Fibromyalgia Treatment in Germany
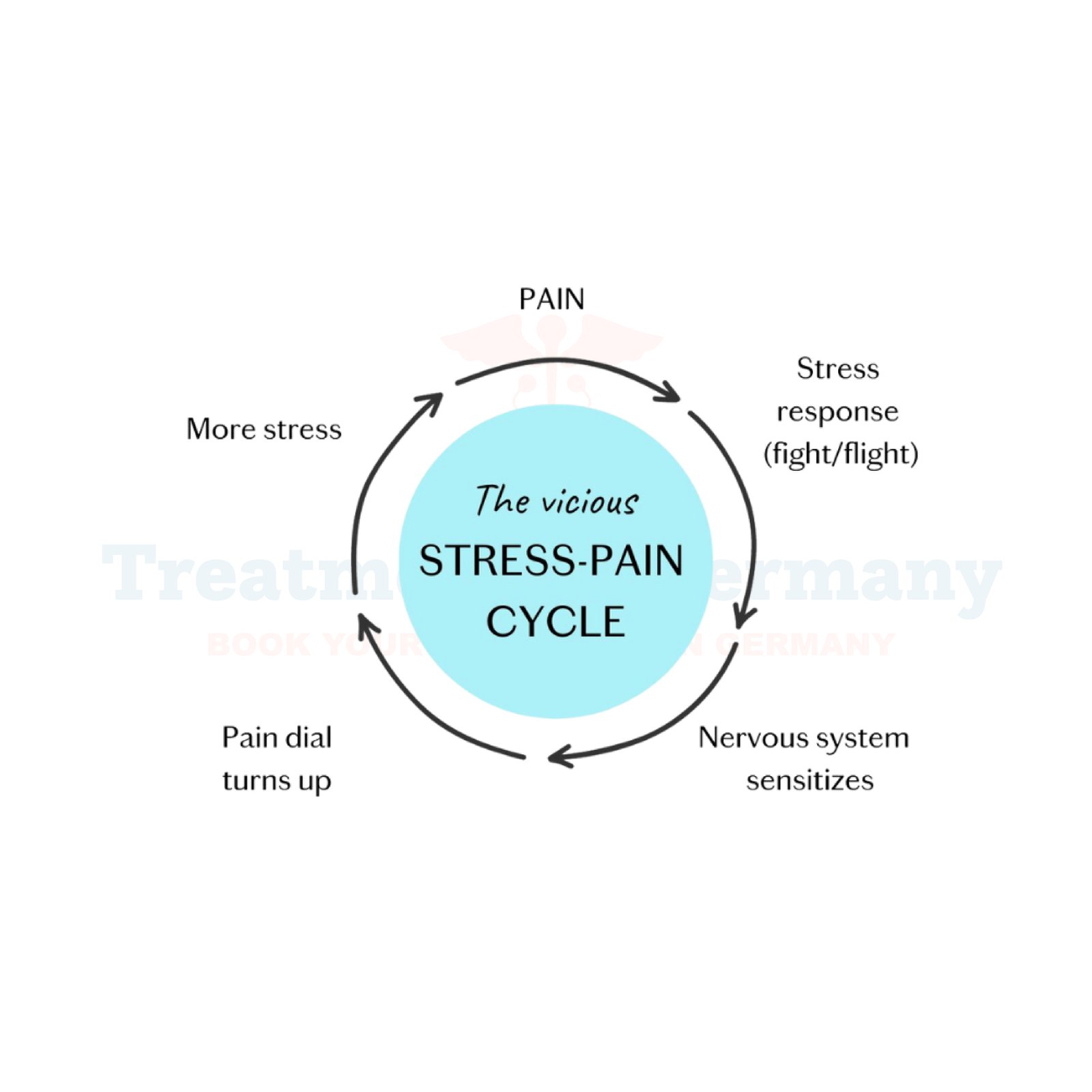
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and cognitive disturbances. It affects millions worldwide, significantly impacting their daily lives. The exact cause remains unknown, but researchers believe it is linked to abnormal pain processing in the brain and spinal cord. Fibromyalgia is often associated with other conditions such as autoimmune diseases, obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol (hyperlipidemia). Germany has become a leading destination for fibromyalgia treatment, offering innovative therapies, state-of-the-art hospitals, and specialized doctors who focus on effective management and long-term relief.
Types of Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is often categorized based on its symptoms and triggers:
- Primary Fibromyalgia: No underlying medical condition; symptoms develop independently.
- Secondary Fibromyalgia: Develops due to autoimmune diseases, injuries, or infections.
- Post-Traumatic Fibromyalgia: Triggered by physical trauma such as accidents or surgery.
- Localized Fibromyalgia: Pain is concentrated in specific areas, often mistaken for arthritis.
Risk Factors for Fibromyalgia
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing fibromyalgia, including:
- Genetic predisposition: Family history of fibromyalgia or chronic pain conditions.
- Autoimmune diseases: Conditions such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- Obesity and high BMI: Excess weight increases stress on muscles and joints.
- Diabetes and high cholesterol: Metabolic disorders can contribute to chronic pain syndromes.
- Infections: Viral infections, such as Epstein-Barr, have been linked to fibromyalgia onset
- Emotional or physical trauma: PTSD, depression, and severe stress can trigger symptoms.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop fibromyalgia than men.
Symptoms of Fibromyalgia
Widespread Pain: Persistent pain affecting both sides of the body and multiple regions.
- Fatigue & Sleep Disturbances: Even after a full night’s sleep, patients feel exhausted.
- Cognitive Issues ("Fibro Fog"): Difficulty concentrating, memory lapses, and mental confusion.
- Headahes & Migraines: Chronic headaches often accompany fibromyalgia.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Digestive issues such as bloating, diarrhea, or constipation.
- Muscle Stiffness & Numbness: Tingling sensations, especially in the arms and legs.
- Sensitivity to Temperature & Light: Extreme sensitivity to cold, heat, and bright lights.
Diagnosis & Diagnostic Tools in Germany
Diagnosing fibromyalgia requires a comprehensive approach. Germany’s top hospitals and specialists utilize advanced diagnostic methods, including:
- X-rays: Rule out arthritis and joint abnormalities.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Identifies potential nerve damage or structural issues.
- CT (Computed Tomography) Scans: Detailed imaging to detect abnormalities in the nervous system.
- Blood Tests: To check for autoimmune diseases, inflammation markers, and vitamin deficiencies.
- Pressure Point Testing: Evaluation of 18 specific tender points.
- Neurological Assessments: To assess cognitive impairment and nervous system function.
Treatment of Fibromyalgia in Germany
Germany offers cutting-edge treatment solutions that combine conventional and innovative therapies to manage fibromyalgia effectively.
Conventional Treatments
- Pain Relievers: NSAIDs and prescription medications to manage pain and inflammation.
- Muscle Relaxants: Reduce muscle stiffness and improve mobility.
- Antidepressants: Used to address mood disorders and sleep disturbances.
- Physical Therapy: Helps restore muscle function and flexibility.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Supports mental health and stress management.
- Acupuncture & Massage Therapy: Provides relief from chronic pain and improves circulation.
Innovative Therapies in Germany
Germany leads in regenerative and holistic treatments for fibromyalgia, including:
- Stem Cell Therapy: Repairs damaged tissues and promotes cellular regeneration.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Uses the patient’s own plasma to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Dendritic Cell Therapy: Enhances the immune system and helps with autoimmune-related fibromyalgia.
- TACE Therapy (Transarterial Chemoembolization): Used in cases where fibromyalgia is linked to inflammatory disorders.
- Neurostimulation Therapy: Modulates pain signals in the brain for long-term pain relief.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT): Boosts oxygen levels to improve healing and reduce fatigue.
Why Choose Germany for Fibromyalgia Treatment?
Germany is known for its world-class medical facilities and high success rates in managing fibromyalgia. Here’s why it is a preferred destination:
- Expert Specialists & Surgeons: Highly qualified doctors specializing in pain management and neurology.
- State-of-the-Art Hospitals: Equipped with the latest imaging and diagnostic tools.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Tailored therapies based on individual patient needs.
- Holistic & Multidisciplinary Approach: Integrates physiotherapy, psychological support, and alternative medicine.
- Medical Tourism-Friendly: Hospitals in Germany offer customized packages for international patients.
- Shorter Recovery Time: Advanced treatment options lead to faster pain relief and mobility improvement.
Solutions & Prevention of Fibromyalgia
Preventive Measures
- Regular Exercise: Low-impact activities such as yoga, swimming, and Pilates.
- Stress Management: Meditation, deep breathing exercises, and counseling.
- Healthy Diet: Anti-inflammatory foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants.
- Adequate Sleep: Establishing a consistent sleep schedule.
- Maintaining a Healthy BMI: Prevents excessive strain on muscles and joints.
- Avoiding Triggers: Limiting exposure to stress, cold temperatures, and overexertion.
Complementary Therapies for Recovery
- Massage Therapy: Helps alleviate muscle stiffness and improves circulation.
- Chiropractic Care: Aligns the spine and reduces nerve pressure.
- Herbal Supplements: Turmeric, magnesium, and CBD oil have shown promising results.
- Hydrotherapy: Warm water therapy eases muscle pain and stiffness.
Conclusion
Fibromyalgia is a complex chronic condition that requires multidisciplinary treatment for effective management. Germany provides top-tier medical expertise, advanced diagnostic tools, and innovative therapies that significantly improve the quality of life for fibromyalgia patients. From regenerative medicine to holistic pain management, German hospitals ensure comprehensive care tailored to each patient’s needs.
By adopting preventive measures and exploring cutting-edge treatments, individuals suffering from fibromyalgia can achieve long-term relief and restore their mobility, mental clarity, and overall well-being.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
