Ganglion Cysts Treatment in Germany
Ganglion cysts are noncancerous, fluid-filled lumps that typically form along the tendons or joints, often on the wrists, hands, and feet. Though the exact cause remains unclear, they tend to develop when the tissue surrounding a joint or tendon weakens, leading to fluid collection. While these cysts are often harmless and may resolve without intervention, they can cause discomfort if they press on surrounding nerves or restrict joint movement. If left untreated, ganglion cysts can grow in size or persist, requiring medical attention.
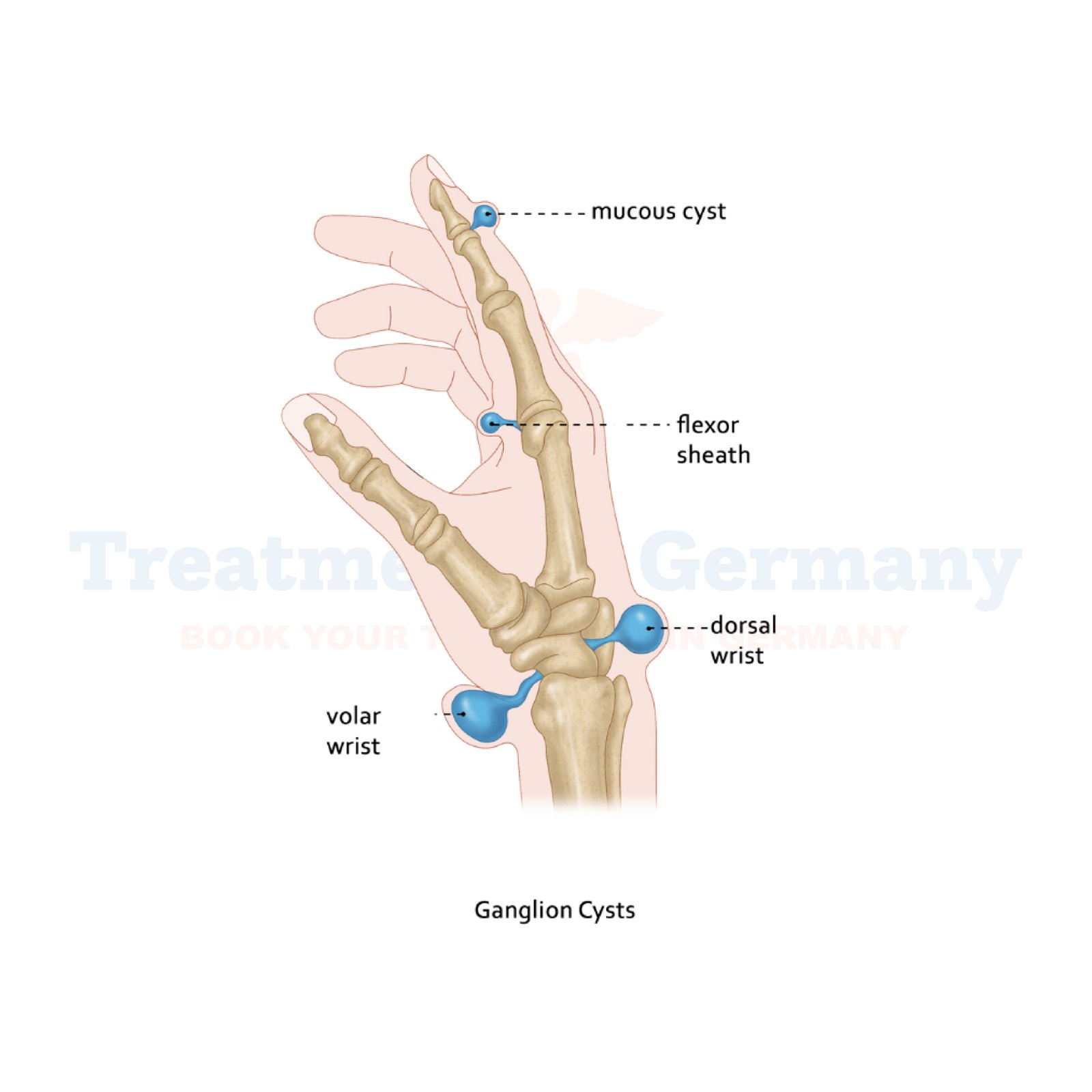
Types of Ganglion Cysts
Ganglion cysts can vary in type depending on their location and the structures they affect. Common types include:
Dorsal Ganglion Cysts: The most common type, typically found on the back of the wrist.
Volar Ganglion Cysts: These cysts occur on the palm side of the wrist, often linked to the carpal tunnel.
Mucous Cysts: These are generally found near the nails, typically attached to finger joints.
Risk Factors for Ganglion Cysts
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing ganglion cysts:
Age: Individuals between the ages of 20 and 40 are more likely to develop ganglion cysts.
Gender: Women are at a higher risk than men.
Previous Joint Injuries: Trauma or stress to the joints or tendons increases the risk of developing cysts.
Underlying Medical Conditions: People with conditions such as autoimmune diseases, obesity, high cholesterol (hyperlipidemia), and diabetes are more prone to these cysts.
Symptoms of Ganglion Cysts
While many ganglion cysts are asymptomatic, they can cause discomfort if they press on nearby nerves. Common symptoms include:
Pain or Tenderness: This occurs when the cyst exerts pressure on surrounding structures.
Visible Swelling: A noticeable lump may form where the cyst is located.
Limited Joint Mobility: If the cyst compresses a nerve, it may impair joint movement or cause weakness in the affected area.
Diagnosis and Diagnostic Tools
Diagnosing ganglion cysts typically involves several methods:
Physical Examination: A doctor will inspect the cyst, noting its size, location, and consistency.
Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans are used to rule out other conditions and confirm the diagnosis. These tools help determine the cyst’s size, location, and any potential complications.
Ultrasound: An ultrasound can provide a clearer view of the fluid-filled nature of the cyst.
Blood Tests: Although not typically required for ganglion cysts, blood tests can help identify underlying health conditions like autoimmune diseases that may predispose individuals to cyst development.
Why Is It Preferable to Get Treatment in Germany?
Germany’s medical system is globally acknowledged for its high standards of care, advanced technology, and patient-centered approach. Here are some of the key reasons why individuals seek treatment in Germany:
High-Quality Healthcare: German medical facilities are among the best in the world, offering cutting-edge technology and highly skilled professionals.
Skilled Doctors and Surgeons: The country is home to some of the most experienced specialists in the treatment of ganglion cysts.
Advanced Diagnostic Tools: Tools like MRI, X-rays, and CT scans ensure precise diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
Comprehensive Care: From diagnosis through to recovery, Germany offers comprehensive care, including physical therapy and complementary therapies, ensuring full recovery and preventing recurrence.
Solutions and Prevention
While it’s not always possible to completely prevent ganglion cysts, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
Manage Joint Stress: Avoid repetitive motion and overuse of joints and tendons.
Control Underlying Health Conditions: Conditions like obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol can increase the likelihood of cyst formation, so keeping them under control is essential.
Physical Therapy: Regular exercises that focus on joint mobility and tendon strength can help reduce the risk of developing cysts.
Patients who opt for treatment in Germany can also benefit from complementary therapies like acupuncture and massage therapy, which help reduce pain, improve mobility, and promote healing.
Treatment Options in Germany
Germany offers several treatment options for ganglion cysts, ranging from conservative to surgical methods:
Non-Surgical Treatments
Aspiration: This involves draining the fluid from the cyst using a needle, which may provide immediate relief. However, cysts can recur after aspiration.
Corticosteroid Injections: After draining the cyst, a corticosteroid injection may help reduce inflammation and prevent recurrence.
Pain Management: Doctors may recommend pain relievers like NSAIDs to manage discomfort.
Surgical Treatment
If conservative treatments fail, surgery may be necessary. The procedure involves removing the cyst and its stalk, ensuring minimal chance of recurrence. This surgery is typically performed under local anesthesia, and patients can often go home the same day.
Innovative Therapies
Dendritic Cell Therapy: This technique uses immune cells to target and reduce cyst growth, harnessing the body’s own healing mechanisms.
Stem Cell Therapy: By regenerating damaged tissues, stem cell therapy accelerates the healing process and helps prevent recurrence of the cysts.
TACE (Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization): A less common treatment, TACE involves injecting chemotherapy drugs into blood vessels that supply the cyst to shrink it effectively.
These advanced treatments are available in hospitals in Germany that specialize in innovative and personalized care.
Conclusion
Ganglion cysts may be non-threatening, but their impact on daily life can be significant. Treatment in Germany offers patients access to world-class care and innovative therapies, including stem cell therapy, dendritic cell therapy, and TACE, which have proven effective in treating more complex cases. The country’s advanced healthcare system, renowned doctors and specialists, and high-tech diagnostic tools make it an attractive destination for those seeking treatment for ganglion cysts.
By choosing treatment in Germany, patients benefit from cutting-edge medical care and personalized attention that ensures a successful outcome. With proper diagnosis, timely intervention, and preventive measures, ganglion cysts can be managed effectively, reducing the risk of recurrence and improving overall quality of life.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
