What is Fibroids (Uterine Leiomyomas):
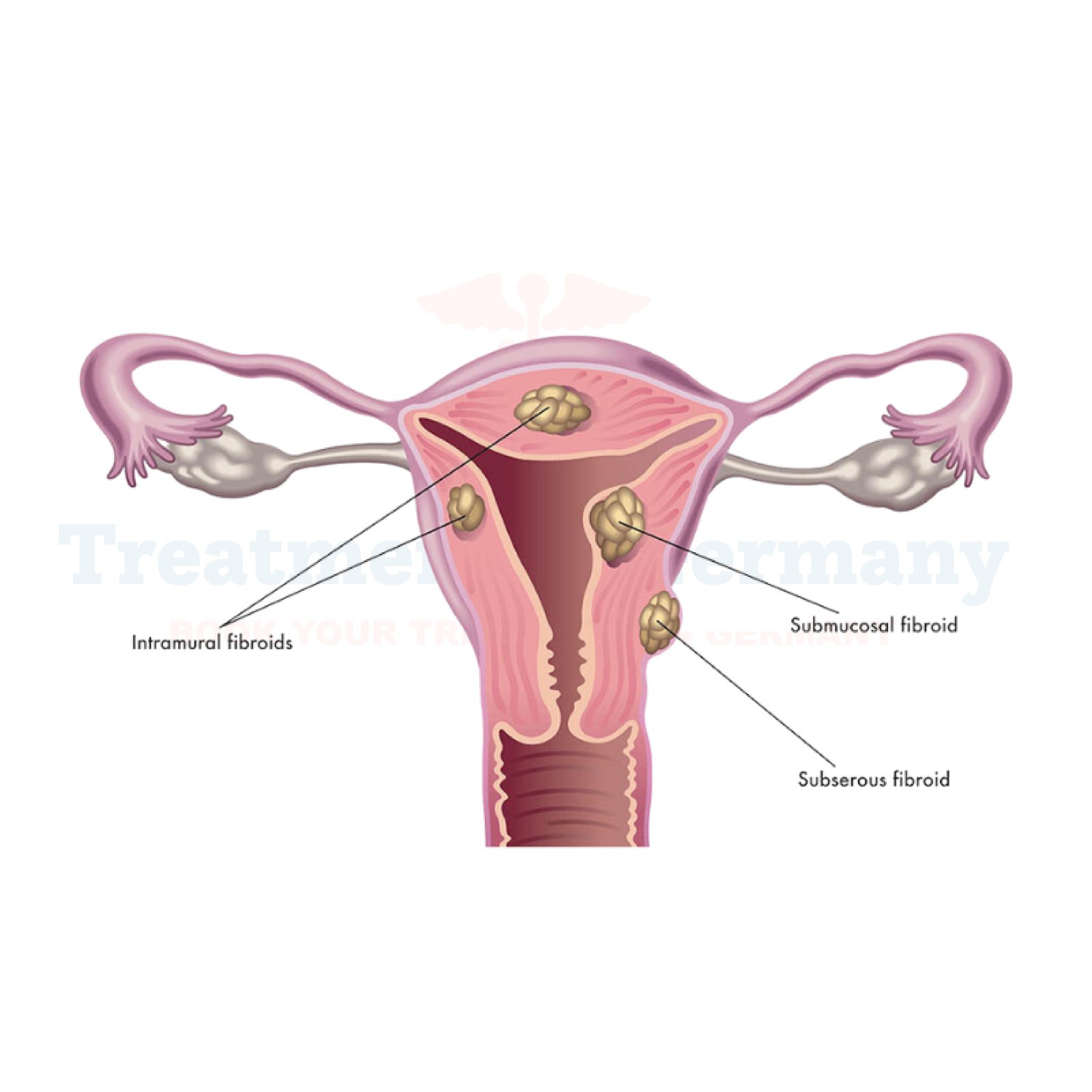
Fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyomas, are noncancerous growths that develop in the uterus. These growths are made up of muscle and connective tissue and can vary in size, ranging from as small as a pea to as large as a grapefruit.
They can occur individually or in clusters and may develop within the uterine wall, protrude into the uterine cavity, or attach to the outer surface of the uterus.
Side effects of Fibroids (Uterine Leiomyomas):
Fibroids can cause a range of symptoms, including heavy menstrual bleeding, prolonged periods, pelvic pain or pressure, frequent urination, constipation, backache, and discomfort during sexual intercourse.
In some cases, fibroids can lead to complications such as anemia due to excessive blood loss during menstruation, infertility, or complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
How is Fibroids (Uterine Leiomyomas) diagnosed?:
Diagnosing Fibroids typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Your healthcare provider may perform pelvic exams to feel for any abnormalities in the uterus.
Imaging tests such as ultrasound, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), or CT (computed tomography) scans may be ordered to visualize the size, number, and location of fibroids. In some cases, a hysteroscopy or laparoscopy may be recommended for a more detailed examination of the uterus.
Potential treatments of Fibroids (Uterine Leiomyomas):
Treatment options for fibroids depend on various factors including the size and location of the fibroids, severity of symptoms, and your overall health and preferences.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
