Germany is renowned for its pioneering, holistic medical treatments of various ailments and is no exception for fibroids. Fibroids are benign uterine growths that usually affect women during their reproductive years. The latest medical technology combined with expert professionals forms the German health system offered to many women seeking the best remedy for fibroids treatment in Germany.
Fibroids are also referred to as leiomyomas and represent noncancerous tumors in the uterus. In size, they can range significantly and have many effects on women, from having no symptoms to experiencing debilitating issues such as excessive or painful bleeding during your period, pressure on nearby organs, and discomfort in daily life. There is no known cause for fibroids, although hormones like estrogen and progesterone do cause them to grow.
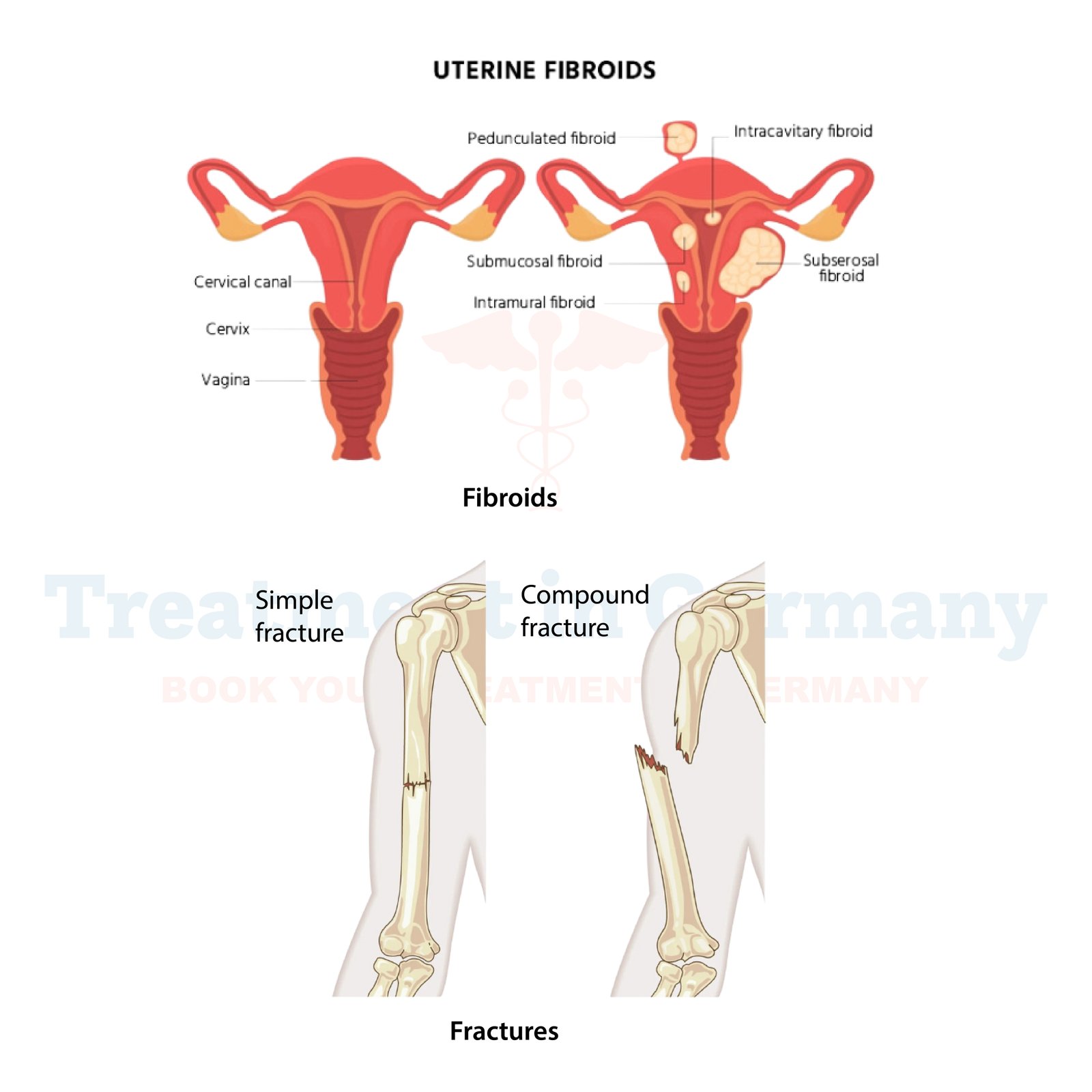
Types of Fibroids
They can appear anywhere in the uterus, resulting in a range of symptoms and frequently necessitating an alternative course of care. The following four fibroids are the most prevalent:
Fibroids Diagnostics in Germany
Germany guarantees state of the art diagnostics for patients with the goal of accurate detection. Often, fibroids are discovered during routine pelvic exams, and additional testing verifies the size and location of the fibroids. Many diagnostic procedures involve:
Pre advanced diagnosis of Fibroids
Early detection is critical to prevent complications such as anemia or fertility issues. Symptoms such as frequent urination, constipation, or abnormal vaginal discharge may lead to early tests. With advanced diagnostic technologies like ultrasonography, physicians in Germany can correctly identify fibroids and provide timely interventions.
Treatment Centers for Fibroids in Germany
Germany has the world's best hospitals and specialists who specialize in the treatment of uterine fibroids. German medical centers treat patients with both non-surgical and surgical options to suit individual needs, providing the best care for them.
Sophisticated Fibroid Treatment
Some of the most sophisticated treatments for fibroids are offered in Germany. A variety of surgeries exist to treat fibroids depending on their size, location, and number. Among these, procedures involve:
Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy do not form a part of the conventional treatment for fibroids, though these might be employed in very rare cases where the fibroids become malignant. In such cases, Germany's oncologists may be approached.
Novel Developments: Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy
Innovators are the first ones to resort to newer technologies at all times, even to get treated by immunotherapy and targeted therapy in Germany. These processes identify the abnormal cells in the fibroids and get them treated through the body's immune systems as well as molecular targets.
Diagnosis of Fibroids
The diagnosis of fibroids requires identifying some initial symptoms, such as Pelvic pain, unusual bleeding, or Pain while making love. The earlier the patients are identified, the better, because they will receive individualized treatment.
Rehabilitation after Fibroids Treatment
Rehabilitation after fibroid treatment in Germany involves support through a process to recover wholly; it includes both physical rehabilitation and reduction of other complications arising post surgery. The duration of the treatment procedure, however, always reinstates a gradual return to activities.
Psychological Counseling
Psychological well-being following fibroid treatment is of paramount importance, especially in people who have undergone crucial procedures, such as a hysterectomy. It has been noted that many German medical centers administer psychological counseling to promote emotional adjustment among women following the treatment.
Fibroids Treatment Cost in Germany
Treatment of fibroids in Germany will differ in price depending on the procedure. Some might prove to be costly, like robotic or laparoscopic myomectomy, but they are more effective, and it would be possible to recover more quickly. However, the international patients do not mind paying that money for the quality treatment and expertise the hospitals ensure.
Top Hospitals for Fibroids in Germany
There are a variety of top-class hospitals in Germany that are treating uterine fibroids inside the country. They include:
These centers treat fibroids with modern technology and highly qualified specialists for the best possible medical treatment.
Why Fibroid Treatment in Germany?
Treating fibroids in Germany presents various benefits. Germany is famous for modern treatment procedures, advanced medical care facilities, as well as highly experienced doctors who believe in and practice avant-garde medical care.
Important Benefits of Treatment in Germany
Germany is renowned for its outstanding quality of health care. Bone injuries, in particular, are treated here by such skilled medical professionals, along with the help of technologically advanced equipment, so that bone fracture treatment can be as successful as possible.
Now, these patients come from any corner of the globe to Germany for their treatment, including bone injuries.
This article is to give an idea regarding thorough fracture treatment in Germany, discussing diagnosis, new methods, and why people prefer coming to Germany for such kinds of treatment.
Fractures are any breaks in a bone, commonly caused by accidents or falls while playing sports. People with such diseases as osteoporosis are very prone to fractures. As simple as the crack may seem, a fracture can shatter into several pieces in more complex cases.
Fractures can be classified in different ways; this depends on the area affected and the cause. Mainly, fractures happen due to high-impact injuries like sports injuries, in which both bones and ligaments can be damaged at once.
Types of Fractures
There are different forms of fractures, with each having a unique treatment procedure:
Diagnosis of Fractures in Germany
Healthcare centers and hospitals in Germany use advanced diagnostic technology to accurately diagnose the nature and extent of the injuries. Early diagnosis is necessary to establish a proper treatment plan.
Early Diagnosis of Fractures
MRIs, CT scans, and X-rays are examples of diagnostic methods that are frequently employed in diagnosis. These will provide clear visualization of the condition that exists in the injury and the surrounding tissues, such as cartilage and ligaments.
Treatment Hospitals for Fractures in Germany
These facilities in Germany provide the best technologies along with qualified professionals. Whether treatment needs to be done by non-surgical methods, like using a splint or a cast, or by complex surgeries, the success rate is at its maximum in hospitals in Germany.
Latest Treatment Options for Fractures
Serious fractures could be subjected to surgery such as bone grafting or arthroplasty—placement of a joint. For more complicated compound fractures, recent surgical techniques are applied so that broken bones are properly aligned and reset to establish stability.
Chemotherapy and Radiation
Fractures could be mostly treated orthopedically, but problems like osteomyelitis (bone infections) could involve chemotherapy or radiation as a way to treat underlying conditions that affect the bones themselves.
Newer Techniques: Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy
Scientists utilize the newer techniques of immunotherapy and targeted therapy to accelerate recovery, particularly in cases complicated with systemic diseases or abnormal cell proliferation in patients.
Detection of Fractures
Based on manifestations such as pain, swelling, and bruising, fractures can be diagnosed. With advanced technology related to imaging, even in difficult-to-diagnose cases, including overuse syndrome or nonunion, wherein bones may not heal in an appropriate time or shape, doctors in Germany can diagnose the precise location and the degree of fracture.
Rehabilitation After Fractures Treatment
Rehabilitation forms an integral component of the treatment process of fractures, particularly complicated fractures of the pelvis or hip. German hospitals plan specific rehabilitation programs along with physiotherapy and exercises to get the patient moving and strong as soon as possible.
Psychological Therapy
Recovery from serious injuries like compression fractures or facial fractures can be very traumatic. German hospitals sometimes provide psychological therapy to patients suffering from some form of psychological trauma before fully regaining strength.
Cost of Treatment of Fractures in Germany
Varied treatment costs exist in Germany, depending on the severity of the fracture and the complexity involved in the appropriate treatment needed. General anesthesia for surgery or even complex repairs that may include pins and wires or even external fixation with related costs are added, but many say the quality of care in Germany is well worth what one pays.
Best Hospitals for Treating Fractures in Germany
Germany is one of the most significant medical centers, with the latest equipment and the most skilled doctors. It provides advanced care to patients who are undergoing different kinds of fractures, including Humerus (upper arm bone), Colles, and Scaphoid.
Why fracture treatment in Germany?
Germany boasts some of the highest levels of care in the medical sector, especially orthopedic surgery. Germany's health care sector ensures that any fracture—be it femur, acetabulum, or talus gets the best available care.
Significant Advantages of Treatment in Germany
Availability of modern medical technology.
Such complex injuries like trimalleolar fractures and Jones fractures are treated with advanced fracture management.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
