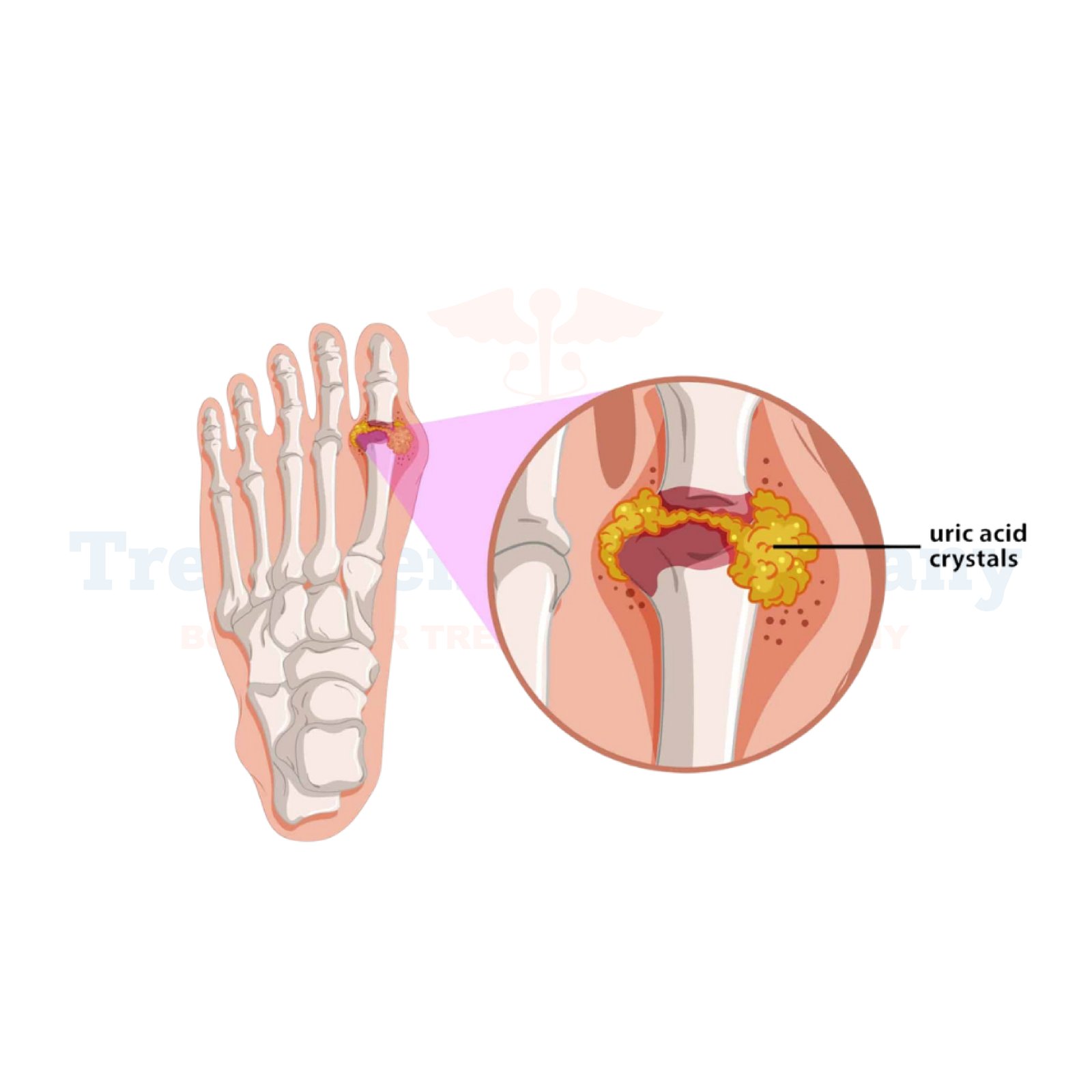
Gout is a type of arthritis characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, redness, and swelling, typically affecting the joints, especially in the lower limbs. It occurs when there is an excess of uric acid in the blood, which forms crystals that accumulate in the joints. These uric acid crystals cause inflammation, leading to painful flare-ups. Gout most commonly affects the big toe but can also impact other joints, including the knees, ankles, and elbows. It can occur as a result of dietary factors, genetics, or certain health conditions, and while it can be managed with treatment, flare-ups may recur if left untreated.
Gout manifests in several forms, each presenting different symptoms:
Acute Gout: This is the most common type, occurring suddenly with intense pain and swelling in one joint, often the big toe.
Chronic Gout: When gout attacks occur frequently and uric acid crystals accumulate over time, it can lead to chronic gout, potentially causing joint damage.
Tophaceous Gout: A severe form where uric acid crystals form lumps called tophi, which can develop under the skin, particularly around joints.
Risk Factors for Gout
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing gout:
High Uric Acid Levels: The primary cause of gout is high uric acid levels in the blood, often due to the body's inability to eliminate it efficiently.
Obesity: Excess body weight is a significant risk factor, as it increases uric acid production and reduces its excretion.
Dietary Factors: A diet high in purine-rich foods (like red meat, seafood, and alcohol, particularly beer) can lead to increased uric acid production.
Genetics: Family history plays a role in the development of gout, as it is often hereditary.
Other Medical Conditions: Conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, kidney disease, and autoimmune diseases can increase the risk of gout.
Medications: Certain medications, including diuretics (used to treat high blood pressure), can elevate uric acid levels.
Symptoms of Gout
Gout attacks typically come on suddenly and are characterized by the following symptoms:
Severe Joint Pain: The pain is often intense and may start suddenly, particularly at night.
Redness and Swelling: The affected joint becomes red, swollen, and warm to the touch.
Tenderness: Even the slightest touch to the affected joint can be extremely painful.
Limited Range of Motion: Due to the pain and swelling, affected joints may become stiff, limiting their range of motion.
Diagnosis and Diagnostic Tools
Gout is diagnosed through a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests:
Physical Examination: Doctors will assess the affected joint, looking for typical signs of inflammation such as redness and swelling.
Blood Tests: A blood test can measure uric acid levels in the blood, although high levels do not always confirm gout.
Joint Aspiration: A doctor may remove fluid from the affected joint to look for uric acid crystals under a microscope, which is the definitive diagnostic test for gout.
Imaging: X-rays or ultrasound may be used to detect joint damage caused by uric acid crystal buildup. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) may also be used to evaluate the joint in more detail.
Why is Treatment in Germany Preferable?
Germany’s medical system is renowned for providing high-quality care with access to the latest treatments and technologies. Here are some reasons why patients choose to receive treatment in Germany:
World-Class Healthcare: Germany is home to some of the world’s best medical facilities and healthcare providers.
Highly Skilled Doctors and Specialists: Germany boasts a network of experts in rheumatology and orthopedics, making it an excellent choice for gout treatment.
Advanced Diagnostic Tools: German hospitals use state-of-the-art diagnostic tools such as X-rays, MRI scans, and ultrasound to accurately diagnose gout and its complications.
Comprehensive Care: From initial diagnosis to long-term management, Germany offers comprehensive care, including dietary advice, physical therapy, and complementary therapies to help manage gout and prevent flare-ups.
Solutions and Prevention
While gout cannot always be fully prevented, there are several steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of attacks:
Manage Uric Acid Levels: Patients should work with their doctor to keep uric acid levels within a healthy range, often through medication and lifestyle changes.
Dietary Modifications: Reducing the intake of purine-rich foods (such as red meats, organ meats, and certain fish) and alcohol, especially beer, can help prevent gout flare-ups.
Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps flush uric acid from the body.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight helps lower uric acid levels and reduces the risk of gout.
Monitor Other Health Conditions: Managing conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, and kidney disease can help prevent gout attacks.
In Germany, patients benefit from ongoing physical therapy and complementary therapies that aim to improve joint mobility and overall well-being, which can help prevent recurring gout flare-ups.
Treatment Options in Germany
Germany offers a wide range of treatments for gout, from conventional to cutting-edge therapies:
Non-Surgical Treatments
Medications: The first line of treatment for gout usually involves NSAIDs, colchicine, and uric acid-lowering medications such as allopurinol.
Lifestyle Changes: Doctors will often recommend dietary changes, weight loss, and increased hydration to help manage gout symptoms.
Pain Management: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications help manage the intense pain of acute gout attacks.
Surgical Treatment
In rare cases, if gout leads to severe joint damage or tophi formation, surgery may be necessary to remove the tophi or repair the joint.
Innovative Treatment
Uric Acid-Lowering Drugs: Medications such as allopurinol and febuxostat are commonly prescribed to lower uric acid levels in the blood, reducing the frequency of gout attacks.
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen are often used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain during an acute gout flare-up.
Colchicine: This medication is used to reduce inflammation and pain during a gout attack.
Biologic Drugs: For severe or chronic gout, biologic drugs such as pegloticase may be used. These drugs help break down uric acid in the blood, reducing symptoms and preventing long-term joint damage.
Stem Cell Therapy: In some advanced cases of gout, stem cell therapy is being explored as an innovative treatment to repair joint damage caused by chronic inflammation.
Conclusion
Gout is a painful and often recurring condition, but with effective treatment, flare-ups can be managed and prevented. Treatment in Germany offers access to world-class healthcare, advanced diagnostic tools, and a variety of treatment options, including innovative therapies like stem cell therapy and biologic treatments. Germany’s highly skilled doctors and specialists are at the forefront of gout care, ensuring that patients receive the most effective and personalized treatment available. Whether through traditional treatments or more innovative approaches, Germany provides some of the best options for those struggling with gout.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
