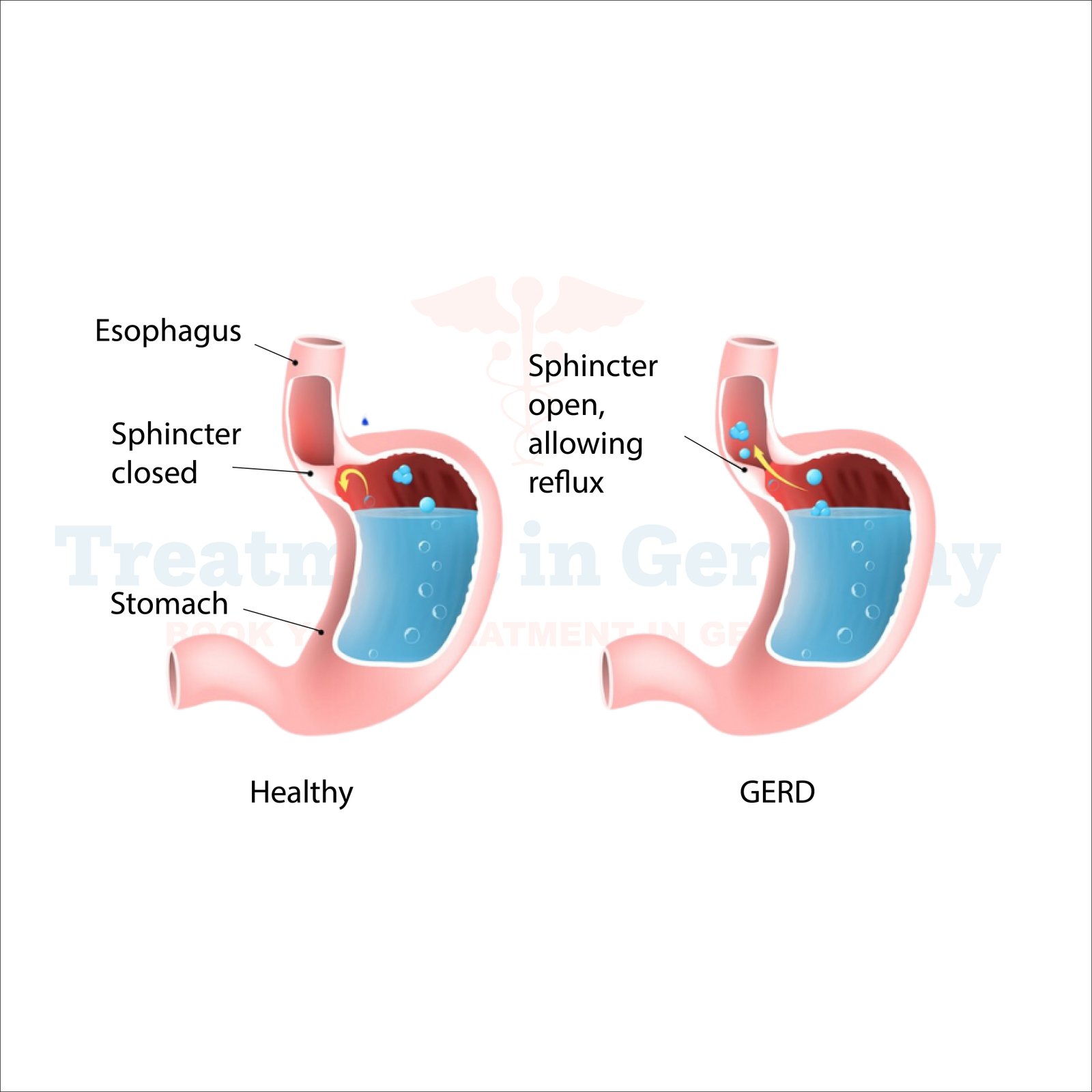
What is Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)?
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, commonly known as GERD, is a chronic digestive disorder characterized by the flow of stomach acid or bile into the esophagus, leading to irritation and inflammation of the lining.
This condition often causes discomfort and can lead to more severe complications if left untreated.
Side effects of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease can manifest through a range of symptoms, including heartburn, regurgitation of acidic or bitter-tasting fluid into the mouth, difficulty swallowing, chest pain, chronic cough, and even asthma-like symptoms.
These symptoms can significantly impact daily life and overall well-being, affecting sleep quality, nutrition, and productivity.
How is Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) diagnosed?
Diagnosing Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease typically involves a comprehensive evaluation of medical history, symptoms, and physical examination by a healthcare professional.
Additionally, various diagnostic tests may be conducted, such as upper endoscopy, esophageal pH monitoring, esophageal manometry, and imaging studies, to assess the extent of esophageal damage and rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.
Potential treatments of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Treatment options for GERD aim to alleviate symptoms, heal esophageal damage, and prevent complications. Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes, weight management, and avoiding trigger foods and beverages, can often provide relief.
Additionally, over-the-counter and prescription medications, including antacids, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), and H2 receptor antagonists, may be prescribed to reduce acid production or neutralize stomach acid.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
