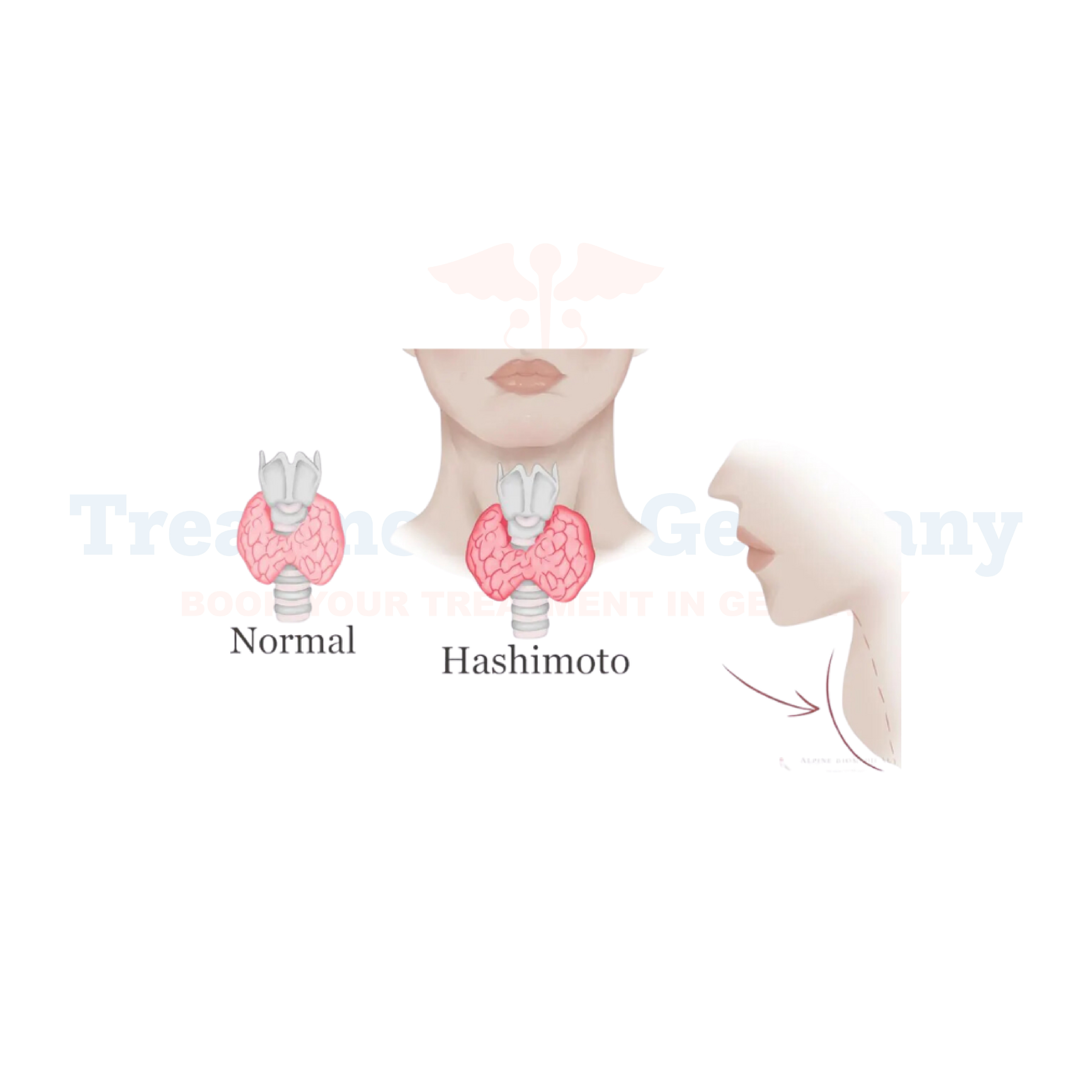
What is Hashimoto's Thyroiditis?
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis is an autoimmune disorder that affects the thyroid gland. In this condition, the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid tissue, leading to inflammation and potential damage to the gland. As a result, the thyroid's ability to produce essential hormones like thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) is compromised. Hashimoto's Thyroiditis is one of the most common causes of hypothyroidism, a condition characterized by an underactive thyroid.
Side effects of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis:
The symptoms of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis can vary widely among individuals and may develop gradually over time. Common signs and symptoms include:
If left untreated, Hashimoto's Thyroiditis can lead to complications such as goiter (enlargement of the thyroid gland), heart problems, infertility, and myxedema coma in severe cases.
How is Hashimoto's Thyroiditis diagnosed?
Diagnosing Hashimoto's Thyroiditis typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Your healthcare provider may perform the following:
1. Thyroid function tests: Blood tests measuring levels of thyroid hormones (TSH, T4, and sometimes T3) can help assess thyroid function. In Hashimoto's Thyroiditis, TSH levels are often elevated, while T4 levels may be decreased.
2. Thyroid antibody tests: Presence of specific antibodies like thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPOAb) and thyroglobulin antibodies (TgAb) in the blood can indicate autoimmune thyroiditis.
3. Ultrasound imaging: Imaging tests like ultrasound may be used to visualize the thyroid gland and evaluate for any abnormalities or signs of inflammation.
Potential treatments of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis:
While there is no cure for Hashimoto's Thyroiditis, treatment aims to alleviate symptoms, restore thyroid hormone levels, and prevent complications. Common treatment approaches include:
1. Thyroid hormone replacement therapy: Synthetic thyroid hormone medication, such as levothyroxine, is prescribed to replace the deficient hormones and normalize thyroid function. Regular blood tests are necessary to adjust the dosage as needed.
2. Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle with balanced nutrition, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep can support overall well-being and thyroid health.
3. Monitoring and follow-up: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor thyroid function, adjust medication dosage, and address any emerging symptoms or concerns.
4. Management of other conditions: Managing comorbidities like depression, anxiety, or other autoimmune disorders is crucial for comprehensive care.
5. Dietary adjustments: Some individuals with Hashimoto's Thyroiditis find relief from symptoms by avoiding certain foods like gluten or incorporating selenium-rich foods into their diet, although scientific evidence supporting these approaches is limited.
6. Alternative therapies: Certain complementary and alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, may provide symptomatic relief for some patients, but their efficacy varies, and they should be used alongside conventional treatment under medical supervision.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
