What is Friedreich's Ataxia?
Friedreich's Ataxia (FA) is a rare, progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects the nervous system and heart. It is characterized by muscle weakness, difficulty with balance and coordination (ataxia), and loss of sensation in the arms and legs.
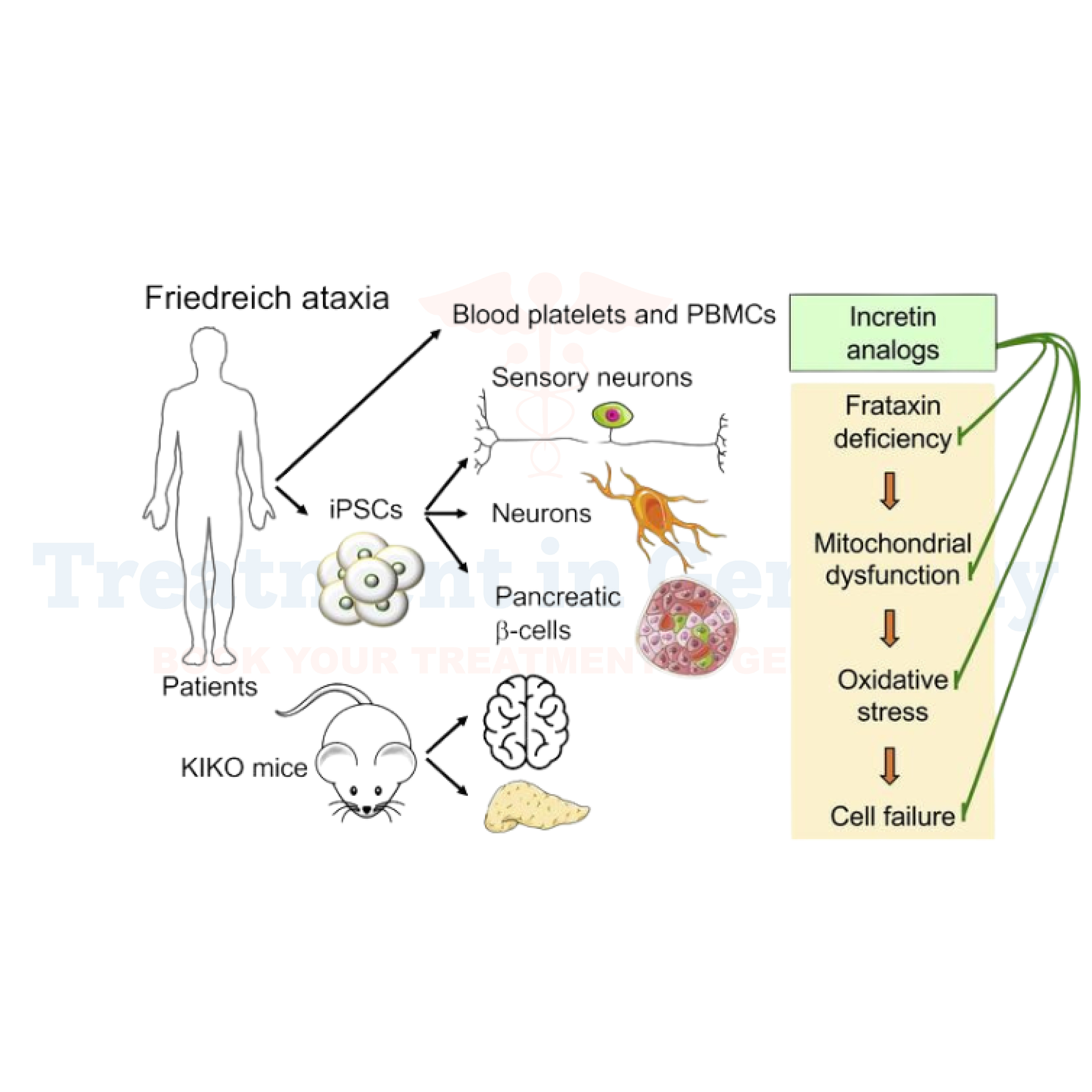
FA is caused by a genetic mutation that leads to impaired production of a protein called frataxin, which is essential for proper function of mitochondria, the energy-producing centers in cells.
Side Effects of Friedreich's Ataxia
Patients with Friedreich's Ataxia may experience a range of symptoms that worsen over time. These can include:
- Loss of coordination: Difficulty walking and performing fine motor tasks.
- Muscle weakness: Especially in the arms and legs, leading to reduced mobility.
- Speech problems: Slurred speech or difficulty articulating words clearly.
- Heart complications: Such as cardiomyopathy (weakened heart muscle) and arrhythmias.
- Spinal deformities: Such as scoliosis (curvature of the spine).
The progression and severity of symptoms can vary among individuals, with most patients experiencing symptoms starting in childhood or adolescence.
How is Friedreich's Ataxia Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Friedreich's Ataxia typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, genetic testing, and neurological assessments:
- Clinical Evaluation: A thorough medical history and physical examination to assess symptoms such as ataxia, muscle weakness, and possible heart abnormalities.
- Genetic Testing: To identify mutations in the FXN gene, which are responsible for Friedreich's Ataxia. This can confirm the diagnosis and help determine the inheritance pattern.
- Neurological Assessments: Including tests of coordination, reflexes, and sensory function to evaluate the extent of neurological involvement.
Potential Treatment of Friedreich's Ataxia
Currently, there is no cure for Friedreich's Ataxia, and treatment focuses on managing symptoms and complications:
- Physical therapy: To improve strength, coordination, and mobility.
- Occupational therapy: To assist with daily activities and maximize independence.
- Speech therapy: To address speech difficulties.
- Orthopedic interventions: Such as braces or surgery for spinal deformities.
- Cardiac care: Regular monitoring and treatment for heart complications.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
