What is Fibromuscular Dysplasia?
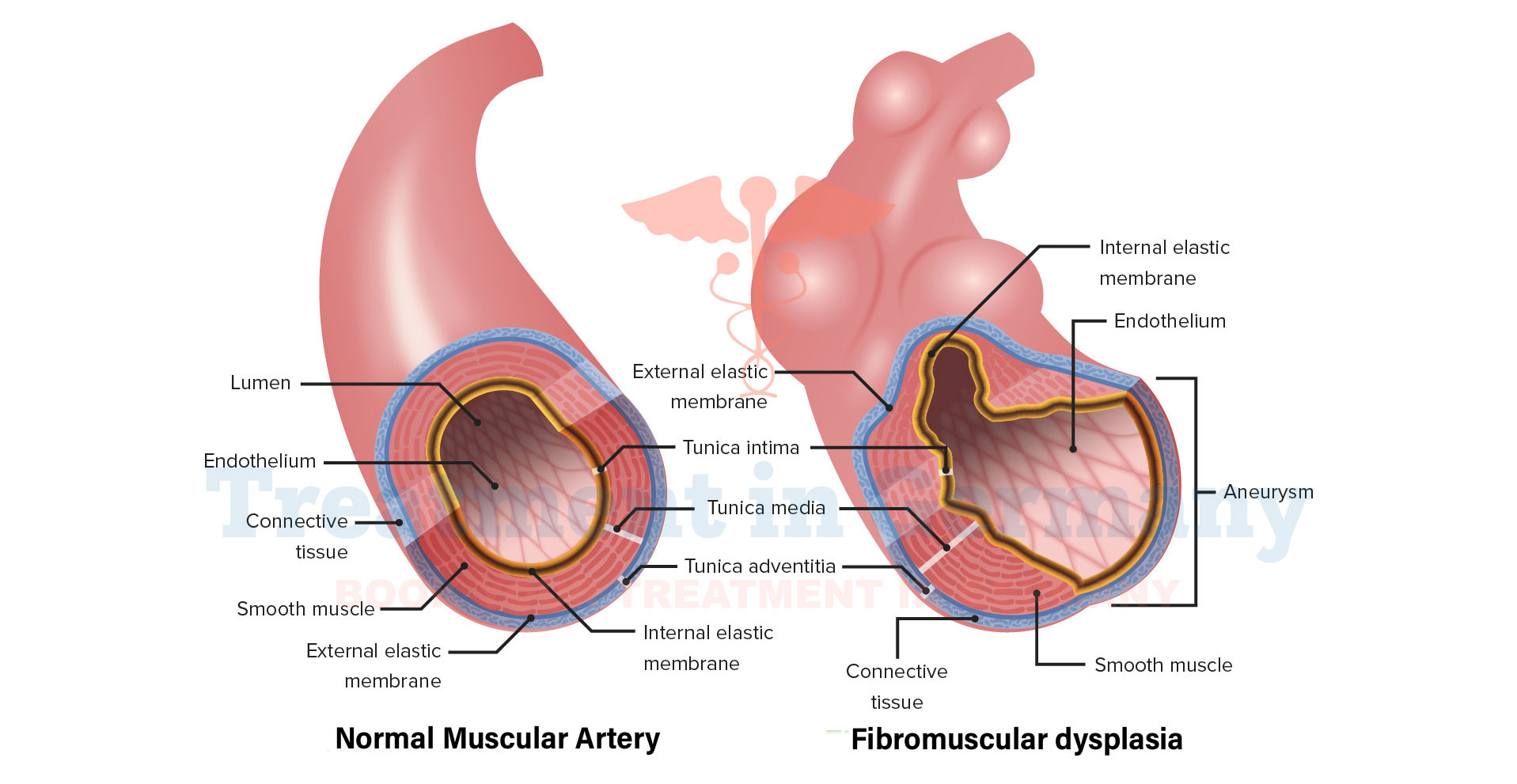
Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) is a rare condition affecting the blood vessels, particularly the arteries, causing abnormal growth within their walls.
This results in the arteries becoming narrow, which can disrupt blood flow to various organs and tissues.
Side Effects of Fibromuscular Dysplasia
The symptoms of Fibromuscular dysplasia depend on which arteries are affected and how severely they are narrowed. Common symptoms include:
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) if arteries supplying the brain are affected
- Abdominal pain, if arteries supplying the intestines are affected
How is Fibromuscular Dysplasia Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Fibromuscular dysplasia typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and imaging tests. These may include:
- Duplex ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to create images of blood flow in the arteries.
- CT angiography (CTA) or MR angiography (MRA): These imaging techniques provide detailed pictures of blood vessels to identify any narrowing or abnormalities.
- Conventional angiography: This involves injecting contrast dye into the arteries and taking X-ray images to visualize blood flow and detect FMD.
Potential Treatment of Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Treatment for Fibromuscular dysplasia focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications:
- Medications: These may include drugs to lower blood pressure or prevent blood clots.
- Angioplasty and stenting: This procedure may be used to widen narrowed arteries and improve blood flow.
- Surgery: In severe cases or when other treatments are ineffective, surgery may be necessary to bypass or repair damaged arteries.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
