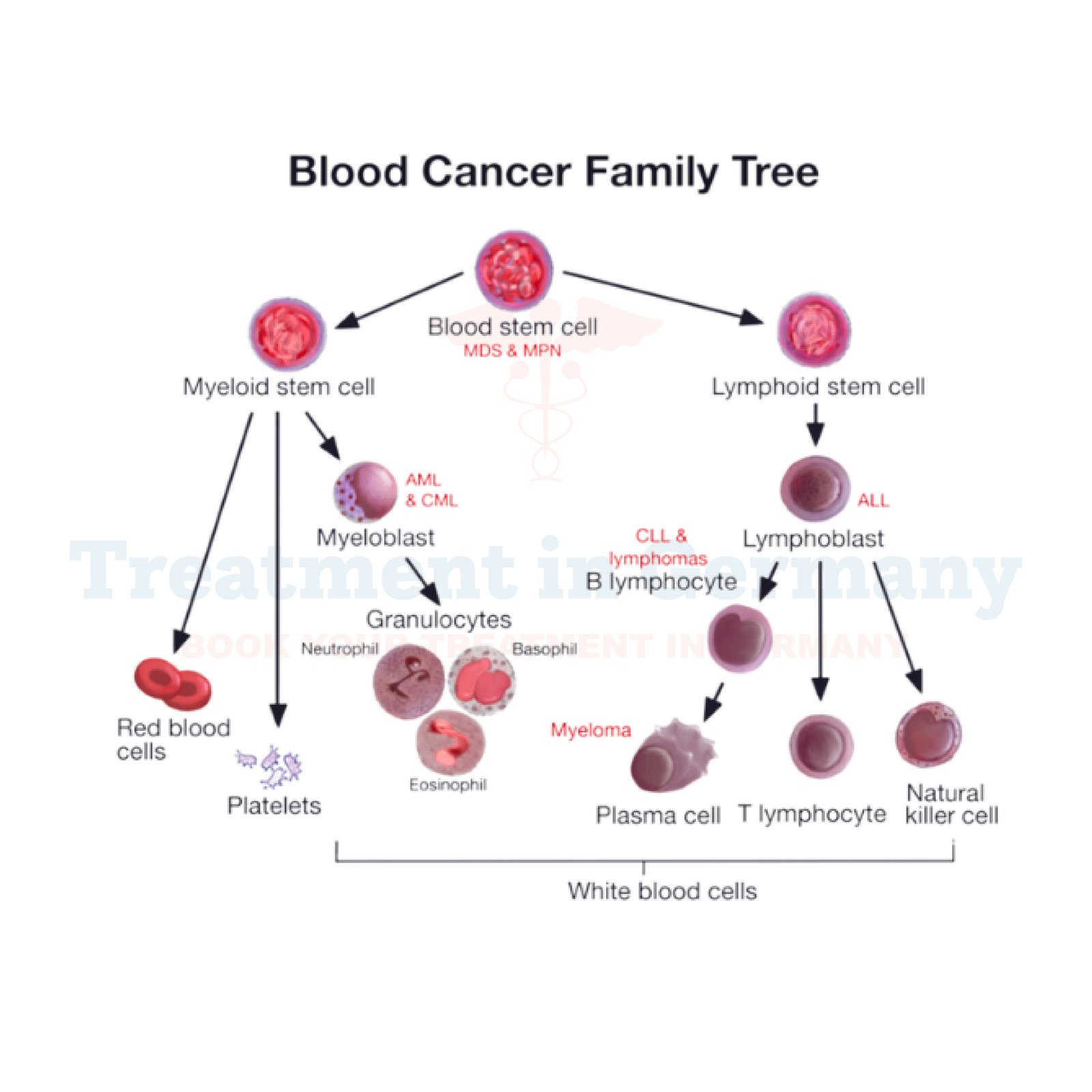
What is Hairy Cell Leukemia?
Hairy Cell Leukemia (HCL) is a rare type of chronic leukemia characterized by the excessive growth of abnormal B cells in the bone marrow. These cells have fine, hair-like projections on their surface, hence the name "hairy" cell leukemia.
While the exact cause remains unknown, certain risk factors such as exposure to certain chemicals or viruses may contribute to its development. HCL progresses slowly and may not always present with noticeable symptoms in the early stages, making timely diagnosis crucial.
Side effects of Hairy Cell Leukemia:
Patients with Hairy Cell Leukemia may experience a range of symptoms and complications, including:
How is Hairy Cell Leukemia diagnosed?
Diagnosing Hairy Cell Leukemia typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, blood tests, and bone marrow biopsy. Specialized tests such as flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry may also be performed to confirm the presence of hairy cells in the bone marrow sample. Accurate diagnosis is essential for determining the appropriate treatment plan.
Potential treatments of Hairy Cell Leukemia:
The treatment approach for Hairy Cell Leukemia depends on several factors, including the patient's overall health, the extent of the disease, and individual preferences. Common treatment options include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
