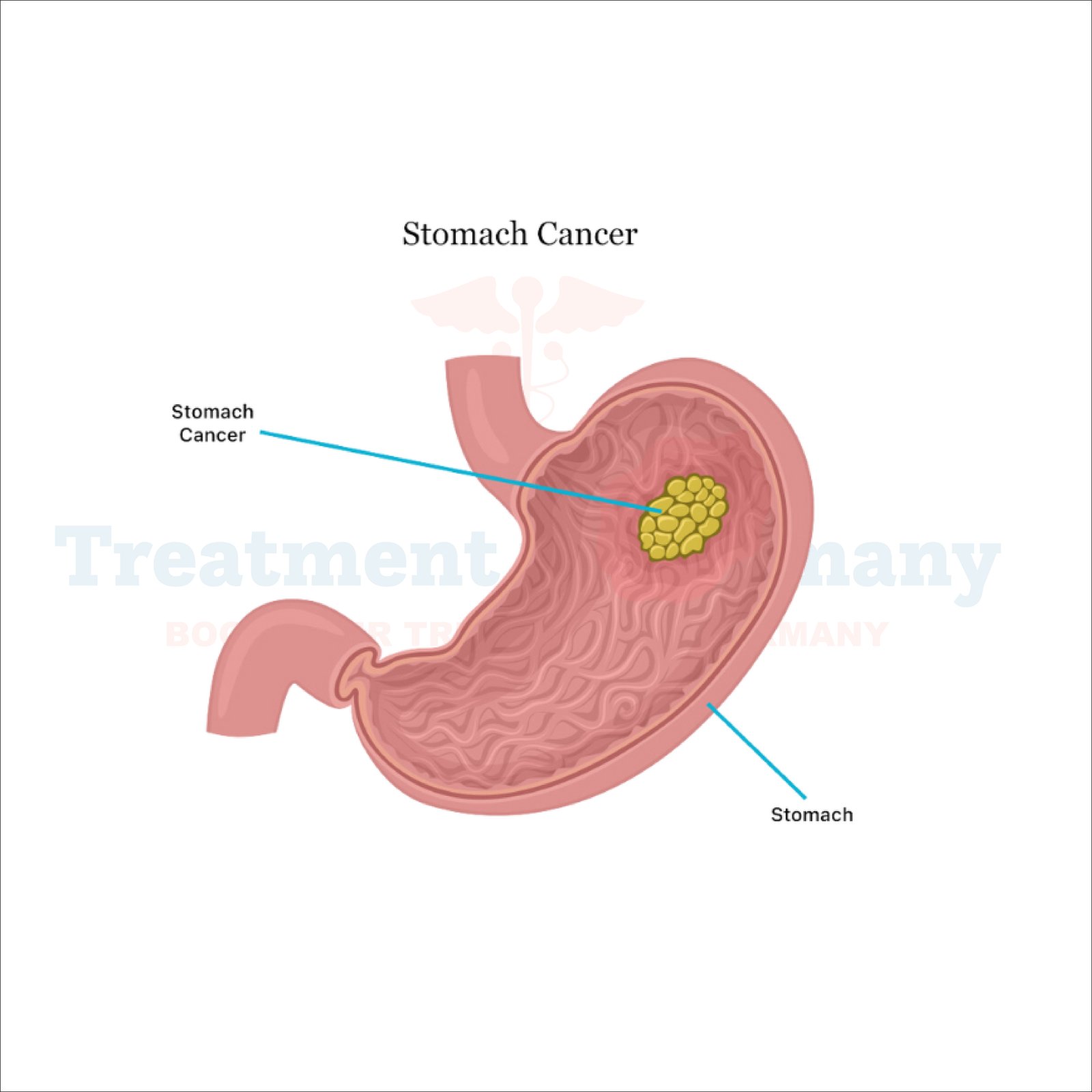
What is Gastric Cancer:
Gastric cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the lining of the stomach begin to grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor. This tumor can then invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body. There are several types of gastric cancer, including adenocarcinoma, which is the most common type, as well as less common types such as lymphoma and gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs).
Side effects of Gastric Cancer:
The symptoms of gastric cancer can vary depending on the stage of the disease and its location within the stomach. Common symptoms may include:
- Persistent abdominal pain or discomfort
- Feeling full or bloated after eating small amounts
- Unexplained weight loss
- Difficulty swallowing
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
- Blood in the stool or vomit
As gastric cancer progresses, it can cause more severe symptoms and complications, such as obstruction of the stomach or intestines, jaundice, and spread to other organs.
How is Gastric Cancer diagnosed:
Diagnosing Gastric Cancer typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. These may include:
- Endoscopy: A procedure in which a thin, flexible tube with a camera on the end is used to examine the inside of the stomach and take tissue samples (biopsies) for analysis.
- Imaging tests: Such as CT scans, MRI scans, and PET scans, may be used to evaluate the extent of the cancer and whether it has spread to other parts of the body.
- Blood tests: Certain blood markers may be elevated in patients with gastric cancer, although these tests are not specific to the disease.
Potential treatments of Gastric Cancer:
The treatment options for gastric cancer depend on factors such as the stage of the disease, the patient's overall health, and personal preferences. Treatment may include:
- Surgery: The primary treatment for early-stage gastric cancer involves removing the tumor and surrounding tissue. In more advanced cases, surgery may also be used to relieve symptoms or remove tumors that are causing complications.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs that kill cancer cells or stop them from growing may be used before or after surgery to shrink tumors, prevent recurrence, or alleviate symptoms.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy beams are used to target and destroy cancer cells. This may be used in combination with surgery and/or chemotherapy.
- Targeted therapy: Drugs that specifically target certain molecules involved in cancer growth may be used to treat advanced gastric cancer, particularly in cases where other treatments have been ineffective.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a
complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
