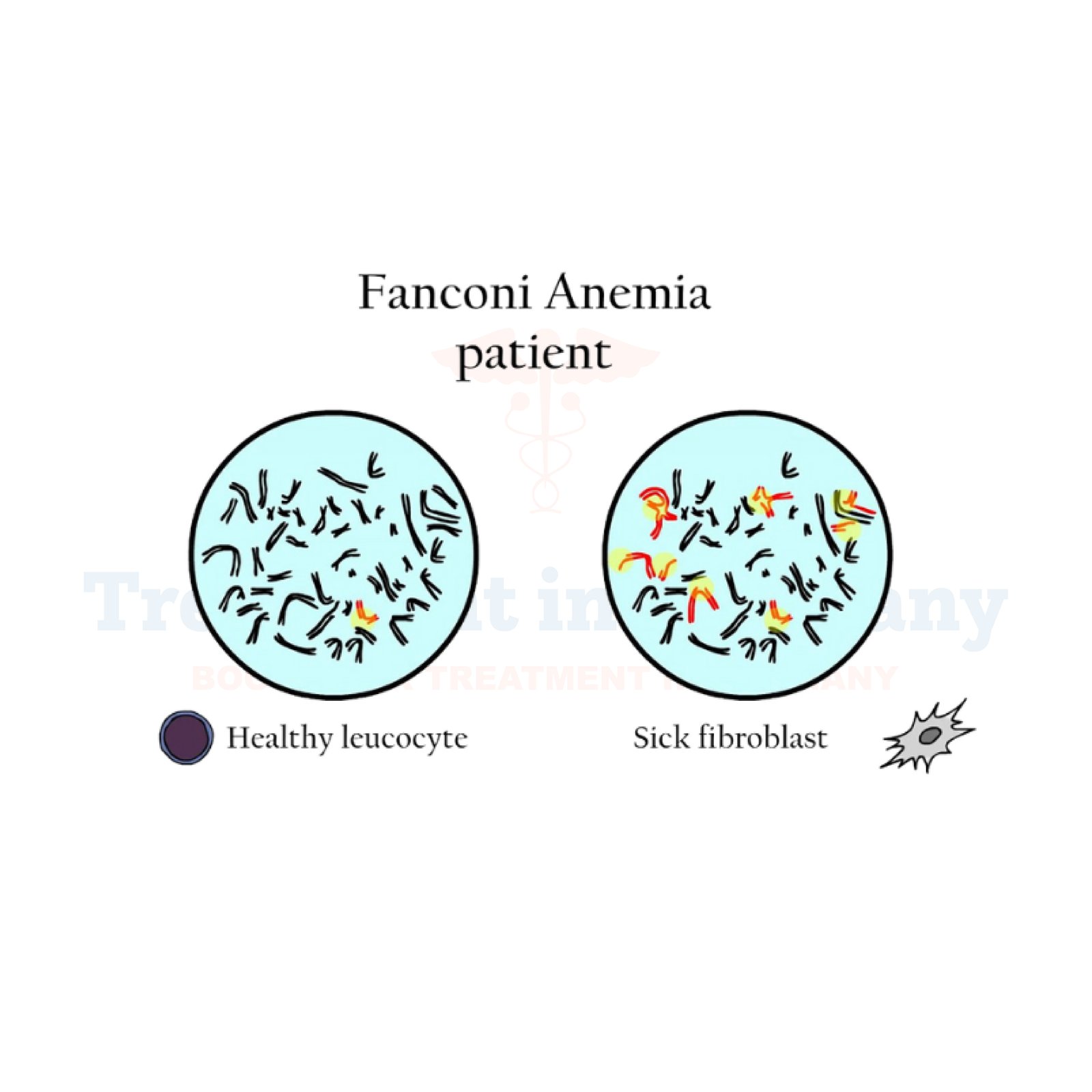
Fanconi Anemia (FA) is a rare genetic disorder that primarily affects the bone marrow, leading to decreased production of all types of blood cells.
It is characterized by a predisposition to certain cancers and physical abnormalities, often affecting multiple organ systems.
FA is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning a child must inherit a mutated gene from both parents to develop the condition.
Side Effects of Fanconi Anemia
The symptoms and severity of Fanconi Anemia can vary widely among individuals. Common side effects include:
- Bone Marrow Failure: This is one of the hallmark features of FA, where the bone marrow fails to produce enough blood cells (red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets).
- Increased Cancer Risk: Individuals with FA have a higher risk of developing certain cancers, such as leukemia, squamous cell carcinoma, and liver tumors.
- Physical Abnormalities: FA can also present with physical abnormalities, such as skeletal deformities, short stature, and abnormalities of the skin, kidneys, or ears.
- Reproductive Issues: Some individuals with FA may experience infertility or difficulties with reproductive health.
How is Fanconi Anemia Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Fanconi Anemia involves a combination of clinical evaluation, genetic testing, and laboratory studies. Key steps in the diagnostic process include:
- Clinical Evaluation: A thorough physical examination to assess for characteristic physical features and symptoms associated with FA.
- Genetic Testing: Identification of mutations in the genes known to cause FA (such as FANCA, FANCC, FANCG, etc.) through genetic testing. This helps confirm the diagnosis and can inform genetic counseling for family members.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: Evaluation of bone marrow function to assess for cytopenias (low blood cell counts) and to determine the extent of bone marrow failure.
Potential Treatment of Fanconi Anemia
Treatment strategies for Fanconi Anemia focus on managing symptoms and complications, as well as addressing bone marrow failure and cancer risk. Options may include:
- Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant (HSCT): The primary curative treatment for FA involves replacing the faulty bone marrow with healthy stem cells from a compatible donor (usually a sibling or unrelated donor).
- Androgen Therapy: Androgens, such as oxymetholone, can stimulate red blood cell production and improve blood counts in some individuals with FA.
- Monitoring and Surveillance: Regular monitoring for cancer development and early intervention if malignancies are detected.
- Supportive Care: Symptomatic treatment to manage complications such as infections, bleeding disorders, and growth abnormalities.
- Genetic Counseling: Counseling for families to understand the inheritance pattern of FA, reproductive options, and the potential for prenatal diagnosis in future pregnancies.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
